Ethical supply chains prioritize transparency, fair labor practices, and environmental responsibility throughout product sourcing and distribution, ensuring alignment with corporate social responsibility goals. Closed-loop supply chains focus on sustainability by integrating product return, reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling processes to minimize waste and resource consumption. Explore the distinctions and benefits of these supply chain models to enhance your business's operational and ethical impact.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between an ethical supply chain and a closed-loop supply chain is crucial for consultants to effectively guide businesses in meeting sustainability goals and regulatory compliance. An ethical supply chain emphasizes fair labor practices, human rights, and environmental stewardship, while a closed-loop supply chain focuses on recycling, reuse, and minimizing waste through circular processes. Consultants must optimize strategies that align with client values and market demands, ensuring both social responsibility and operational efficiency. Accurate differentiation enhances decision-making in supply chain risk management and corporate social responsibility reporting.
Comparison Table
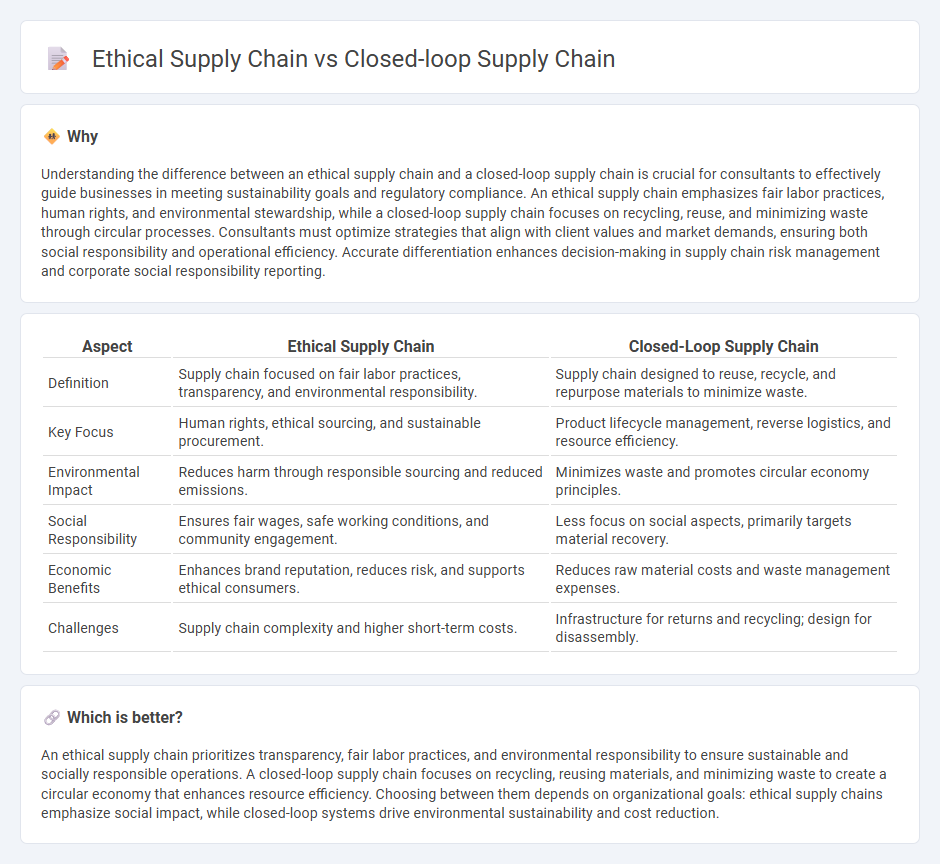
| Aspect | Ethical Supply Chain | Closed-Loop Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supply chain focused on fair labor practices, transparency, and environmental responsibility. | Supply chain designed to reuse, recycle, and repurpose materials to minimize waste. |
| Key Focus | Human rights, ethical sourcing, and sustainable procurement. | Product lifecycle management, reverse logistics, and resource efficiency. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces harm through responsible sourcing and reduced emissions. | Minimizes waste and promotes circular economy principles. |
| Social Responsibility | Ensures fair wages, safe working conditions, and community engagement. | Less focus on social aspects, primarily targets material recovery. |
| Economic Benefits | Enhances brand reputation, reduces risk, and supports ethical consumers. | Reduces raw material costs and waste management expenses. |
| Challenges | Supply chain complexity and higher short-term costs. | Infrastructure for returns and recycling; design for disassembly. |
Which is better?
An ethical supply chain prioritizes transparency, fair labor practices, and environmental responsibility to ensure sustainable and socially responsible operations. A closed-loop supply chain focuses on recycling, reusing materials, and minimizing waste to create a circular economy that enhances resource efficiency. Choosing between them depends on organizational goals: ethical supply chains emphasize social impact, while closed-loop systems drive environmental sustainability and cost reduction.
Connection
Ethical supply chains prioritize transparency, fair labor practices, and environmental responsibility, which align closely with closed-loop supply chains that focus on sustainability through recycling and waste reduction. Both models emphasize minimizing negative social and environmental impacts while promoting resource efficiency throughout product lifecycles. Implementing a closed-loop system supports ethical supply chains by ensuring materials are reused responsibly, reducing exploitation of natural resources and enhancing corporate social responsibility.
Key Terms
Circularity
Closed-loop supply chains prioritize circularity by designing products for reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling, minimizing waste and resource consumption throughout the product lifecycle. Ethical supply chains emphasize social responsibility, fair labor practices, and environmental sustainability but may not always implement circular processes. Explore the distinct strategies driving circularity in closed-loop versus ethical supply chains to optimize sustainable business practices.
Transparency
Closed-loop supply chains prioritize transparency by tracking product lifecycle stages from production to recycling, ensuring materials are reused efficiently and waste is minimized. Ethical supply chains emphasize transparency in labor practices, sourcing, and environmental impact to uphold social responsibility and regulatory compliance. Explore how transparency in these supply chain models drives sustainability and corporate accountability.
Traceability
Closed-loop supply chains emphasize traceability through the complete tracking of products from production to recycling, enabling efficient resource recovery and waste reduction. Ethical supply chains prioritize transparency in sourcing and manufacturing practices to ensure compliance with labor rights, environmental standards, and social responsibility. Explore the distinct methods each supply chain employs to enhance traceability and promote sustainability.
Source and External Links
Unlocking the Potential of a Closed Loop Supply Chain - A closed loop supply chain (CLSC) integrates forward logistics with reverse logistics, creating a circular flow where end-of-life products are recovered and reintegrated into production, reducing costs, environmental impact, and enhancing sustainability and regulatory compliance.
What is a Closed-Loop Supply Chain? - Revolutionized - A closed-loop supply chain uses reverse logistics to bring products back from consumers for repair, resale, or reuse, supporting waste reduction and sustainable business practices within the circular economy.
Closed Loop Supply Chain (CLSC): Meaning & Examples - CLSC manages the entire product lifecycle by combining forward flow from supplier to consumer with a backward flow of used products for recycling or remanufacturing, often enhanced by automation for efficiency and real-time tracking.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com