Green logistics emphasizes sustainable practices by reducing carbon emissions, optimizing resource use, and promoting eco-friendly transportation methods to minimize environmental impact. Urban logistics focuses on the efficient management of goods delivery within city environments, addressing challenges like congestion, limited space, and local regulations to ensure timely distribution. Explore how these logistics approaches transform commerce efficiency and sustainability in modern urban settings.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Green logistics and Urban logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain sustainability and efficiency in different environments. Green logistics focuses on minimizing environmental impact through eco-friendly transportation and packaging methods, contributing to reduced carbon footprints. Urban logistics addresses the challenges of delivering goods in densely populated cities, emphasizing traffic management and last-mile delivery solutions. Differentiating these concepts enables businesses to implement tailored strategies that enhance operational performance while meeting regulatory and consumer demands.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Logistics | Urban Logistics |
|---|---|---|
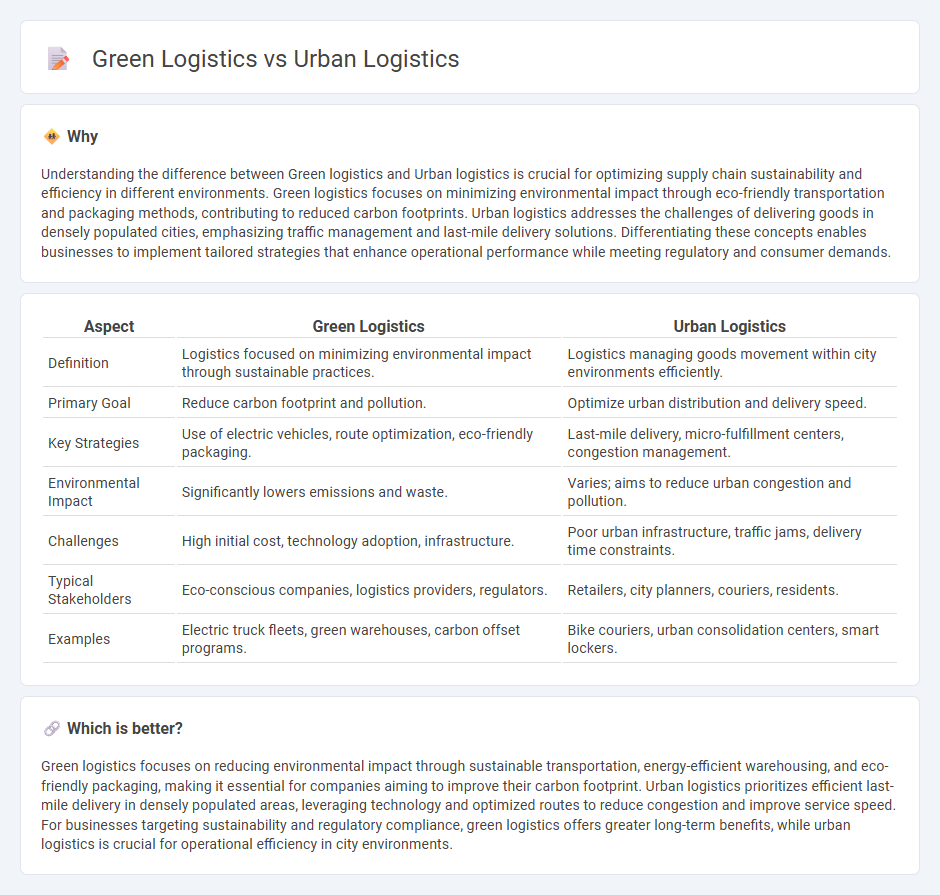
| Definition | Logistics focused on minimizing environmental impact through sustainable practices. | Logistics managing goods movement within city environments efficiently. |
| Primary Goal | Reduce carbon footprint and pollution. | Optimize urban distribution and delivery speed. |
| Key Strategies | Use of electric vehicles, route optimization, eco-friendly packaging. | Last-mile delivery, micro-fulfillment centers, congestion management. |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly lowers emissions and waste. | Varies; aims to reduce urban congestion and pollution. |
| Challenges | High initial cost, technology adoption, infrastructure. | Poor urban infrastructure, traffic jams, delivery time constraints. |
| Typical Stakeholders | Eco-conscious companies, logistics providers, regulators. | Retailers, city planners, couriers, residents. |
| Examples | Electric truck fleets, green warehouses, carbon offset programs. | Bike couriers, urban consolidation centers, smart lockers. |
Which is better?
Green logistics focuses on reducing environmental impact through sustainable transportation, energy-efficient warehousing, and eco-friendly packaging, making it essential for companies aiming to improve their carbon footprint. Urban logistics prioritizes efficient last-mile delivery in densely populated areas, leveraging technology and optimized routes to reduce congestion and improve service speed. For businesses targeting sustainability and regulatory compliance, green logistics offers greater long-term benefits, while urban logistics is crucial for operational efficiency in city environments.
Connection
Green logistics and urban logistics intersect through the shared goal of reducing environmental impact within city supply chains by optimizing transportation routes, utilizing eco-friendly vehicles, and implementing efficient last-mile delivery solutions. The integration of green logistics principles in urban logistics supports sustainable commerce by lowering carbon emissions, minimizing traffic congestion, and promoting the use of renewable energy sources in densely populated areas. This convergence enhances overall urban mobility and aligns commercial distribution practices with growing environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainability.
Key Terms
Last-mile delivery
Urban logistics concentrates on optimizing last-mile delivery through efficient routing and consolidation hubs to reduce congestion in densely populated areas. Green logistics emphasizes sustainable practices such as electric vehicles and cargo bikes to minimize carbon emissions during last-mile deliveries. Explore innovative solutions blending urban efficiency with eco-friendly methods to revolutionize last-mile logistics.
Carbon footprint
Urban logistics involves the efficient movement of goods within cities, often contributing significantly to carbon emissions due to traffic congestion and frequent delivery routes. Green logistics prioritizes sustainability by integrating eco-friendly practices such as electric vehicles, optimized routing, and reduced packaging to minimize the carbon footprint. Discover how these strategies transform urban freight transport and support environmental goals.
Smart transportation
Urban logistics increasingly integrates smart transportation technologies to optimize delivery routes and reduce congestion in city environments. Green logistics emphasizes eco-friendly practices such as electric vehicles and renewable energy-powered freight systems to minimize carbon emissions. Explore the latest advancements in smart transportation shaping sustainable urban and green logistics solutions.
Source and External Links
What is Urban Logistics? Definition, Challenges, and Strategies - Urban logistics focuses on optimizing the logistics and distribution of goods and services within urban areas, addressing last-mile delivery, warehousing, inventory management, sustainable transportation, and traffic management to improve efficiency and reduce congestion and environmental impact in cities.
Transforming Urban Logistics in Cities - The World Economic Forum - This report outlines strategies for sustainable and efficient last-mile delivery in cities, aiming to reduce emissions, alleviate congestion, and improve safety by encouraging collaboration among public and private stakeholders and investing in innovation and infrastructure.
Five things you should know about urban logistics - JLL - Urban logistics is a fast-growing supply chain segment driven by e-commerce, requiring strategically located facilities near city centers that enable quick parcel transfer between transport modes, to meet the rising demand from consumers and businesses in densely populated urban areas.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com