Outside-in benchmarking focuses on comparing a company's processes and outcomes against external industry leaders to identify best practices and innovative strategies. Performance benchmarking measures internal metrics against set standards or competitors to evaluate efficiency and identify areas for improvement. Explore these benchmarking methods further to enhance your organization's competitive edge.
Why it is important
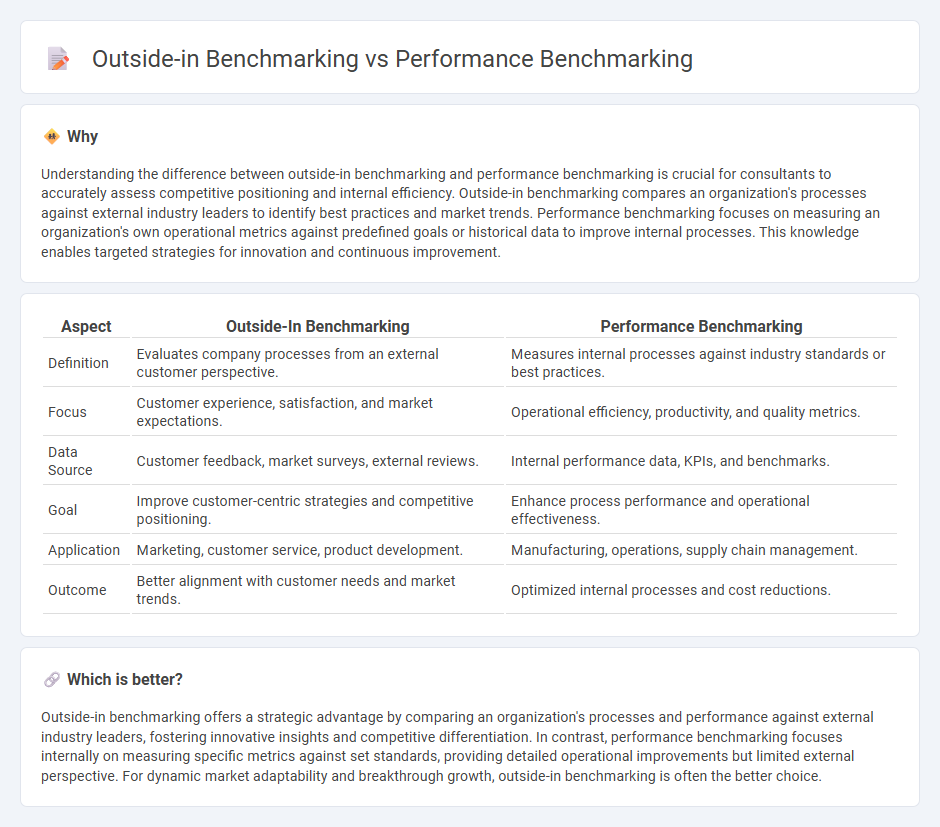
Understanding the difference between outside-in benchmarking and performance benchmarking is crucial for consultants to accurately assess competitive positioning and internal efficiency. Outside-in benchmarking compares an organization's processes against external industry leaders to identify best practices and market trends. Performance benchmarking focuses on measuring an organization's own operational metrics against predefined goals or historical data to improve internal processes. This knowledge enables targeted strategies for innovation and continuous improvement.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Outside-In Benchmarking | Performance Benchmarking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluates company processes from an external customer perspective. | Measures internal processes against industry standards or best practices. |
| Focus | Customer experience, satisfaction, and market expectations. | Operational efficiency, productivity, and quality metrics. |
| Data Source | Customer feedback, market surveys, external reviews. | Internal performance data, KPIs, and benchmarks. |
| Goal | Improve customer-centric strategies and competitive positioning. | Enhance process performance and operational effectiveness. |
| Application | Marketing, customer service, product development. | Manufacturing, operations, supply chain management. |
| Outcome | Better alignment with customer needs and market trends. | Optimized internal processes and cost reductions. |
Which is better?
Outside-in benchmarking offers a strategic advantage by comparing an organization's processes and performance against external industry leaders, fostering innovative insights and competitive differentiation. In contrast, performance benchmarking focuses internally on measuring specific metrics against set standards, providing detailed operational improvements but limited external perspective. For dynamic market adaptability and breakthrough growth, outside-in benchmarking is often the better choice.
Connection
Outside-in benchmarking involves comparing a company's processes and performance with external industry leaders to identify best practices, while performance benchmarking measures specific internal metrics against those standards. The connection lies in using insights gained from outside-in benchmarking to set realistic performance benchmarks and drive continuous improvement. Integrating these approaches enables organizations to align their internal performance with external market leaders, enhancing competitiveness and operational efficiency.
Key Terms
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Performance benchmarking centers on measuring internal Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as efficiency, productivity, and quality to evaluate an organization's current performance against its historical data or industry standards. Outside-in benchmarking compares these KPIs against external competitors or best-in-class entities to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement. Explore further to understand how leveraging both approaches can optimize strategic decision-making and drive competitive advantage.
Industry Best Practices
Performance benchmarking measures internal processes and outcomes against predefined standards to identify efficiency gaps and improvement areas. Outside-in benchmarking compares a company's practices and performance metrics with industry best practices from leading competitors to drive innovation and operational excellence. Explore detailed strategies to leverage outside-in benchmarking for competitive advantage in your industry.
External Data Sources
Performance benchmarking primarily assesses internal metrics such as productivity, efficiency, and financial outcomes, using historical data to gauge an organization's progress against set standards. Outside-in benchmarking leverages external data sources including competitor performance, industry trends, and market dynamics to provide a broader context for strategic decision-making and innovation. Explore more to understand how integrating external data sources enhances benchmarking accuracy and drives competitive advantage.
Source and External Links
What Is benchmarking? How to set a benchmark - Performance benchmarking evaluates a company's performance by comparing key metrics like productivity, efficiency, and profitability against competitors or industry standards to identify gaps and improve continuously.
Performance Benchmarking: Your Quick Guide - Performance benchmarking helps organizations assess their strengths and weaknesses by comparing performance to industry norms or best practices, enabling focused improvements in areas such as customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Performance Benchmarking In Manufacturing - In manufacturing, performance benchmarking is a comparative exercise that reveals performance gaps and accountability, assists in setting goals, and leverages data analytics to drive competitive advantage and efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com