Zero-based budgeting requires building budgets from the ground up, justifying every expense, in contrast to incremental budgeting which adjusts previous budgets by a fixed percentage. Zero-based budgeting offers precise cost control and resource allocation, while incremental budgeting provides simplicity and stability in financial planning. Discover how these budgeting methods impact organizational efficiency and decision-making.
Why it is important
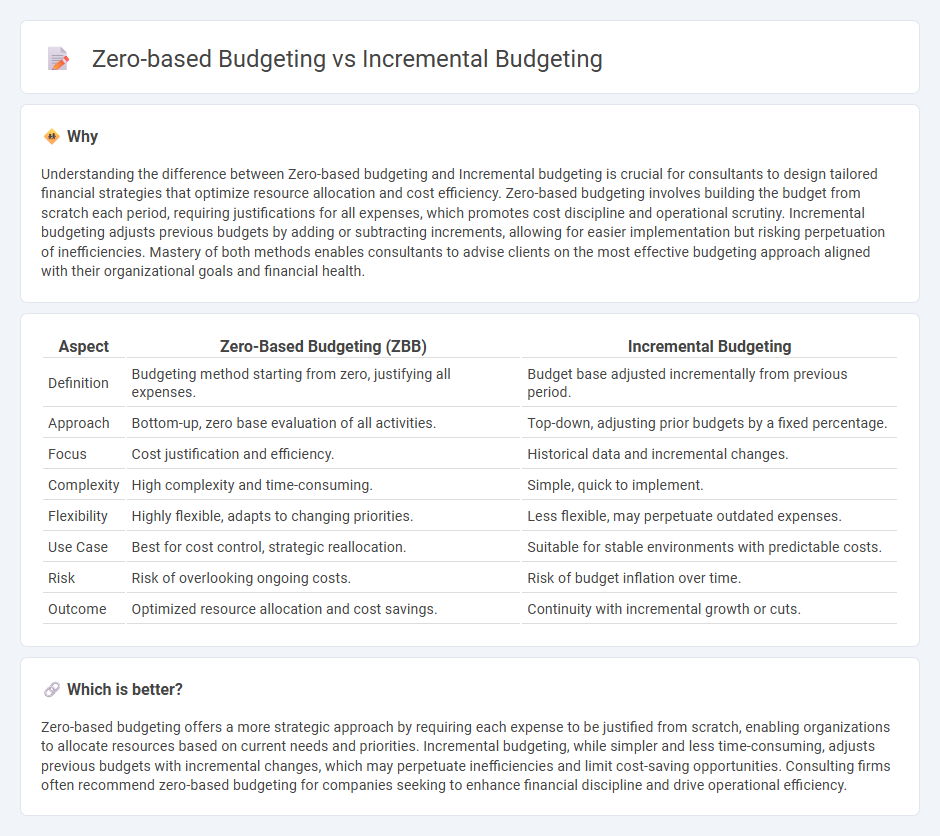
Understanding the difference between Zero-based budgeting and Incremental budgeting is crucial for consultants to design tailored financial strategies that optimize resource allocation and cost efficiency. Zero-based budgeting involves building the budget from scratch each period, requiring justifications for all expenses, which promotes cost discipline and operational scrutiny. Incremental budgeting adjusts previous budgets by adding or subtracting increments, allowing for easier implementation but risking perpetuation of inefficiencies. Mastery of both methods enables consultants to advise clients on the most effective budgeting approach aligned with their organizational goals and financial health.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) | Incremental Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Budgeting method starting from zero, justifying all expenses. | Budget base adjusted incrementally from previous period. |
| Approach | Bottom-up, zero base evaluation of all activities. | Top-down, adjusting prior budgets by a fixed percentage. |
| Focus | Cost justification and efficiency. | Historical data and incremental changes. |
| Complexity | High complexity and time-consuming. | Simple, quick to implement. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, adapts to changing priorities. | Less flexible, may perpetuate outdated expenses. |
| Use Case | Best for cost control, strategic reallocation. | Suitable for stable environments with predictable costs. |
| Risk | Risk of overlooking ongoing costs. | Risk of budget inflation over time. |
| Outcome | Optimized resource allocation and cost savings. | Continuity with incremental growth or cuts. |
Which is better?
Zero-based budgeting offers a more strategic approach by requiring each expense to be justified from scratch, enabling organizations to allocate resources based on current needs and priorities. Incremental budgeting, while simpler and less time-consuming, adjusts previous budgets with incremental changes, which may perpetuate inefficiencies and limit cost-saving opportunities. Consulting firms often recommend zero-based budgeting for companies seeking to enhance financial discipline and drive operational efficiency.
Connection
Zero-based budgeting and incremental budgeting are connected through their foundational role in financial planning and resource allocation within organizations. While incremental budgeting builds on previous budget levels with slight modifications, zero-based budgeting requires starting from a baseline of zero and justifying every expense, promoting efficient cost management. Both methods aim to optimize budget accuracy and enhance organizational financial control by addressing spending priorities.
Key Terms
Cost Justification
Incremental budgeting allocates funds based on previous budgets with adjustments for new expenses, making it simpler but potentially less efficient in cost justification. Zero-based budgeting requires justifying every expense from scratch, ensuring resources are allocated effectively but demanding more detailed analysis and time. Explore how these budgeting methods impact financial planning and decision-making in organizations.
Baseline Allocation
Incremental budgeting allocates funds based on the previous period's budget, adjusting only for incremental changes, which streamlines baseline allocation but may perpetuate inefficiencies. Zero-based budgeting requires all expenses to be justified from scratch, enabling a more precise and needs-based baseline allocation that aligns spending with current organizational priorities. Explore more about optimizing baseline allocation through these budgeting methods for improved financial management.
Resource Optimization
Incremental budgeting allocates resources based on previous periods' budgets with slight adjustments, promoting stability but potentially perpetuating inefficiencies. Zero-based budgeting requires justification for every expense from scratch, ensuring optimal resource allocation aligned with current priorities and reducing waste. Explore how these budgeting methods impact your organization's resource optimization strategies.
Source and External Links
Who Should & Shouldn't Use Incremental Budgeting - Incremental budgeting uses the current year's budget as a baseline and adjusts it by small, incremental amounts to create the next budget, making it simple and adaptable for most business functions.
What is Incremental Budgeting? - This approach starts with the previous budget as the foundation, then makes minor increases or decreases to account for changes like inflation or growth, resulting in a straightforward and predictable budgeting process.
Incremental Budgeting - Overview, Advantages, Disadvantages - Incremental budgeting is a conservative method that develops new budgets by making only marginal adjustments to the current one, ensuring stability and reducing the complexity of annual budget preparation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com