Crowdsourced delivery leverages a network of independent drivers using personal vehicles to fulfill orders quickly and flexibly, making it ideal for urban and last-mile logistics. Autonomous vehicle delivery relies on self-driving technology to reduce labor costs and improve efficiency, promising scalable, contactless service for future commerce. Explore the evolving landscape of delivery models to understand how each innovation shapes the future of commerce.
Why it is important
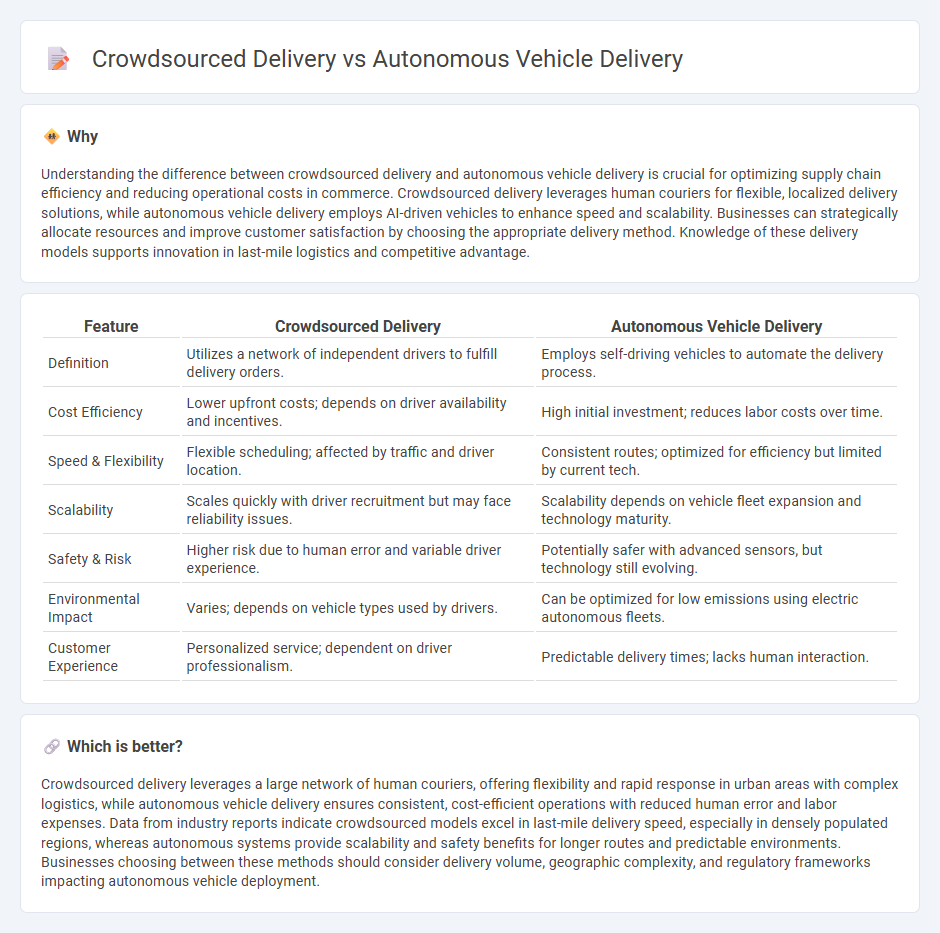
Understanding the difference between crowdsourced delivery and autonomous vehicle delivery is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing operational costs in commerce. Crowdsourced delivery leverages human couriers for flexible, localized delivery solutions, while autonomous vehicle delivery employs AI-driven vehicles to enhance speed and scalability. Businesses can strategically allocate resources and improve customer satisfaction by choosing the appropriate delivery method. Knowledge of these delivery models supports innovation in last-mile logistics and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Crowdsourced Delivery | Autonomous Vehicle Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Utilizes a network of independent drivers to fulfill delivery orders. | Employs self-driving vehicles to automate the delivery process. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower upfront costs; depends on driver availability and incentives. | High initial investment; reduces labor costs over time. |
| Speed & Flexibility | Flexible scheduling; affected by traffic and driver location. | Consistent routes; optimized for efficiency but limited by current tech. |
| Scalability | Scales quickly with driver recruitment but may face reliability issues. | Scalability depends on vehicle fleet expansion and technology maturity. |
| Safety & Risk | Higher risk due to human error and variable driver experience. | Potentially safer with advanced sensors, but technology still evolving. |
| Environmental Impact | Varies; depends on vehicle types used by drivers. | Can be optimized for low emissions using electric autonomous fleets. |
| Customer Experience | Personalized service; dependent on driver professionalism. | Predictable delivery times; lacks human interaction. |
Which is better?
Crowdsourced delivery leverages a large network of human couriers, offering flexibility and rapid response in urban areas with complex logistics, while autonomous vehicle delivery ensures consistent, cost-efficient operations with reduced human error and labor expenses. Data from industry reports indicate crowdsourced models excel in last-mile delivery speed, especially in densely populated regions, whereas autonomous systems provide scalability and safety benefits for longer routes and predictable environments. Businesses choosing between these methods should consider delivery volume, geographic complexity, and regulatory frameworks impacting autonomous vehicle deployment.
Connection
Crowdsourced delivery leverages local, on-demand couriers to fulfill last-mile logistics, enhancing flexibility and reducing delivery times in commerce. Autonomous vehicle delivery integrates self-driving technology to optimize route efficiency and lower operational costs in the same last-mile segment. Both methods aim to revolutionize commerce logistics by improving speed, scalability, and cost-effectiveness through innovative delivery solutions.
Key Terms
Last-mile logistics
Autonomous vehicle delivery leverages self-driving technology to provide consistent, efficient last-mile logistics with reduced labor costs and increased delivery speed, particularly in urban environments. Crowdsourced delivery relies on local drivers or couriers using personal vehicles, offering flexibility, scalability, and faster response times during peak demand, but it may face challenges with reliability and quality control. Explore the evolving landscape of last-mile logistics to understand which delivery method best suits your business needs.
Cost efficiency
Autonomous vehicle delivery significantly reduces labor expenses by eliminating the need for human drivers, leading to lower operational costs in the long term. Crowdsourced delivery leverages existing resources but often incurs higher variable costs due to driver incentives and route inefficiencies. Explore detailed cost comparisons to determine which delivery method optimizes your budget.
Scalability
Autonomous vehicle delivery offers unparalleled scalability by enabling continuous operation without human constraints, significantly reducing labor costs and increasing delivery efficiency. Crowdsourced delivery relies heavily on the availability and willingness of human drivers, limiting its scalability due to variable workforce participation and inconsistent service quality. Explore the evolving dynamics of these delivery methods to understand which approach best suits expanding logistics needs.
Source and External Links
Automated Vehicle and Drone Delivery Are on the Horizon - ISM - Autonomous vehicles (AVs) in delivery optimize routes, reduce times, enhance efficiency, lower costs, and cut emissions, especially in urban areas; drones complement these with speed and access to remote locations.
Autonomous Delivery: Robots Delivering the Future of Logistics - Major companies like Amazon and Uber are deploying autonomous delivery robots and trucks, including Amazon's Scout and Uber's partnerships for robot-based food delivery in various cities, while autonomous freight trucks are scaling in markets like China and the U.S.
udelv | A driverless, multi-stop delivery EV for last-mile and middle ... - Udelv offers the first cab-less autonomous electric vehicle built specifically for multi-stop delivery routes, focusing on reducing total ownership cost by up to 50% and enabling efficient last- and middle-mile deliveries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com