Anticipatory governance focuses on proactive identification and management of emerging risks through strategic foresight and scenario planning, enhancing long-term resilience. Risk-based governance prioritizes current threats and compliance requirements, emphasizing mitigation and control to safeguard organizational assets. Explore how integrating both approaches can optimize your organization's governance framework.
Why it is important
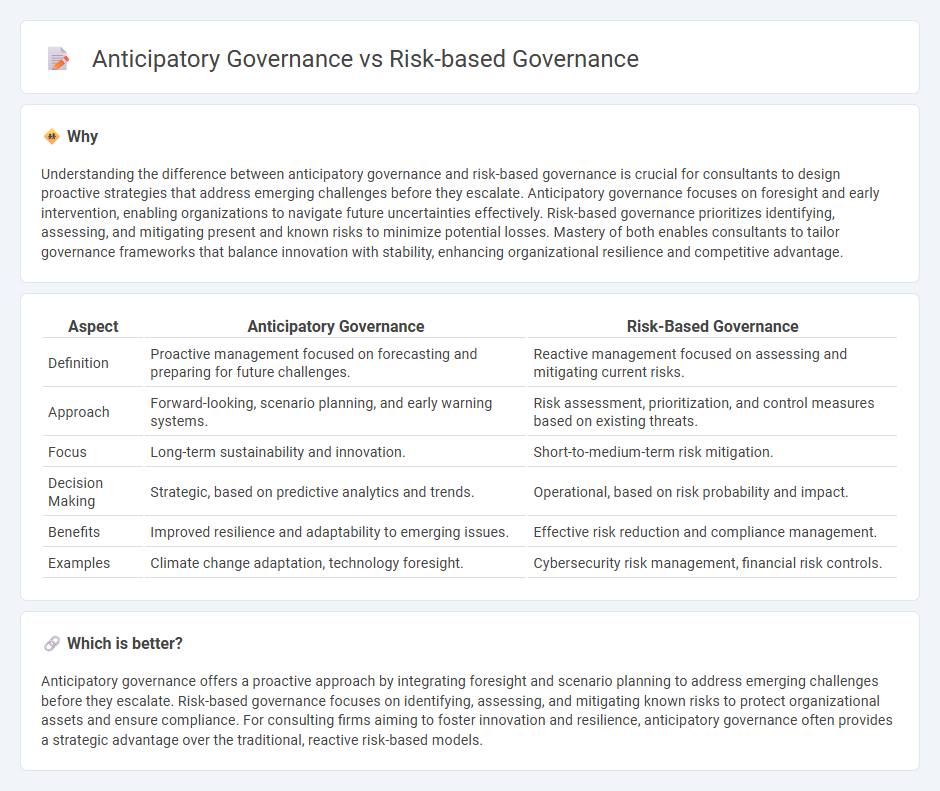
Understanding the difference between anticipatory governance and risk-based governance is crucial for consultants to design proactive strategies that address emerging challenges before they escalate. Anticipatory governance focuses on foresight and early intervention, enabling organizations to navigate future uncertainties effectively. Risk-based governance prioritizes identifying, assessing, and mitigating present and known risks to minimize potential losses. Mastery of both enables consultants to tailor governance frameworks that balance innovation with stability, enhancing organizational resilience and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Anticipatory Governance | Risk-Based Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proactive management focused on forecasting and preparing for future challenges. | Reactive management focused on assessing and mitigating current risks. |
| Approach | Forward-looking, scenario planning, and early warning systems. | Risk assessment, prioritization, and control measures based on existing threats. |
| Focus | Long-term sustainability and innovation. | Short-to-medium-term risk mitigation. |
| Decision Making | Strategic, based on predictive analytics and trends. | Operational, based on risk probability and impact. |
| Benefits | Improved resilience and adaptability to emerging issues. | Effective risk reduction and compliance management. |
| Examples | Climate change adaptation, technology foresight. | Cybersecurity risk management, financial risk controls. |
Which is better?
Anticipatory governance offers a proactive approach by integrating foresight and scenario planning to address emerging challenges before they escalate. Risk-based governance focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating known risks to protect organizational assets and ensure compliance. For consulting firms aiming to foster innovation and resilience, anticipatory governance often provides a strategic advantage over the traditional, reactive risk-based models.
Connection
Anticipatory governance and risk-based governance are interconnected through their shared focus on proactively identifying and managing potential challenges before they escalate. Anticipatory governance employs foresight tools and scenario planning to predict emerging risks, while risk-based governance prioritizes resources and decision-making based on the probability and impact of identified risks. Together, these approaches enhance organizational resilience and strategic decision-making in consulting practices.
Key Terms
Risk Assessment
Risk-based governance prioritizes risk assessment by identifying, evaluating, and mitigating potential threats to achieve compliance and safeguard assets. Anticipatory governance enhances this approach by integrating foresight methodologies and scenario planning to proactively address emerging risks and uncertainties. Explore more to understand how combining these frameworks can optimize organizational resilience and strategic decision-making.
Foresight
Risk-based governance prioritizes identifying and managing potential threats through probability assessments and mitigation strategies, ensuring resilience and regulatory compliance. Anticipatory governance emphasizes foresight by integrating predictive analytics, scenario planning, and early-warning systems to proactively shape policy and innovation. Explore how foresight enhances governance frameworks to stay ahead of emerging challenges and opportunities.
Scenario Planning
Risk-based governance emphasizes managing uncertainties by identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks through structured frameworks and controls, while anticipatory governance proactively prepares for future challenges using scenario planning to envision multiple plausible futures. Scenario planning enables organizations to create flexible strategies that adapt to changing conditions, enhancing resilience and long-term decision-making. Explore how integrating scenario planning into governance models drives innovation and preparedness in complex environments.
Source and External Links
Risk Governance and Risk Management - Risk-based governance is a structured approach where organizations integrate accountability, decision-making frameworks, and stakeholder roles at all levels to identify, assess, manage, and communicate risks in alignment with strategic objectives and regulations.
What is the Risk Governance Framework [& How to Create It] - A risk governance framework systematically manages risks by defining objectives, establishing risk appetite and tolerance, and involving key stakeholders to enhance decision-making, regulatory compliance, and organizational resilience.
The Risk Governance Power Structure: How Does it Work? - GARP - Risk-based governance functions as a decision-making system that manages risk-taking within agreed limits, ensuring accountability, transparency, and agility, and clarifying who is authorized to take risks and how they are managed across an organization.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com