Consulting firms specializing in dark pattern compliance help organizations identify and eliminate manipulative design tactics that deceive users, aligning business practices with ethical standards and legal requirements. Balancing dark pattern compliance with corporate social responsibility (CSR) enhances brand trust and fosters long-term customer loyalty by promoting transparency and user-centric experiences. Explore how integrating dark pattern compliance into CSR strategies can safeguard your business and elevate stakeholder trust.
Why it is important
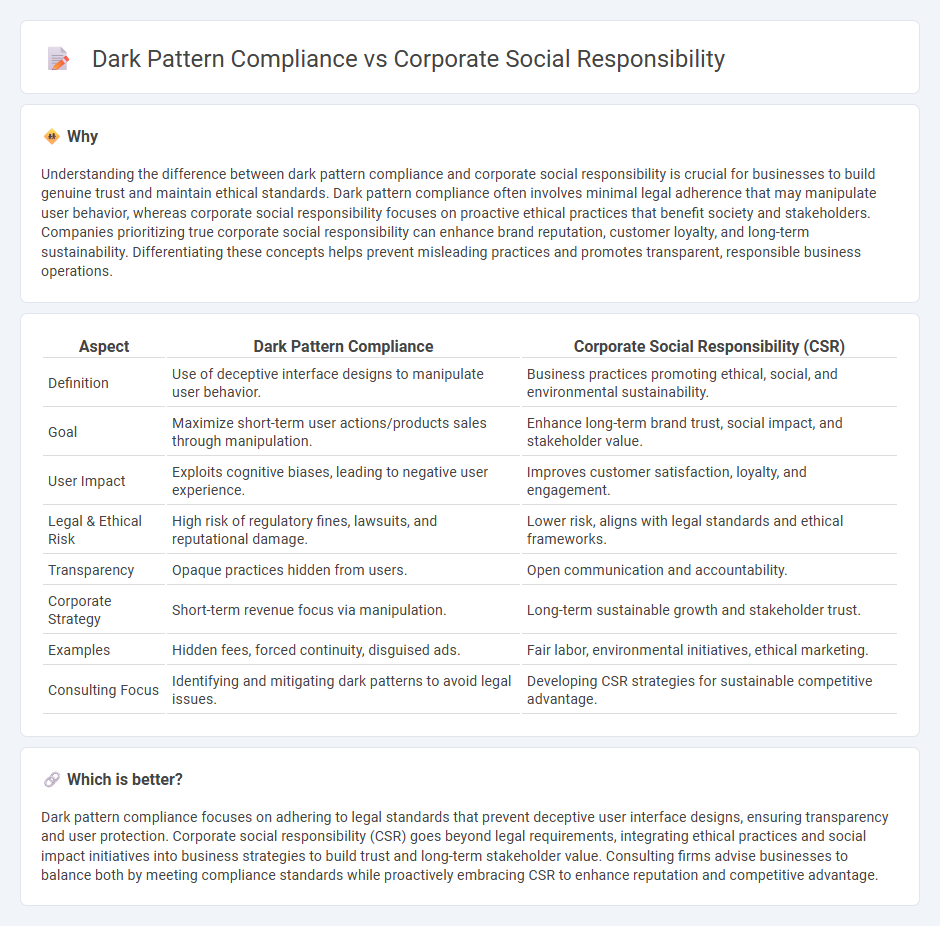
Understanding the difference between dark pattern compliance and corporate social responsibility is crucial for businesses to build genuine trust and maintain ethical standards. Dark pattern compliance often involves minimal legal adherence that may manipulate user behavior, whereas corporate social responsibility focuses on proactive ethical practices that benefit society and stakeholders. Companies prioritizing true corporate social responsibility can enhance brand reputation, customer loyalty, and long-term sustainability. Differentiating these concepts helps prevent misleading practices and promotes transparent, responsible business operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Pattern Compliance | Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of deceptive interface designs to manipulate user behavior. | Business practices promoting ethical, social, and environmental sustainability. |
| Goal | Maximize short-term user actions/products sales through manipulation. | Enhance long-term brand trust, social impact, and stakeholder value. |
| User Impact | Exploits cognitive biases, leading to negative user experience. | Improves customer satisfaction, loyalty, and engagement. |
| Legal & Ethical Risk | High risk of regulatory fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage. | Lower risk, aligns with legal standards and ethical frameworks. |
| Transparency | Opaque practices hidden from users. | Open communication and accountability. |
| Corporate Strategy | Short-term revenue focus via manipulation. | Long-term sustainable growth and stakeholder trust. |
| Examples | Hidden fees, forced continuity, disguised ads. | Fair labor, environmental initiatives, ethical marketing. |
| Consulting Focus | Identifying and mitigating dark patterns to avoid legal issues. | Developing CSR strategies for sustainable competitive advantage. |
Which is better?
Dark pattern compliance focuses on adhering to legal standards that prevent deceptive user interface designs, ensuring transparency and user protection. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) goes beyond legal requirements, integrating ethical practices and social impact initiatives into business strategies to build trust and long-term stakeholder value. Consulting firms advise businesses to balance both by meeting compliance standards while proactively embracing CSR to enhance reputation and competitive advantage.
Connection
Dark pattern compliance is crucial for consulting firms aiming to uphold corporate social responsibility (CSR) by ensuring transparent and ethical user interactions. Implementing strict guidelines against manipulative design enhances trustworthiness and aligns client businesses with regulatory standards. This connection strengthens brand reputation while promoting sustainable business practices.
Key Terms
Ethical Standards
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) emphasizes transparent business practices and prioritizes ethical standards to protect consumer rights and promote social welfare. In contrast, dark pattern compliance involves manipulative design tactics that exploit user behavior, undermining trust and violating ethical guidelines. Explore how aligning CSR with ethical digital design can enhance corporate integrity and consumer trust.
Transparency
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) emphasizes transparency to build trust by openly sharing company practices, impacts, and ethical standards. Dark pattern compliance, by contrast, masks deceptive design elements that manipulate user behavior, undermining transparency and ethical accountability. Explore how aligning CSR with genuine transparency can counteract dark patterns and foster consumer trust.
Regulatory Adherence
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) emphasizes ethical business practices that promote transparency, consumer protection, and sustainable development, directly influencing regulatory adherence. Dark pattern compliance entails manipulating user behavior through deceptive design techniques, which conflicts with regulatory frameworks such as GDPR and CCPA aimed at safeguarding user consent and data privacy. Explore further to understand how balancing CSR and dark pattern compliance impacts legal obligations and corporate reputation.
Source and External Links
What is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)? Guide & Examples - Corporate social responsibility (CSR) refers to a company's voluntary efforts to improve society through social, environmental, and community initiatives that go beyond profit-making, impacting the company, employees, nonprofits, and society as a whole.
Corporate social responsibility - Wikipedia - CSR is a form of international private business self-regulation aiming to contribute to societal goals via philanthropy, ethical business practices, and community engagement, evolving from voluntary policies to increasingly mandatory schemes globally.
What Is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)? - CSR involves ethical and sustainable business practices such as environmental stewardship and social investments, exemplified by companies like Google, LEGO, and Starbucks with initiatives targeting sustainability, waste reduction, and ethical sourcing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com