Crowdsourced delivery leverages a large pool of anonymous, independent drivers to fulfill delivery requests, optimizing flexibility and speed for e-commerce businesses. Peer-to-peer delivery involves individuals personally transporting goods for others within their community or network, often reducing costs and fostering local trust. Explore the nuances and benefits of each model to determine which best fits your business needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between crowdsourced delivery and peer-to-peer delivery is crucial for optimizing logistics strategies, enhancing customer satisfaction, and reducing operational costs in commerce. Crowdsourced delivery leverages a large network of third-party drivers coordinated by a company, while peer-to-peer delivery involves individuals directly delivering goods to each other without a centralized platform. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses select the best model based on scalability, reliability, and regulatory compliance to improve efficiency. This knowledge drives better decision-making in e-commerce, last-mile delivery, and supply chain management.
Comparison Table
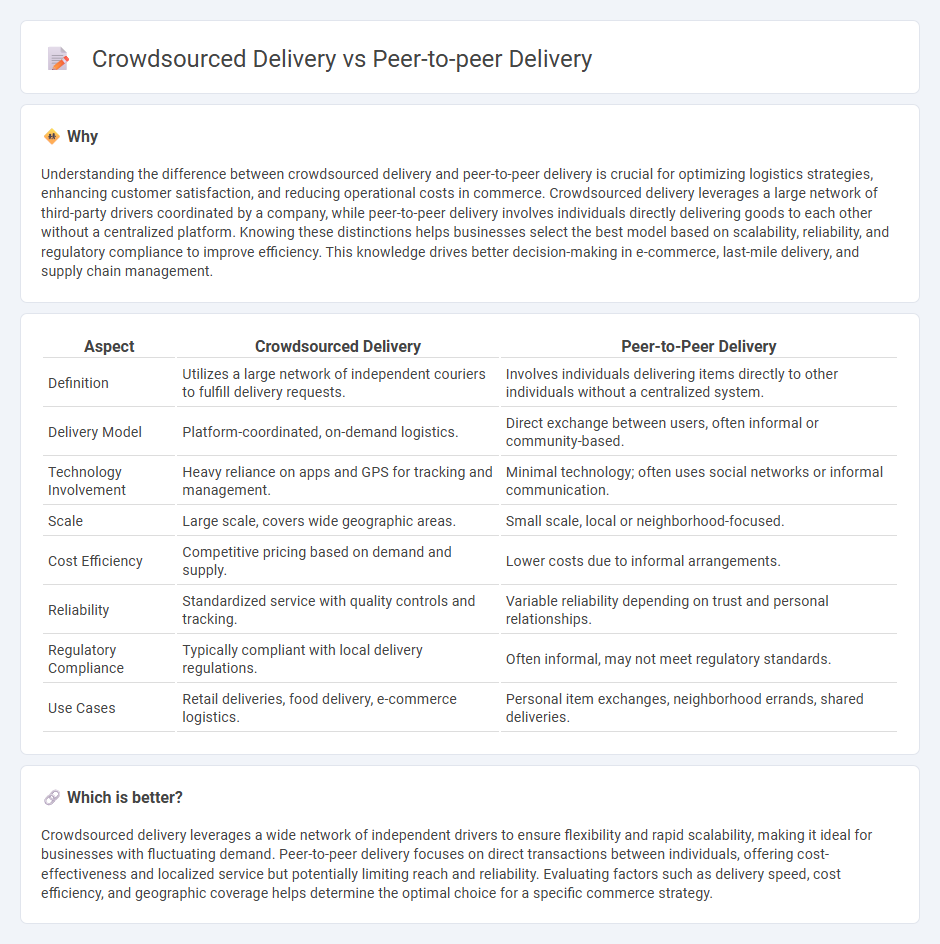
| Aspect | Crowdsourced Delivery | Peer-to-Peer Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Utilizes a large network of independent couriers to fulfill delivery requests. | Involves individuals delivering items directly to other individuals without a centralized system. |
| Delivery Model | Platform-coordinated, on-demand logistics. | Direct exchange between users, often informal or community-based. |
| Technology Involvement | Heavy reliance on apps and GPS for tracking and management. | Minimal technology; often uses social networks or informal communication. |
| Scale | Large scale, covers wide geographic areas. | Small scale, local or neighborhood-focused. |
| Cost Efficiency | Competitive pricing based on demand and supply. | Lower costs due to informal arrangements. |
| Reliability | Standardized service with quality controls and tracking. | Variable reliability depending on trust and personal relationships. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Typically compliant with local delivery regulations. | Often informal, may not meet regulatory standards. |
| Use Cases | Retail deliveries, food delivery, e-commerce logistics. | Personal item exchanges, neighborhood errands, shared deliveries. |
Which is better?
Crowdsourced delivery leverages a wide network of independent drivers to ensure flexibility and rapid scalability, making it ideal for businesses with fluctuating demand. Peer-to-peer delivery focuses on direct transactions between individuals, offering cost-effectiveness and localized service but potentially limiting reach and reliability. Evaluating factors such as delivery speed, cost efficiency, and geographic coverage helps determine the optimal choice for a specific commerce strategy.
Connection
Crowdsourced delivery and peer-to-peer delivery both leverage decentralized networks of individuals to fulfill orders, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs in commerce logistics. These models rely on non-professional couriers, often using mobile apps to match delivery requests with local drivers or riders, enabling faster last-mile delivery. By tapping into shared resources and local networks, they democratize logistics and support scalable, flexible distribution channels in the e-commerce ecosystem.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Peer-to-peer delivery leverages a decentralized network of individual users to exchange goods directly, reducing reliance on centralized logistics hubs and enhancing flexibility. Crowdsourced delivery also employs a distributed workforce but often operates through platform-controlled systems that coordinate tasks and maintain oversight. Explore the nuances of decentralization in delivery models to understand their impact on efficiency and scalability.
Gig Economy
Peer-to-peer delivery leverages individual consumers to transport goods directly between each other, reducing the need for traditional logistics infrastructure and promoting cost-effectiveness in the gig economy. Crowdsourced delivery mobilizes a distributed network of freelance couriers, enabling rapid, flexible shipment fulfillment across urban areas with scalable workforce engagement. Explore detailed insights on how these models are transforming last-mile logistics within the evolving gig economy landscape.
Platform Mediation
Peer-to-peer delivery relies on direct exchanges between users, minimizing platform intervention, while crowdsourced delivery platforms actively mediate by coordinating drivers, orders, and payments to ensure reliability and scalability. Platform mediation in crowdsourced delivery enhances trust through real-time tracking, ratings, and dispute resolution, making it more suitable for urban areas with high demand. Explore more about how platform mediation shapes the efficiency and user experience in various delivery models.
Source and External Links
Carrycome - P2P Courier Service - A peer-to-peer platform that connects senders with travelers to deliver packages quickly and securely, no matter the distance.
GoShare - Connects users to a network of vetted drivers with various vehicles for on-demand, same-day delivery of items ranging from parcels to large furniture.
Grabr - Enables international peer-to-peer shopping and delivery by matching buyers with travelers who can bring overseas products directly to them.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com