Zero party data refers to information that customers intentionally and proactively share with brands, such as preferences, interests, and feedback, ensuring high accuracy and privacy compliance. Derived data is collected through customer behavior analysis and algorithms, inferring insights from actions rather than explicit communication, which may involve assumptions and less transparency. Explore deeper to understand how these data types impact personalized commerce strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between zero party data and derived data is crucial for accurate customer targeting and personalized marketing strategies. Zero party data is voluntarily shared by customers, ensuring higher accuracy and trust, while derived data is inferred from behaviors and may carry assumptions. Using zero party data enhances consent compliance and data privacy by aligning with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses optimize data-driven decisions and improve customer engagement effectively.
Comparison Table
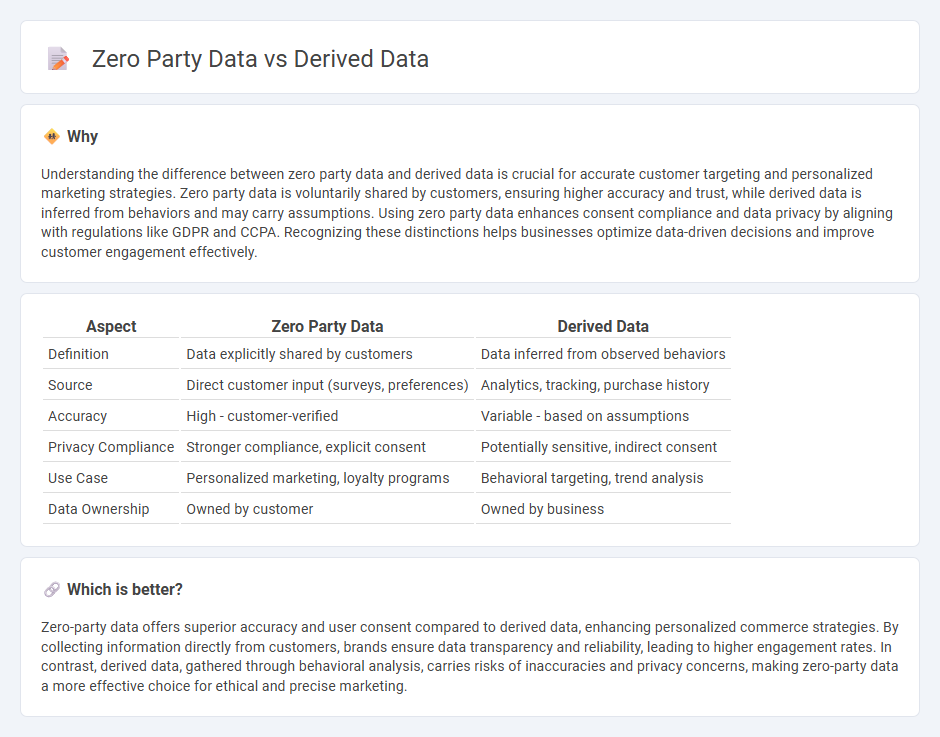
| Aspect | Zero Party Data | Derived Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data explicitly shared by customers | Data inferred from observed behaviors |
| Source | Direct customer input (surveys, preferences) | Analytics, tracking, purchase history |
| Accuracy | High - customer-verified | Variable - based on assumptions |
| Privacy Compliance | Stronger compliance, explicit consent | Potentially sensitive, indirect consent |
| Use Case | Personalized marketing, loyalty programs | Behavioral targeting, trend analysis |
| Data Ownership | Owned by customer | Owned by business |
Which is better?
Zero-party data offers superior accuracy and user consent compared to derived data, enhancing personalized commerce strategies. By collecting information directly from customers, brands ensure data transparency and reliability, leading to higher engagement rates. In contrast, derived data, gathered through behavioral analysis, carries risks of inaccuracies and privacy concerns, making zero-party data a more effective choice for ethical and precise marketing.
Connection
Zero party data, collected directly from consumers through explicit interactions, provides authentic insights into preferences and intentions, serving as a reliable foundation for personalized commerce strategies. Derived data, generated by analyzing behavioral patterns and transaction histories, complements zero party data by filling gaps and predicting future consumer behavior. Combining zero party data with derived data enables businesses to create more accurate, customer-centric marketing campaigns and optimize product offerings for increased engagement and sales.
Key Terms
Data Ownership
Derived data is collected through user interactions and analyzed to infer preferences, while zero party data is explicitly provided by users, ensuring clear data ownership and consent. Zero party data offers brands direct insights and greater control over customer information, reducing privacy risks associated with inferred data. Explore how prioritizing zero party data can enhance transparency and strengthen customer trust.
User Consent
Derived data is information inferred from user behavior and interactions, often collected passively without explicit consent, raising concerns about transparency and privacy. Zero-party data is voluntarily shared directly by users, ensuring clear consent and fostering trust through personalized experiences. Explore the distinctions and implications of user consent in data collection to enhance compliance and user engagement.
Data Collection Method
Derived data is collected through analysis of user behavior and interactions, often using algorithms to infer preferences from existing data sets. Zero-party data, by contrast, is expressly provided by users, such as through surveys or direct input, ensuring explicit consent and accuracy. Explore further to understand how these data collection methods impact customer insights and personalization strategies.
Source and External Links
What is derived data (with examples) - Optimizely - Derived data is new information created by processing and combining existing raw data sets to reveal insights not immediately obvious from the original data, involving advanced analysis and cross-referencing different datasets.
What Does Derive Mean | Dagster - In data engineering, deriving data refers to extracting, transforming, and generating new data from existing datasets through operations like filtering, joining, or applying algorithms to enhance understanding or meet business needs.
Be Careful with Derived Data - DATAVERSITY - Derived data can be computed from other base data and although storing it may accelerate data retrieval, it should often be computed on the fly to avoid synchronization issues with underlying data updates.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com