Acquihire strategy involves acquiring a company primarily to gain its skilled workforce and talent, enabling rapid team expansion and integration of expertise within a business. Outsourcing, in contrast, delegates specific business functions or projects to external service providers, optimizing cost-efficiency and operational focus without permanent internal team growth. Discover the key differences and strategic benefits of acquihire versus outsourcing for your organization's growth objectives.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between acquihire strategy and outsourcing is crucial in consulting to tailor business growth approaches effectively. Acquihire focuses on acquiring talent through company purchase, promoting innovation and integration, while outsourcing delegates tasks to external agencies enhancing cost efficiency. Misinterpreting these strategies can lead to suboptimal resource allocation and impact project outcomes. Consulting firms leverage this knowledge to optimize client investment and deliver targeted solutions.
Comparison Table
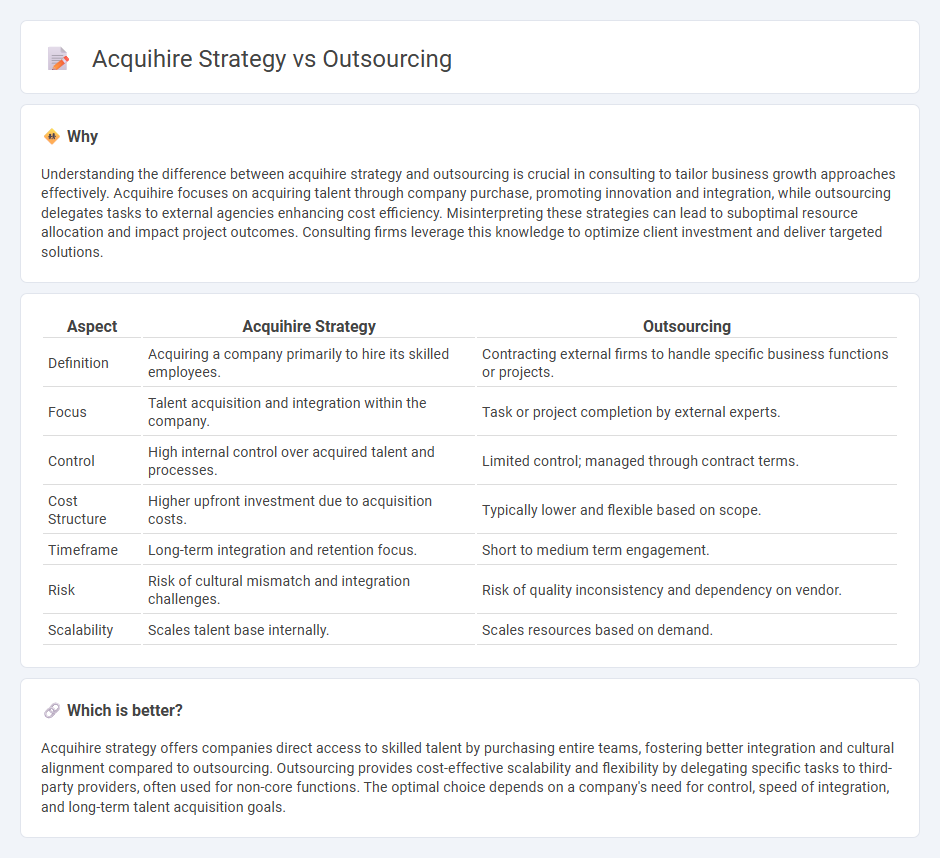
| Aspect | Acquihire Strategy | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acquiring a company primarily to hire its skilled employees. | Contracting external firms to handle specific business functions or projects. |
| Focus | Talent acquisition and integration within the company. | Task or project completion by external experts. |
| Control | High internal control over acquired talent and processes. | Limited control; managed through contract terms. |
| Cost Structure | Higher upfront investment due to acquisition costs. | Typically lower and flexible based on scope. |
| Timeframe | Long-term integration and retention focus. | Short to medium term engagement. |
| Risk | Risk of cultural mismatch and integration challenges. | Risk of quality inconsistency and dependency on vendor. |
| Scalability | Scales talent base internally. | Scales resources based on demand. |
Which is better?
Acquihire strategy offers companies direct access to skilled talent by purchasing entire teams, fostering better integration and cultural alignment compared to outsourcing. Outsourcing provides cost-effective scalability and flexibility by delegating specific tasks to third-party providers, often used for non-core functions. The optimal choice depends on a company's need for control, speed of integration, and long-term talent acquisition goals.
Connection
Acquihire strategy involves acquiring a company primarily to recruit its talented workforce, which can complement outsourcing by integrating external expertise directly into the acquiring firm. Both approaches aim to enhance a company's capabilities and accelerate growth by leveraging external talent or services. Combining acquihire with outsourcing allows businesses to manage resources flexibly while maintaining control over critical skills and knowledge.
Key Terms
Talent Acquisition
Outsourcing leverages external expertise to fulfill specific project needs, enabling companies to access specialized skills without expanding full-time headcount. Acquihire strategies prioritize talent acquisition by acquiring entire teams or startups to rapidly integrate skilled personnel and foster innovation within the organization. Explore the benefits and challenges of each approach to optimize your talent acquisition strategy.
Cost Efficiency
Outsourcing leverages external vendors to reduce operational expenses and access specialized skills without long-term commitments, significantly lowering upfront costs and overhead. Acquihire involves acquiring a company primarily to gain its talent, often resulting in higher immediate expenses but providing strategic human capital and integration benefits. Explore more about how these strategies impact cost efficiency and long-term value for businesses.
Capability Integration
Outsourcing involves contracting third-party vendors to handle specific business functions, enabling companies to access specialized skills and reduce operational costs while maintaining flexibility. Acquihire strategy focuses on acquiring entire teams primarily for their skills and expertise, integrating these capabilities directly into the core organization to accelerate innovation and strengthen talent pools. Explore further insights on how capability integration influences strategic decision-making in outsourcing vs acquihire approaches.
Source and External Links
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - Outsourcing is a business practice where a company hires a third party to perform tasks or services, which can range from IT and customer service to manufacturing and HR functions, either onsite or externally.
What is outsourcing? | Definition and examples - Outsourcing involves passing specific tasks, subareas, or entire business processes to an external contractor, often to achieve cost savings, commonly used in customer service, IT, marketing, and manufacturing.
Outsourcing - Outsourcing is the practice of using external providers for business processes originally handled internally, involving both domestic and foreign contractors, and distinct from but often combined with offshoring.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com