Diversity washing audits focus on assessing an organization's superficial commitment to diversity without embedding inclusive practices, while ESG audits evaluate environmental, social, and governance factors to ensure sustainable and ethical operations. Consulting firms help businesses identify discrepancies in diversity efforts compared to genuine ESG strategies, promoting transparency and authentic impact. Discover how thorough audits can transform your diversity initiatives and ESG performance.
Why it is important
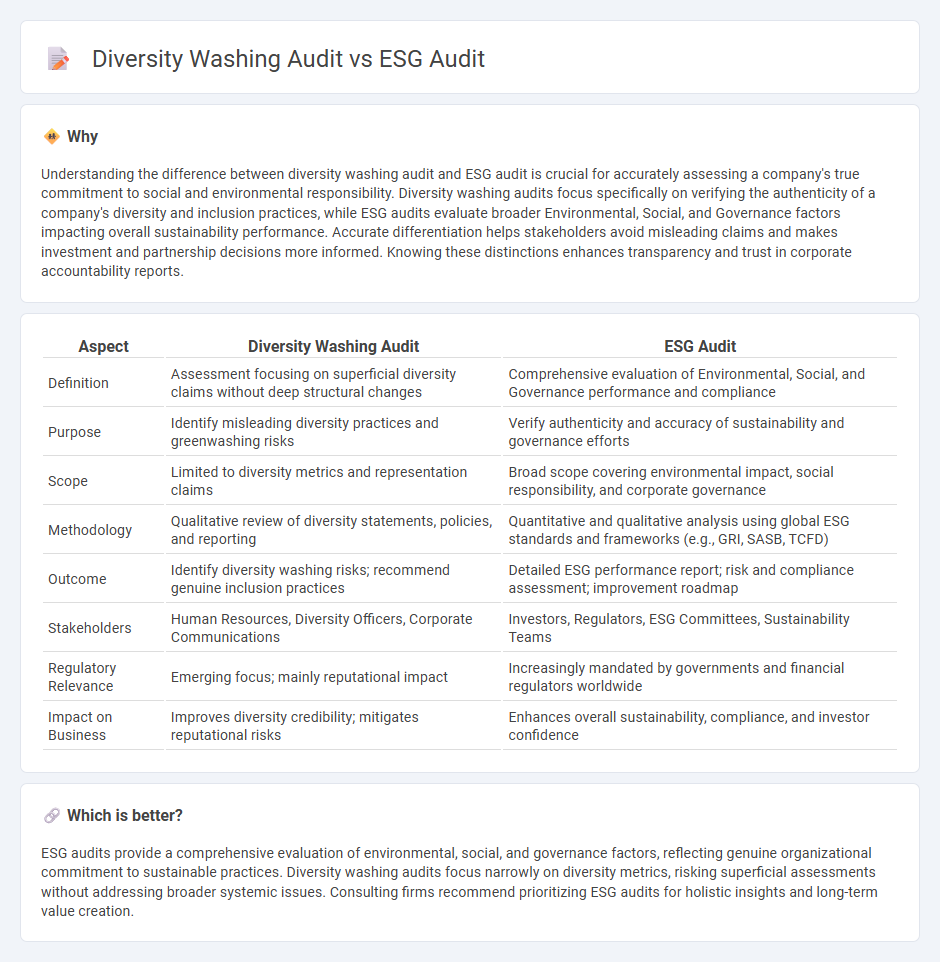
Understanding the difference between diversity washing audit and ESG audit is crucial for accurately assessing a company's true commitment to social and environmental responsibility. Diversity washing audits focus specifically on verifying the authenticity of a company's diversity and inclusion practices, while ESG audits evaluate broader Environmental, Social, and Governance factors impacting overall sustainability performance. Accurate differentiation helps stakeholders avoid misleading claims and makes investment and partnership decisions more informed. Knowing these distinctions enhances transparency and trust in corporate accountability reports.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Diversity Washing Audit | ESG Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment focusing on superficial diversity claims without deep structural changes | Comprehensive evaluation of Environmental, Social, and Governance performance and compliance |
| Purpose | Identify misleading diversity practices and greenwashing risks | Verify authenticity and accuracy of sustainability and governance efforts |
| Scope | Limited to diversity metrics and representation claims | Broad scope covering environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance |
| Methodology | Qualitative review of diversity statements, policies, and reporting | Quantitative and qualitative analysis using global ESG standards and frameworks (e.g., GRI, SASB, TCFD) |
| Outcome | Identify diversity washing risks; recommend genuine inclusion practices | Detailed ESG performance report; risk and compliance assessment; improvement roadmap |
| Stakeholders | Human Resources, Diversity Officers, Corporate Communications | Investors, Regulators, ESG Committees, Sustainability Teams |
| Regulatory Relevance | Emerging focus; mainly reputational impact | Increasingly mandated by governments and financial regulators worldwide |
| Impact on Business | Improves diversity credibility; mitigates reputational risks | Enhances overall sustainability, compliance, and investor confidence |
Which is better?
ESG audits provide a comprehensive evaluation of environmental, social, and governance factors, reflecting genuine organizational commitment to sustainable practices. Diversity washing audits focus narrowly on diversity metrics, risking superficial assessments without addressing broader systemic issues. Consulting firms recommend prioritizing ESG audits for holistic insights and long-term value creation.
Connection
Diversity washing audits evaluate a company's superficial claims about workplace inclusivity without substantial actions, while ESG audits assess Environmental, Social, and Governance practices comprehensively, including genuine diversity efforts. Both audits are interconnected as they scrutinize corporate transparency and accountability in social governance factors, influencing investor decisions and regulatory compliance. Effective ESG audits incorporate thorough diversity metrics to prevent diversity washing, ensuring credible reporting on social responsibility.
Key Terms
Compliance
ESG audits prioritize verifying compliance with environmental, social, and governance standards to ensure transparent and ethical corporate practices. Diversity washing audits specifically assess the authenticity of diversity initiatives, detecting superficial claims that fail to meet genuine inclusivity benchmarks. Explore deeper insights into compliance strategies and effective audit methodologies.
Materiality
An ESG audit rigorously assesses a company's environmental, social, and governance practices with a focus on materiality, ensuring that reported data reflects genuine impacts and risks relevant to stakeholders and regulatory requirements. In contrast, a diversity washing audit often emphasizes superficial metrics, potentially masking true inclusivity efforts and overlooking material factors crucial to organizational culture and performance. Explore deeper insights into how materiality differentiates authentic ESG compliance from performative diversity claims.
Stakeholder engagement
ESG audit rigorously evaluates stakeholder engagement by assessing transparency, accountability, and authentic inclusion of diverse voices in corporate decision-making processes. Diversity washing audit often reveals superficial efforts, lacking meaningful dialogue or measurable impact on stakeholder relationships, focusing instead on image rather than substantial change. Explore how genuine stakeholder engagement drives credible ESG performance and avoids the pitfalls of diversity washing.
Source and External Links
ESG Audit Checklist and Best Practices - An ESG audit is an assessment of environmental, social, and governance risks that organizations face, providing assurance over the integrity of their ESG reporting and helping align with risk management and compliance requirements.
A Simple 9-Step ESG Audit Checklist - An ESG audit involves evaluating a company's practices in environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance, collecting data through document reviews and interviews, and analyzing results to identify improvement opportunities and integrate ESG risks into the organization's broader risk management framework.
What is an ESG Audit? - An ESG audit is a process that evaluates a company's environmental and social risks, identifies potential issues before they escalate, and assesses the effectiveness of ESG policies, systems, and communication within the organization, separate from financial audits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com