Corporate venturing involves strategic investments and partnerships that foster innovation through direct collaboration with startups or emerging companies, enabling access to new technologies and markets. Licensing agreements grant companies the rights to use intellectual property or technology developed by third parties, providing controlled access without ownership or equity stakes. Explore these approaches in detail to determine the best strategy for your organization's growth and innovation objectives.
Why it is important
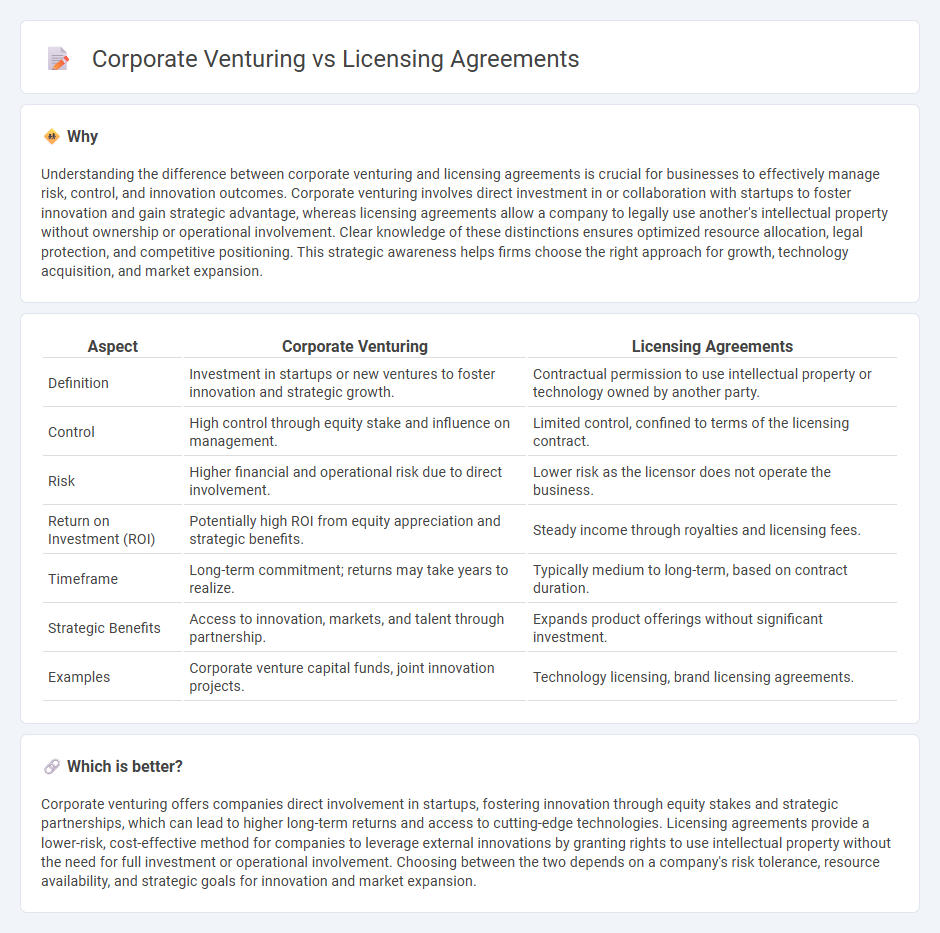
Understanding the difference between corporate venturing and licensing agreements is crucial for businesses to effectively manage risk, control, and innovation outcomes. Corporate venturing involves direct investment in or collaboration with startups to foster innovation and gain strategic advantage, whereas licensing agreements allow a company to legally use another's intellectual property without ownership or operational involvement. Clear knowledge of these distinctions ensures optimized resource allocation, legal protection, and competitive positioning. This strategic awareness helps firms choose the right approach for growth, technology acquisition, and market expansion.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Corporate Venturing | Licensing Agreements |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in startups or new ventures to foster innovation and strategic growth. | Contractual permission to use intellectual property or technology owned by another party. |
| Control | High control through equity stake and influence on management. | Limited control, confined to terms of the licensing contract. |
| Risk | Higher financial and operational risk due to direct involvement. | Lower risk as the licensor does not operate the business. |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Potentially high ROI from equity appreciation and strategic benefits. | Steady income through royalties and licensing fees. |
| Timeframe | Long-term commitment; returns may take years to realize. | Typically medium to long-term, based on contract duration. |
| Strategic Benefits | Access to innovation, markets, and talent through partnership. | Expands product offerings without significant investment. |
| Examples | Corporate venture capital funds, joint innovation projects. | Technology licensing, brand licensing agreements. |
Which is better?
Corporate venturing offers companies direct involvement in startups, fostering innovation through equity stakes and strategic partnerships, which can lead to higher long-term returns and access to cutting-edge technologies. Licensing agreements provide a lower-risk, cost-effective method for companies to leverage external innovations by granting rights to use intellectual property without the need for full investment or operational involvement. Choosing between the two depends on a company's risk tolerance, resource availability, and strategic goals for innovation and market expansion.
Connection
Corporate venturing accelerates innovation by allowing companies to invest in or partner with startups, often leveraging licensing agreements to access proprietary technologies or intellectual property. Licensing agreements formalize the use of these innovations, enabling corporations to integrate new products or services without full acquisition. This strategic connection facilitates risk-sharing and faster market entry while expanding the corporation's technological portfolio.
Key Terms
Intellectual Property Rights
Licensing agreements grant companies the right to use intellectual property (IP) owned by another entity, typically involving royalties or fees, which provides a clear framework for monetizing patents, trademarks, and copyrights without direct operational control. Corporate venturing, meanwhile, involves strategic investments or partnerships in startups or external innovation projects, offering access to emerging technologies and IP while sharing risks and rewards. Explore deeper insights into how these approaches optimize IP management and innovation strategies.
Equity Stake
Licensing agreements typically involve granting rights to use intellectual property without transferring ownership, whereas corporate venturing often entails acquiring an equity stake to foster strategic partnerships and innovation. Equity stakes in corporate venturing enable firms to actively participate in the growth and decision-making of startups, aligning interests more directly than licensing deals. Explore the key advantages and strategic implications of equity investments compared to licensing models to understand which best suits your business goals.
Strategic Alliances
Licensing agreements enable companies to monetize intellectual property by granting rights for use while retaining ownership, facilitating market expansion with controlled risk. Corporate venturing involves strategic investments or partnerships with startups that offer innovation and growth potential aligned with long-term business goals. Discover how leveraging strategic alliances through these approaches can accelerate competitive advantage and drive sustainable success.
Source and External Links
Types of Licensing Agreements - BrewerLong - This webpage provides an overview of different types of licensing agreements, including exclusive, non-exclusive, and sole licenses, and discusses the duration of licensing agreements.
What Is a Licensing Agreement? - Icertis - This webpage explains the common terms found in licensing agreements, such as the type of intellectual property, grant of license, and compensation.
Licensing Agreements: Everything You Need to Know - Docusign - This webpage offers insights into the types of licensing agreements, including patent, trademark, copyright, and trade secret licensing, and their applications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com