Drop servicing is a business model where entrepreneurs sell services fulfilled by third-party providers, while dropshipping involves selling physical products that suppliers ship directly to customers. Both models minimize inventory risks and upfront costs, making them popular for e-commerce startups aiming to maximize profitability with limited capital. Explore the advantages and challenges of drop servicing versus dropshipping to choose the best approach for your online commerce venture.
Why it is important
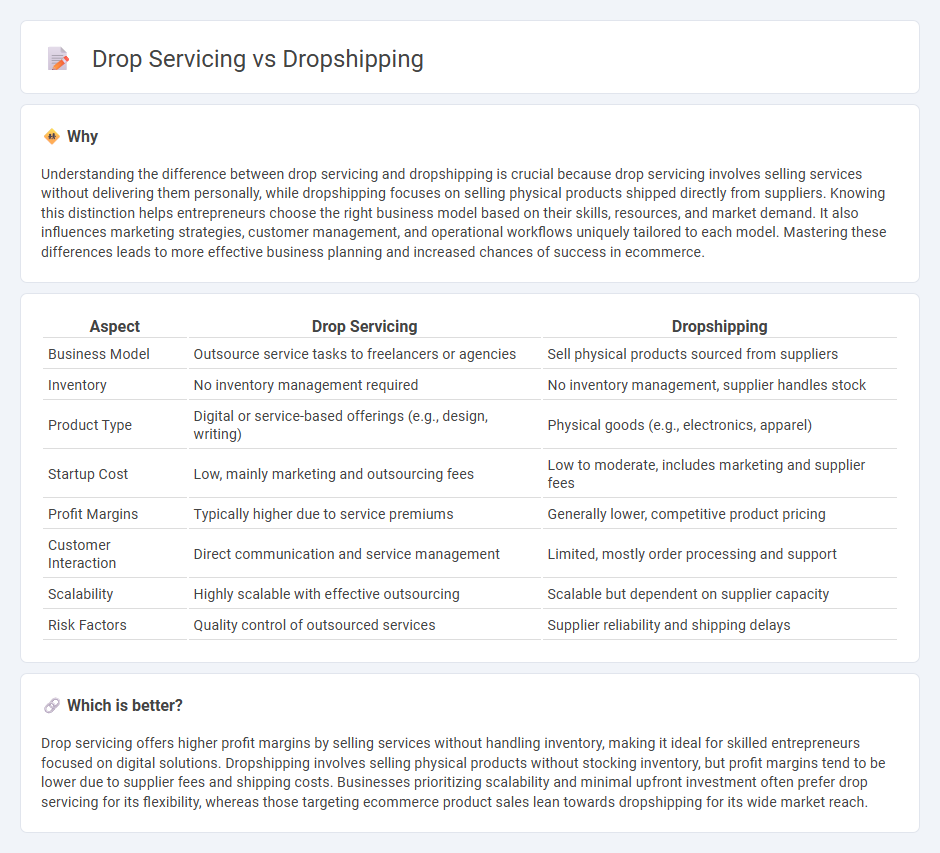
Understanding the difference between drop servicing and dropshipping is crucial because drop servicing involves selling services without delivering them personally, while dropshipping focuses on selling physical products shipped directly from suppliers. Knowing this distinction helps entrepreneurs choose the right business model based on their skills, resources, and market demand. It also influences marketing strategies, customer management, and operational workflows uniquely tailored to each model. Mastering these differences leads to more effective business planning and increased chances of success in ecommerce.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Drop Servicing | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Outsource service tasks to freelancers or agencies | Sell physical products sourced from suppliers |
| Inventory | No inventory management required | No inventory management, supplier handles stock |
| Product Type | Digital or service-based offerings (e.g., design, writing) | Physical goods (e.g., electronics, apparel) |
| Startup Cost | Low, mainly marketing and outsourcing fees | Low to moderate, includes marketing and supplier fees |
| Profit Margins | Typically higher due to service premiums | Generally lower, competitive product pricing |
| Customer Interaction | Direct communication and service management | Limited, mostly order processing and support |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with effective outsourcing | Scalable but dependent on supplier capacity |
| Risk Factors | Quality control of outsourced services | Supplier reliability and shipping delays |
Which is better?
Drop servicing offers higher profit margins by selling services without handling inventory, making it ideal for skilled entrepreneurs focused on digital solutions. Dropshipping involves selling physical products without stocking inventory, but profit margins tend to be lower due to supplier fees and shipping costs. Businesses prioritizing scalability and minimal upfront investment often prefer drop servicing for its flexibility, whereas those targeting ecommerce product sales lean towards dropshipping for its wide market reach.
Connection
Drop servicing and dropshipping both leverage e-commerce models that minimize inventory management by outsourcing services or products to third-party providers. These approaches streamline operations through digital platforms, enabling entrepreneurs to sell without holding physical stock or directly performing services. The connection lies in their reliance on intermediaries, making them scalable and cost-effective solutions in online commerce.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory management by allowing sellers to forward customer orders directly to suppliers, who handle storage and shipping. Drop servicing requires managing digital assets and client schedules rather than physical inventory, streamlining operational processes without stock concerns. Explore in-depth strategies to optimize inventory management and service delivery for both business models.
Service Fulfillment
Dropshipping involves product fulfillment through third-party suppliers who handle inventory and shipping directly to customers, minimizing the seller's logistical responsibilities. Drop servicing emphasizes service fulfillment by outsourcing tasks such as graphic design, content writing, or digital marketing to skilled professionals while managing client interactions and quality control. Explore the key differences in operational workflows and profit models to determine which business model aligns best with your goals.
Profit Margin
Dropshipping involves selling physical products without holding inventory, often resulting in profit margins between 10%-30% due to supplier costs and competition. Drop servicing sells digital services or outsourcing tasks, typically yielding higher profit margins of 50%-80% by minimizing overhead and supply chain expenses. Explore detailed comparisons to maximize your profit potential in both business models.
Source and External Links
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Wix.com - Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment business model where the seller does not keep inventory but forwards customer orders to a third-party supplier who handles production, warehousing, and shipping directly to customers.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Shopify - Dropshipping involves partnering with suppliers who handle product storage and shipping, while the retailer creates an online store to sell and market products, receiving orders that are then forwarded to the supplier for fulfillment.
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a retail method where the seller accepts orders without stock and forwards them to wholesalers, manufacturers, or fulfillment centers to ship directly to customers, offering minimal initial investment but less control over product quality and shipping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com