Outside-in benchmarking compares a company's performance against external industry leaders to identify best practices and innovation opportunities, while internal benchmarking focuses on measuring and improving processes within the organization by comparing different departments or units. This strategic approach helps businesses leverage competitive insights and optimize internal operations for enhanced efficiency and growth. Discover how adopting the right benchmarking method can drive your company's transformation and success.
Why it is important
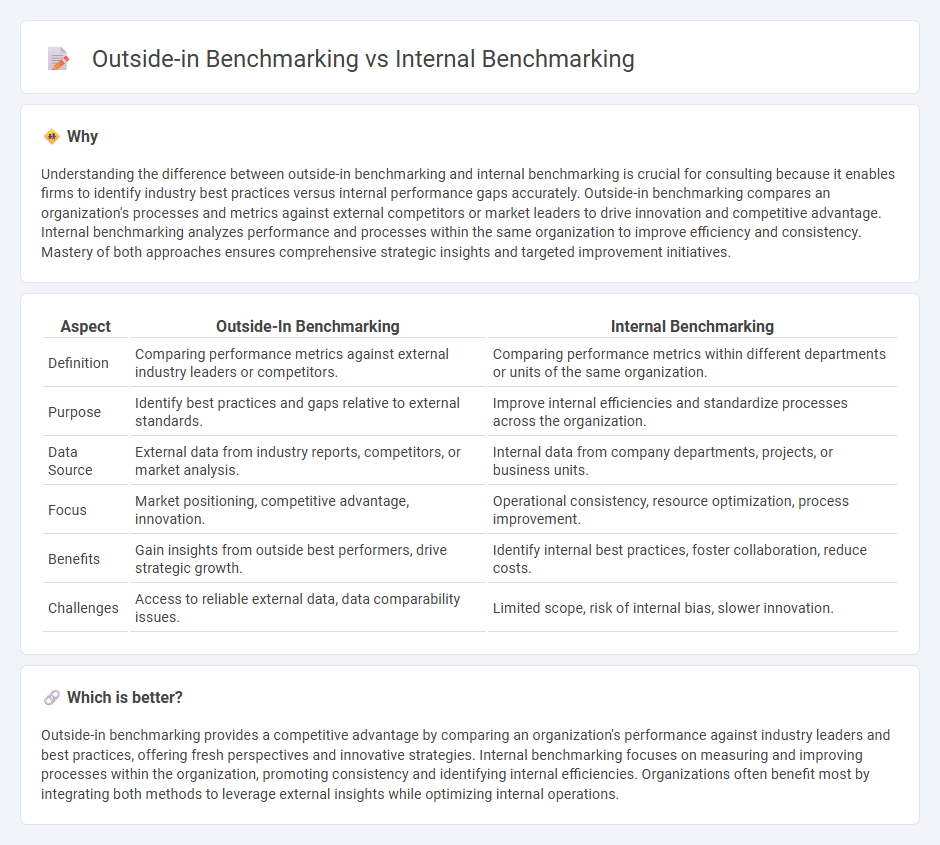
Understanding the difference between outside-in benchmarking and internal benchmarking is crucial for consulting because it enables firms to identify industry best practices versus internal performance gaps accurately. Outside-in benchmarking compares an organization's processes and metrics against external competitors or market leaders to drive innovation and competitive advantage. Internal benchmarking analyzes performance and processes within the same organization to improve efficiency and consistency. Mastery of both approaches ensures comprehensive strategic insights and targeted improvement initiatives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Outside-In Benchmarking | Internal Benchmarking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comparing performance metrics against external industry leaders or competitors. | Comparing performance metrics within different departments or units of the same organization. |
| Purpose | Identify best practices and gaps relative to external standards. | Improve internal efficiencies and standardize processes across the organization. |
| Data Source | External data from industry reports, competitors, or market analysis. | Internal data from company departments, projects, or business units. |
| Focus | Market positioning, competitive advantage, innovation. | Operational consistency, resource optimization, process improvement. |
| Benefits | Gain insights from outside best performers, drive strategic growth. | Identify internal best practices, foster collaboration, reduce costs. |
| Challenges | Access to reliable external data, data comparability issues. | Limited scope, risk of internal bias, slower innovation. |
Which is better?
Outside-in benchmarking provides a competitive advantage by comparing an organization's performance against industry leaders and best practices, offering fresh perspectives and innovative strategies. Internal benchmarking focuses on measuring and improving processes within the organization, promoting consistency and identifying internal efficiencies. Organizations often benefit most by integrating both methods to leverage external insights while optimizing internal operations.
Connection
Outside-in benchmarking provides insights into industry standards and competitor strategies, forming a foundation for internal benchmarking processes. Internal benchmarking uses these external performance metrics to evaluate and improve a company's own operational practices and efficiency. This connection ensures continuous improvement by aligning internal processes with best-in-class external benchmarks.
Key Terms
Performance Metrics
Internal benchmarking compares key performance metrics within an organization's departments to identify best practices and improve operational efficiency, emphasizing consistency and internal standards. Outside-in benchmarking evaluates performance metrics against external competitors or industry leaders to identify gaps and drive innovation through competitive insights. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which benchmarking strategy best aligns with your organizational goals and performance objectives.
Best Practices
Internal benchmarking analyzes best practices within an organization by comparing performance across departments or units to identify areas for improvement. Outside-in benchmarking examines industry leaders and competitors to adopt external best practices that drive innovation and operational excellence. Explore how integrating both approaches can elevate your company's competitive edge and efficiency.
Competitive Analysis
Internal benchmarking focuses on comparing processes and performance within the same organization to identify best practices and improve efficiency, while outside-in benchmarking analyzes competitors and market leaders to gain insights into industry standards and competitive positioning. Competitive analysis benefits from outside-in benchmarking by revealing strengths and weaknesses relative to industry rivals, enabling strategic adjustments based on external market dynamics. Discover more about how these benchmarking approaches enhance competitive analysis in your business strategy.
Source and External Links
Cracking the Code: The Ultimate Guide to Effective Internal Benchmarking Practices in Industry - Internal benchmarking is the process of comparing internal processes and performance metrics within the same organization to identify best practices, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement, often proving more resource-efficient than external benchmarking.
Internal Benchmarking 101: A Beginner's Guide - Internal benchmarking involves analyzing a company's own processes, departments, or performance over different time periods to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement, with types including strategic, performance, digital, and practice benchmarking.
What are the Four Types of Benchmarking? - Internal benchmarking compares metrics and practices between different units or departments within an organization to establish current performance standards and identify efficiencies, often serving as a starting point before engaging in external benchmarking.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com