Distributed ledger marketplaces leverage blockchain technology to enable transparent, secure, and decentralized transactions, reducing reliance on intermediaries and minimizing fraud risks compared to traditional e-commerce platforms. These marketplaces offer enhanced data integrity and real-time settlement, improving trust among buyers and sellers. Explore the benefits and challenges of distributed ledger marketplaces versus traditional e-commerce platforms to understand the future of online commerce.
Why it is important
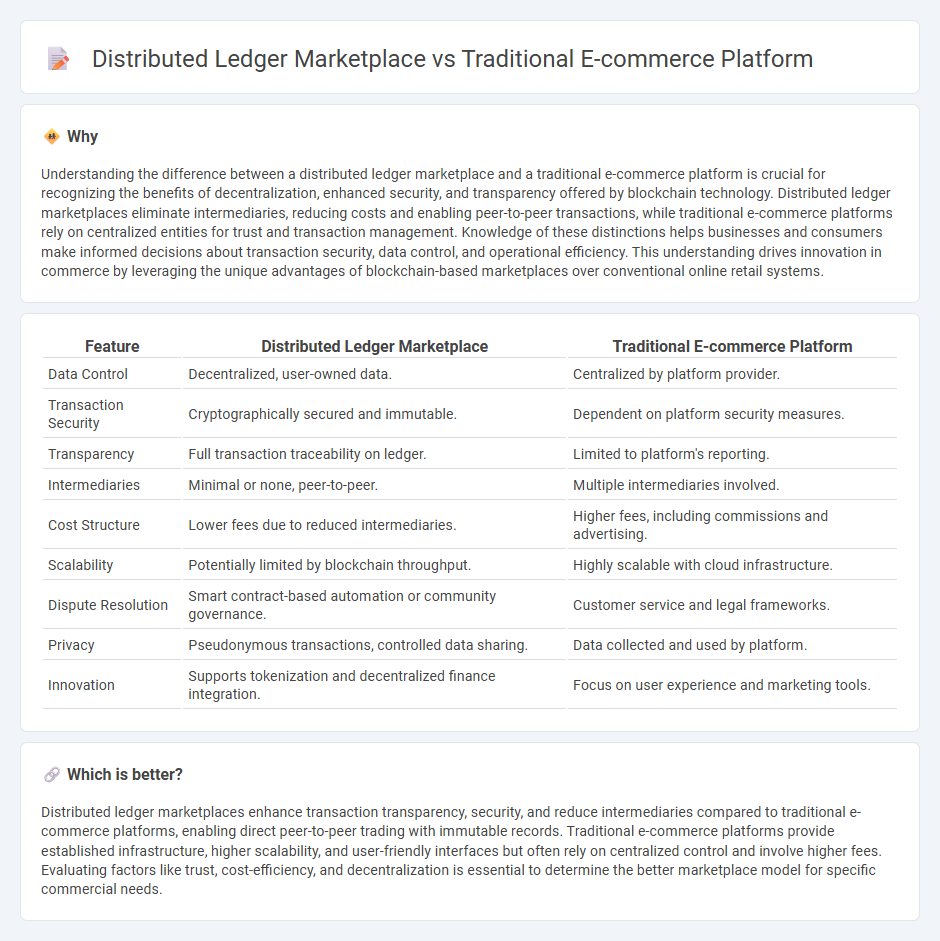
Understanding the difference between a distributed ledger marketplace and a traditional e-commerce platform is crucial for recognizing the benefits of decentralization, enhanced security, and transparency offered by blockchain technology. Distributed ledger marketplaces eliminate intermediaries, reducing costs and enabling peer-to-peer transactions, while traditional e-commerce platforms rely on centralized entities for trust and transaction management. Knowledge of these distinctions helps businesses and consumers make informed decisions about transaction security, data control, and operational efficiency. This understanding drives innovation in commerce by leveraging the unique advantages of blockchain-based marketplaces over conventional online retail systems.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Distributed Ledger Marketplace | Traditional E-commerce Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Data Control | Decentralized, user-owned data. | Centralized by platform provider. |
| Transaction Security | Cryptographically secured and immutable. | Dependent on platform security measures. |
| Transparency | Full transaction traceability on ledger. | Limited to platform's reporting. |
| Intermediaries | Minimal or none, peer-to-peer. | Multiple intermediaries involved. |
| Cost Structure | Lower fees due to reduced intermediaries. | Higher fees, including commissions and advertising. |
| Scalability | Potentially limited by blockchain throughput. | Highly scalable with cloud infrastructure. |
| Dispute Resolution | Smart contract-based automation or community governance. | Customer service and legal frameworks. |
| Privacy | Pseudonymous transactions, controlled data sharing. | Data collected and used by platform. |
| Innovation | Supports tokenization and decentralized finance integration. | Focus on user experience and marketing tools. |
Which is better?
Distributed ledger marketplaces enhance transaction transparency, security, and reduce intermediaries compared to traditional e-commerce platforms, enabling direct peer-to-peer trading with immutable records. Traditional e-commerce platforms provide established infrastructure, higher scalability, and user-friendly interfaces but often rely on centralized control and involve higher fees. Evaluating factors like trust, cost-efficiency, and decentralization is essential to determine the better marketplace model for specific commercial needs.
Connection
Distributed ledger marketplaces enhance traditional e-commerce platforms by providing decentralized transaction records, increasing transparency and security for buyers and sellers. Integration of blockchain technology in e-commerce reduces fraud risks and streamlines payment processes through smart contracts. This connection fosters trust, lowers operational costs, and enables direct peer-to-peer transactions within conventional online retail environments.
Key Terms
Centralized Authority
Traditional e-commerce platforms operate under a centralized authority that controls transactions, manages user data, and enforces policies, which can create single points of failure and raise concerns about data privacy and censorship. Distributed ledger marketplaces eliminate central authority by utilizing blockchain technology, enabling peer-to-peer transactions with increased transparency, security, and user control over personal information. Explore the distinct advantages of decentralized systems to understand how they reshape online commerce ecosystems.
Decentralization
Traditional e-commerce platforms centralize control over transactions, user data, and payment processing, creating potential single points of failure and vulnerabilities to censorship or data breaches. Distributed ledger marketplaces leverage blockchain technology to enable decentralized transaction validation, transparent record-keeping, and user autonomy, enhancing security and trust without intermediaries. Explore the advantages and challenges of decentralized marketplaces to understand how they reshape digital commerce governance.
Trustless Transactions
Traditional e-commerce platforms rely on centralized authorities to manage transactions, which can introduce trust issues and increase the risk of fraud or data breaches. Distributed ledger marketplaces utilize blockchain technology to enable trustless transactions, where smart contracts automatically enforce agreements without intermediaries, ensuring transparency and security. Explore how these innovative systems redefine online commerce by eliminating the need for trust in third parties.
Source and External Links
Differentiating Social Commerce from Traditional E ... - TechAhead - Traditional e-commerce refers to buying and selling goods or services online through dedicated platforms, featuring online stores, browsing and checkout processes, various payment methods, and order fulfillment with shipping to customers without physical interaction.
Quick Commerce vs. Traditional E-Commerce - A Core Differences - Traditional e-commerce operates like regular website shopping with many product selections, longer delivery times than quick commerce, high scalability, and established delivery methods often exemplified by sites like Amazon and eBay.
Composable commerce vs. traditional commerce - Traditional commerce platforms are typically monolithic systems combining the front-end, back-end, and database into a single integrated unit, representing a conventional architecture for building e-commerce sites.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com