Regenerative business strategy focuses on restoring and enhancing natural ecosystems while promoting social equity, contrasting with net positive strategy that aims to create more value for stakeholders than the negative impact caused. Both approaches drive sustainable growth, yet regenerative strategies prioritize system-wide renewal beyond just offsetting harms. Explore the differences and benefits of these forward-thinking frameworks to elevate your business impact.
Why it is important
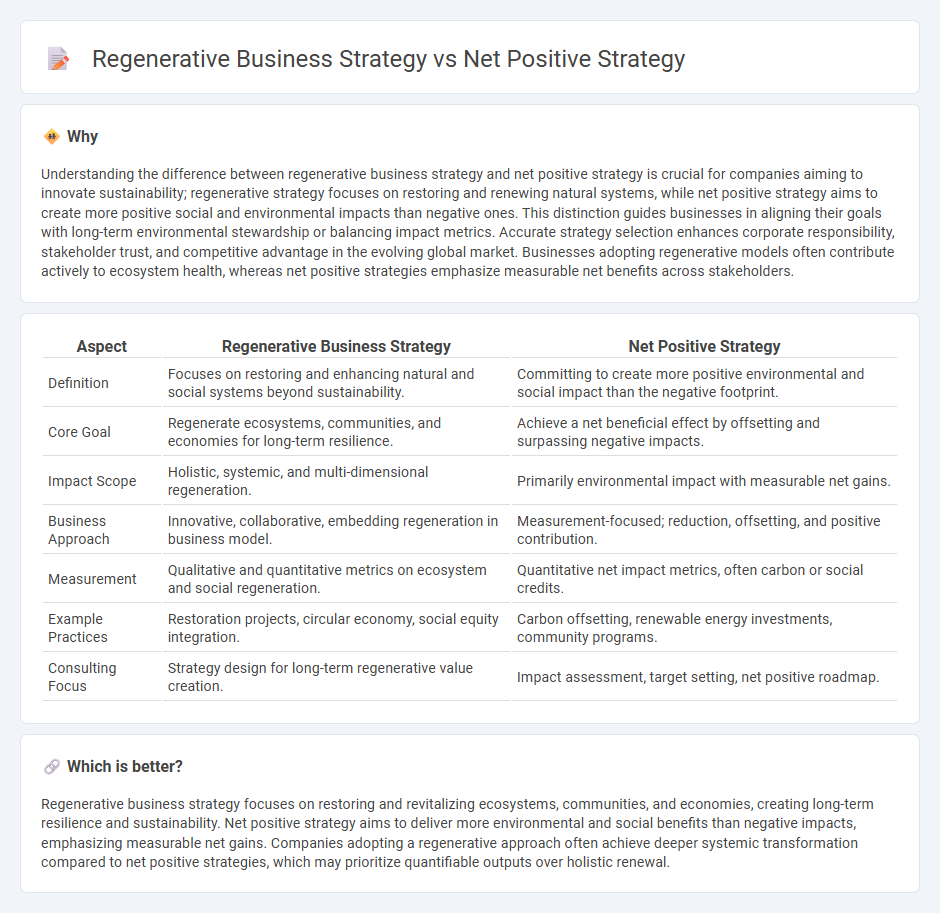
Understanding the difference between regenerative business strategy and net positive strategy is crucial for companies aiming to innovate sustainability; regenerative strategy focuses on restoring and renewing natural systems, while net positive strategy aims to create more positive social and environmental impacts than negative ones. This distinction guides businesses in aligning their goals with long-term environmental stewardship or balancing impact metrics. Accurate strategy selection enhances corporate responsibility, stakeholder trust, and competitive advantage in the evolving global market. Businesses adopting regenerative models often contribute actively to ecosystem health, whereas net positive strategies emphasize measurable net benefits across stakeholders.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Regenerative Business Strategy | Net Positive Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on restoring and enhancing natural and social systems beyond sustainability. | Committing to create more positive environmental and social impact than the negative footprint. |
| Core Goal | Regenerate ecosystems, communities, and economies for long-term resilience. | Achieve a net beneficial effect by offsetting and surpassing negative impacts. |
| Impact Scope | Holistic, systemic, and multi-dimensional regeneration. | Primarily environmental impact with measurable net gains. |
| Business Approach | Innovative, collaborative, embedding regeneration in business model. | Measurement-focused; reduction, offsetting, and positive contribution. |
| Measurement | Qualitative and quantitative metrics on ecosystem and social regeneration. | Quantitative net impact metrics, often carbon or social credits. |
| Example Practices | Restoration projects, circular economy, social equity integration. | Carbon offsetting, renewable energy investments, community programs. |
| Consulting Focus | Strategy design for long-term regenerative value creation. | Impact assessment, target setting, net positive roadmap. |
Which is better?
Regenerative business strategy focuses on restoring and revitalizing ecosystems, communities, and economies, creating long-term resilience and sustainability. Net positive strategy aims to deliver more environmental and social benefits than negative impacts, emphasizing measurable net gains. Companies adopting a regenerative approach often achieve deeper systemic transformation compared to net positive strategies, which may prioritize quantifiable outputs over holistic renewal.
Connection
Regenerative business strategy and Net Positive strategy both emphasize creating value that exceeds the environmental and social costs of business operations. Regenerative strategies focus on restoring ecosystems and communities, driving innovation in sustainable resource management and circular economy models. Net Positive aims for companies to leave a positive impact, requiring integrated approaches that align with regenerative principles to achieve long-term resilience and stakeholder trust.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Net positive strategy aims to create more environmental and social value than it consumes, resulting in a net benefit to ecosystems and communities, while regenerative business strategy goes further by restoring and enhancing natural systems through innovative practices that promote long-term resilience. Both approaches prioritize sustainability, but regenerative strategies integrate circular economy principles and biomimicry to regenerate resources and biodiversity. Discover how leading companies implement these strategies to achieve measurable impacts and drive sustainable growth.
Value Creation
Net positive strategy emphasizes creating more environmental and social benefits than harms, aiming to achieve a net gain in sustainability metrics. Regenerative business strategy goes beyond sustainability by restoring and revitalizing ecosystems and communities, fostering continuous value creation that heals and replenishes resources. Explore how both approaches drive transformative value creation in modern business practices.
Systems Thinking
Net positive strategy aims to create more value and positive impact than negative outputs by integrating sustainability into core business operations, while regenerative business strategy goes further by restoring and enhancing ecological and social systems through systemic innovation. Both approaches leverage Systems Thinking to understand interdependencies and feedback loops, enabling adaptive and resilient business models that contribute to long-term prosperity. Explore how implementing these strategies can transform organizational impact and drive sustainable growth.
Source and External Links
The Net Positive mindset: Why building a better world ... - A net positive strategy involves shifting from merely reducing harm to actively contributing positively to environmental and social outcomes, creating value rather than just cutting costs, and embedding these changes into business performance and innovation.
Net Positive vs. Net Zero: Why Climate-Ready Businesses ... - A net positive strategy means a company contributes more to the environment and society than it takes, aiming for restorative impact beyond just achieving net zero emissions, such as investing in renewable energy and community well-being.
A Net Positive imperative: Why and how business must ... - Net positive businesses actively create positive handprints through ethical labor, sustainable products, ecosystem restoration, and transparent metrics, leading to trust, customer loyalty, innovation, and long-term resilience.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com