Anticipatory governance focuses on predicting and preparing for future challenges by integrating foresight, risk assessment, and proactive policy design into decision-making frameworks. Participatory governance emphasizes inclusive involvement of stakeholders, ensuring diverse perspectives and collaborative problem-solving in shaping policies and strategies. Discover how combining these governance models can enhance organizational resilience and responsiveness.
Why it is important
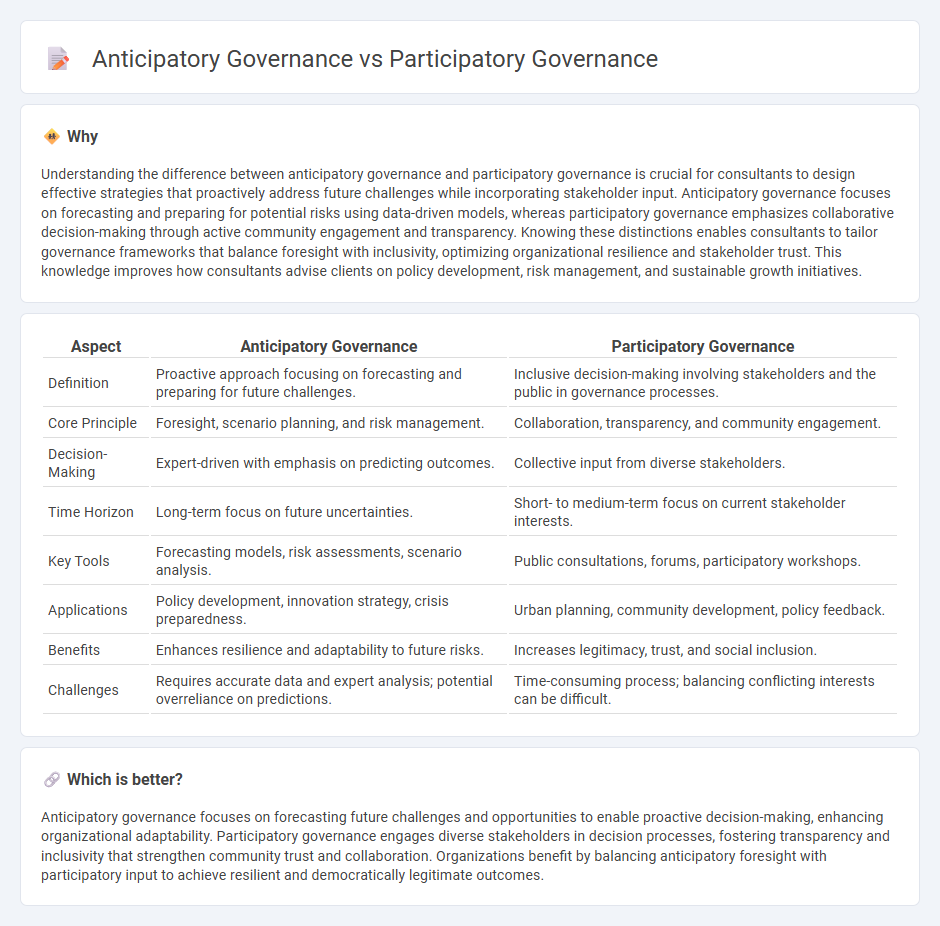
Understanding the difference between anticipatory governance and participatory governance is crucial for consultants to design effective strategies that proactively address future challenges while incorporating stakeholder input. Anticipatory governance focuses on forecasting and preparing for potential risks using data-driven models, whereas participatory governance emphasizes collaborative decision-making through active community engagement and transparency. Knowing these distinctions enables consultants to tailor governance frameworks that balance foresight with inclusivity, optimizing organizational resilience and stakeholder trust. This knowledge improves how consultants advise clients on policy development, risk management, and sustainable growth initiatives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Anticipatory Governance | Participatory Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proactive approach focusing on forecasting and preparing for future challenges. | Inclusive decision-making involving stakeholders and the public in governance processes. |
| Core Principle | Foresight, scenario planning, and risk management. | Collaboration, transparency, and community engagement. |
| Decision-Making | Expert-driven with emphasis on predicting outcomes. | Collective input from diverse stakeholders. |
| Time Horizon | Long-term focus on future uncertainties. | Short- to medium-term focus on current stakeholder interests. |
| Key Tools | Forecasting models, risk assessments, scenario analysis. | Public consultations, forums, participatory workshops. |
| Applications | Policy development, innovation strategy, crisis preparedness. | Urban planning, community development, policy feedback. |
| Benefits | Enhances resilience and adaptability to future risks. | Increases legitimacy, trust, and social inclusion. |
| Challenges | Requires accurate data and expert analysis; potential overreliance on predictions. | Time-consuming process; balancing conflicting interests can be difficult. |
Which is better?
Anticipatory governance focuses on forecasting future challenges and opportunities to enable proactive decision-making, enhancing organizational adaptability. Participatory governance engages diverse stakeholders in decision processes, fostering transparency and inclusivity that strengthen community trust and collaboration. Organizations benefit by balancing anticipatory foresight with participatory input to achieve resilient and democratically legitimate outcomes.
Connection
Anticipatory governance and participatory governance intersect by enabling organizations to proactively address future challenges through inclusive stakeholder engagement. Anticipatory governance focuses on foresight and scenario planning, while participatory governance ensures diverse input and collaboration in decision-making processes. Their integration enhances adaptive strategies, leveraging collective intelligence to improve policy implementation and organizational resilience.
Key Terms
Stakeholder Engagement
Participatory governance centers on direct stakeholder involvement in decision-making processes, fostering transparency and accountability through collaborative dialogue and consensus-building. Anticipatory governance emphasizes proactive engagement by incorporating stakeholders' insights to foresee future challenges and opportunities, enabling adaptive strategies and informed policy development. Explore how these governance models enhance stakeholder engagement for resilient and inclusive outcomes.
Foresight
Participatory governance emphasizes inclusive decision-making by engaging diverse stakeholders in shaping policies, while anticipatory governance centers on foresight techniques to predict and address future challenges proactively. Foresight tools such as scenario planning, horizon scanning, and Delphi methods are integral to anticipatory governance, enabling adaptive and forward-looking strategies. Explore deeper insights into how foresight enhances governance models for resilient and sustainable futures.
Co-creation
Participatory governance emphasizes direct involvement of citizens and stakeholders in decision-making processes to enhance transparency and accountability, fostering co-creation through collaborative platforms and community engagement. Anticipatory governance focuses on proactive strategies that integrate foresight, scenario planning, and early-warning systems to anticipate future challenges and enable adaptive policy-making, promoting co-creation by involving diverse actors in shaping resilient solutions. Discover how co-creation bridges these governance models to drive innovative and inclusive societal transformations.
Source and External Links
What is Participatory Government? Definition, Model, ... - Participatory governance is a decision-making model that actively involves citizens in shaping policies and community projects, promoting democratization, trust, and social justice through practices like participatory budgeting, citizen assemblies, and community planning.
Participatory Governance: From Theory To Practice - This concept emphasizes democratic engagement via deliberative processes, aiming to empower citizens, build competence, and improve social equity and representation in governance.
The Participatory Governance Index - The Participatory Governance Index (PGI) is a tool to help governments assess and improve their public engagement systems, ensuring that citizen input is effectively incorporated into policymaking for healthier democracies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com