Sustainability benchmarking measures a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance against industry standards to identify areas for improvement, while circular economy analysis focuses on designing processes that minimize waste and maximize resource reuse throughout product lifecycles. Both approaches drive strategic decision-making for businesses aiming to enhance eco-efficiency and regulatory compliance. Discover how integrating these methods can accelerate your organization's sustainability journey.
Why it is important
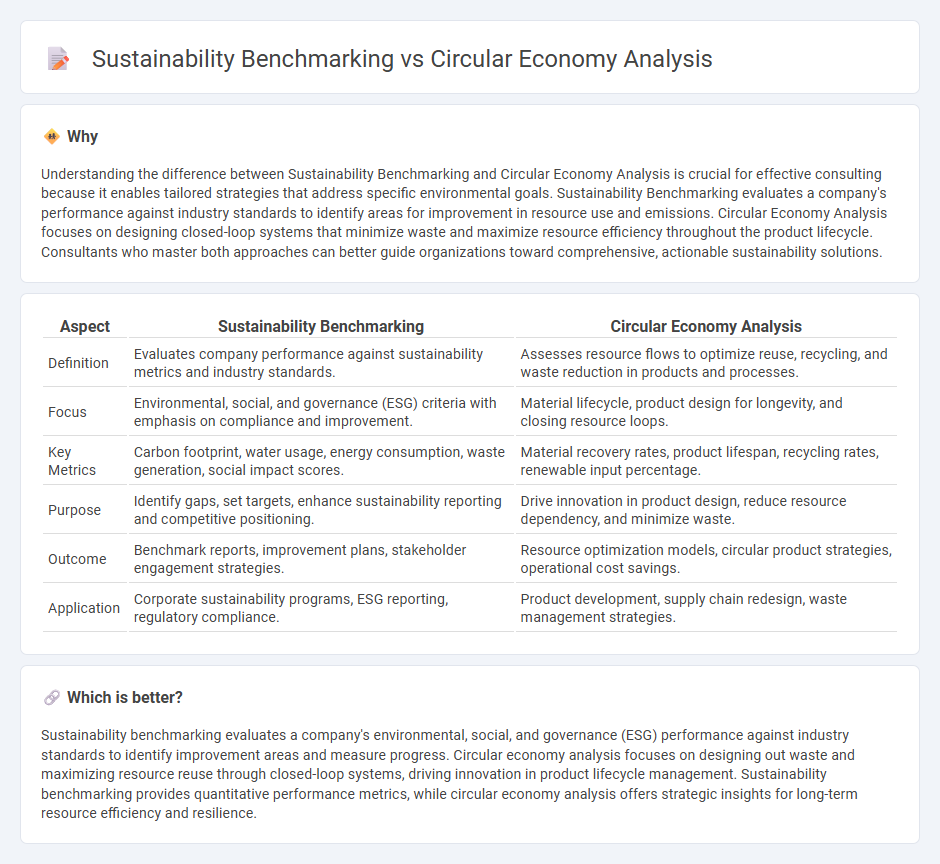
Understanding the difference between Sustainability Benchmarking and Circular Economy Analysis is crucial for effective consulting because it enables tailored strategies that address specific environmental goals. Sustainability Benchmarking evaluates a company's performance against industry standards to identify areas for improvement in resource use and emissions. Circular Economy Analysis focuses on designing closed-loop systems that minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency throughout the product lifecycle. Consultants who master both approaches can better guide organizations toward comprehensive, actionable sustainability solutions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainability Benchmarking | Circular Economy Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluates company performance against sustainability metrics and industry standards. | Assesses resource flows to optimize reuse, recycling, and waste reduction in products and processes. |
| Focus | Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria with emphasis on compliance and improvement. | Material lifecycle, product design for longevity, and closing resource loops. |
| Key Metrics | Carbon footprint, water usage, energy consumption, waste generation, social impact scores. | Material recovery rates, product lifespan, recycling rates, renewable input percentage. |
| Purpose | Identify gaps, set targets, enhance sustainability reporting and competitive positioning. | Drive innovation in product design, reduce resource dependency, and minimize waste. |
| Outcome | Benchmark reports, improvement plans, stakeholder engagement strategies. | Resource optimization models, circular product strategies, operational cost savings. |
| Application | Corporate sustainability programs, ESG reporting, regulatory compliance. | Product development, supply chain redesign, waste management strategies. |
Which is better?
Sustainability benchmarking evaluates a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance against industry standards to identify improvement areas and measure progress. Circular economy analysis focuses on designing out waste and maximizing resource reuse through closed-loop systems, driving innovation in product lifecycle management. Sustainability benchmarking provides quantitative performance metrics, while circular economy analysis offers strategic insights for long-term resource efficiency and resilience.
Connection
Sustainability benchmarking evaluates an organization's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance against industry standards, highlighting areas for improvement in resource efficiency and waste reduction. Circular economy analysis complements this by identifying opportunities to redesign processes for reuse, recycling, and closed-loop systems, minimizing resource input and waste output. Together, these methodologies enable consultants to develop actionable strategies that drive sustainable business models and long-term value creation.
Key Terms
Resource Efficiency
Circular economy analysis evaluates material flow and waste reduction strategies to enhance resource efficiency by promoting reuse, recycling, and regeneration of products. Sustainability benchmarking measures organizational performance against industry standards to identify gaps and improve resource utilization practices systematically. Explore comprehensive insights to optimize resource efficiency through integrated circular economy and sustainability assessment approaches.
Environmental Impact Metrics
Circular economy analysis evaluates resource efficiency and waste reduction by measuring material loops and lifecycle impacts, emphasizing metrics like carbon footprint, energy consumption, and water use. Sustainability benchmarking compares these environmental impact metrics across industries to set performance standards and identify best practices in reducing ecological footprints. Explore detailed methodologies and case studies to understand their role in advancing sustainable development.
Lifecycle Assessment
Circular economy analysis emphasizes the reuse, recycling, and regeneration of materials to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency throughout a product's lifecycle. Sustainability benchmarking evaluates environmental, social, and economic performance metrics against industry leaders, often incorporating Lifecycle Assessment (LCA) to measure a product's environmental impacts from raw material extraction to disposal. Explore detailed methodologies and case studies to understand how integrating Circular Economy principles with LCA enhances sustainability performance.
Source and External Links
The circular economy in detail - Ellen MacArthur Foundation - Analyzes economic, material, and employment impacts of a circular economy, including growth from circular activities, up to $630 billion in EU material cost savings for complex products, and job creation through recycling and remanufacturing.
What is a circular economy? | Ellen MacArthur Foundation - Defines the circular economy as a system eliminating waste and pollution by designing for reuse and regeneration, circulating materials at their highest value, and decoupling economic activity from consumption of finite resources to tackle climate and biodiversity challenges.
What is a Circular Economy? | US EPA - Describes the circular economy as keeping materials and products in use as long as possible, redesigning for less resource intensity, recapturing waste as new resources, and aiming to eliminate waste through superior design of materials, products, and systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com