Micro fulfillment centers optimize inventory placement by using automated systems near urban areas, enabling faster order processing and reduced last-mile delivery costs. Direct store delivery relies on suppliers delivering products straight to retail locations, ensuring high product freshness and immediate shelf replenishment. Explore the advantages and challenges of micro fulfillment versus direct store delivery to enhance your commerce strategy.
Why it is important
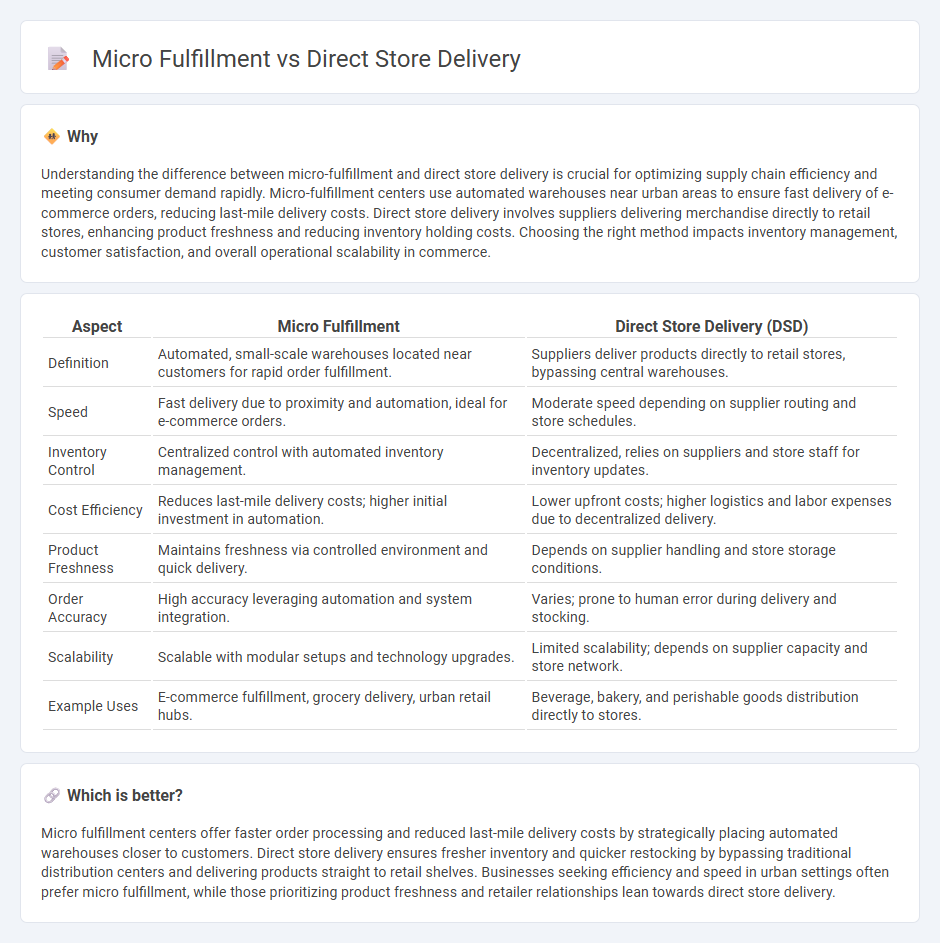
Understanding the difference between micro-fulfillment and direct store delivery is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and meeting consumer demand rapidly. Micro-fulfillment centers use automated warehouses near urban areas to ensure fast delivery of e-commerce orders, reducing last-mile delivery costs. Direct store delivery involves suppliers delivering merchandise directly to retail stores, enhancing product freshness and reducing inventory holding costs. Choosing the right method impacts inventory management, customer satisfaction, and overall operational scalability in commerce.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Micro Fulfillment | Direct Store Delivery (DSD) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated, small-scale warehouses located near customers for rapid order fulfillment. | Suppliers deliver products directly to retail stores, bypassing central warehouses. |
| Speed | Fast delivery due to proximity and automation, ideal for e-commerce orders. | Moderate speed depending on supplier routing and store schedules. |
| Inventory Control | Centralized control with automated inventory management. | Decentralized, relies on suppliers and store staff for inventory updates. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces last-mile delivery costs; higher initial investment in automation. | Lower upfront costs; higher logistics and labor expenses due to decentralized delivery. |
| Product Freshness | Maintains freshness via controlled environment and quick delivery. | Depends on supplier handling and store storage conditions. |
| Order Accuracy | High accuracy leveraging automation and system integration. | Varies; prone to human error during delivery and stocking. |
| Scalability | Scalable with modular setups and technology upgrades. | Limited scalability; depends on supplier capacity and store network. |
| Example Uses | E-commerce fulfillment, grocery delivery, urban retail hubs. | Beverage, bakery, and perishable goods distribution directly to stores. |
Which is better?
Micro fulfillment centers offer faster order processing and reduced last-mile delivery costs by strategically placing automated warehouses closer to customers. Direct store delivery ensures fresher inventory and quicker restocking by bypassing traditional distribution centers and delivering products straight to retail shelves. Businesses seeking efficiency and speed in urban settings often prefer micro fulfillment, while those prioritizing product freshness and retailer relationships lean towards direct store delivery.
Connection
Micro fulfillment centers accelerate inventory processing by locating storage closer to consumers, enabling faster order preparation in commerce. Direct store delivery complements this by bypassing centralized warehouses, allowing suppliers to replenish products directly on retail shelves. Together, these strategies optimize supply chain efficiency and enhance product availability for end customers.
Key Terms
Distribution Channel
Direct store delivery (DSD) streamlines the distribution channel by allowing manufacturers to deliver products straight to retail stores, bypassing traditional warehouses and reducing lead times. Micro fulfillment centers (MFC) optimize last-mile delivery by using automated warehouses located near urban retail hubs to quickly replenish stock and fulfill online orders. Explore the strategic impact of these models on supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Inventory Management
Direct store delivery (DSD) enables real-time inventory replenishment by shipping products directly from suppliers to retail locations, reducing stockouts and improving product freshness. Micro fulfillment centers leverage automated systems and local distribution hubs to optimize inventory accuracy, shorten delivery times, and enhance order fulfillment efficiency. Explore how these inventory management strategies can streamline your supply chain and boost operational performance.
Last Mile Delivery
Direct store delivery (DSD) streamlines last mile delivery by allowing suppliers to deliver products directly to retail stores, reducing handling time and enhancing inventory freshness. Micro fulfillment centers (MFCs) optimize last mile delivery for e-commerce by locating small, automated warehouses closer to urban consumers, enabling faster order processing and reduced delivery distances. Explore how integrating DSD and MFC strategies can revolutionize your last mile delivery efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Is Direct-Store Delivery (DSD)? What Are Its Benefits? - FarEye - Direct-store delivery (DSD) is a retail distribution model where manufacturers or suppliers deliver products directly to individual stores, bypassing distribution centers, enhancing product freshness, and enabling suppliers to manage order placement, delivery, and in-store merchandising.
What Is Direct Store Delivery? - Bernick's - DSD delivers products from manufacturer or supplier directly to retail stores, bypassing warehouse stages, allowing frequent deliveries, in-store merchandising, and closer supplier-retailer relationships especially beneficial for fast-moving, perishable goods.
What is Direct Store Delivery? Logistics Glossary - Penske - Direct-store delivery ships products straight from manufacturer or supplier facilities to retail stores, reducing touchpoints and labor costs, supporting just-in-time deliveries and control over inventory and product handling.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com