Green logistics focuses on minimizing the environmental impact of transportation, warehousing, and distribution by optimizing energy use, reducing emissions, and adopting sustainable practices. Supply chain management encompasses the entire process of sourcing, producing, and delivering goods, emphasizing efficiency, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction throughout the value chain. Explore how integrating green logistics into supply chain management can drive sustainability and competitive advantage in modern commerce.
Why it is important
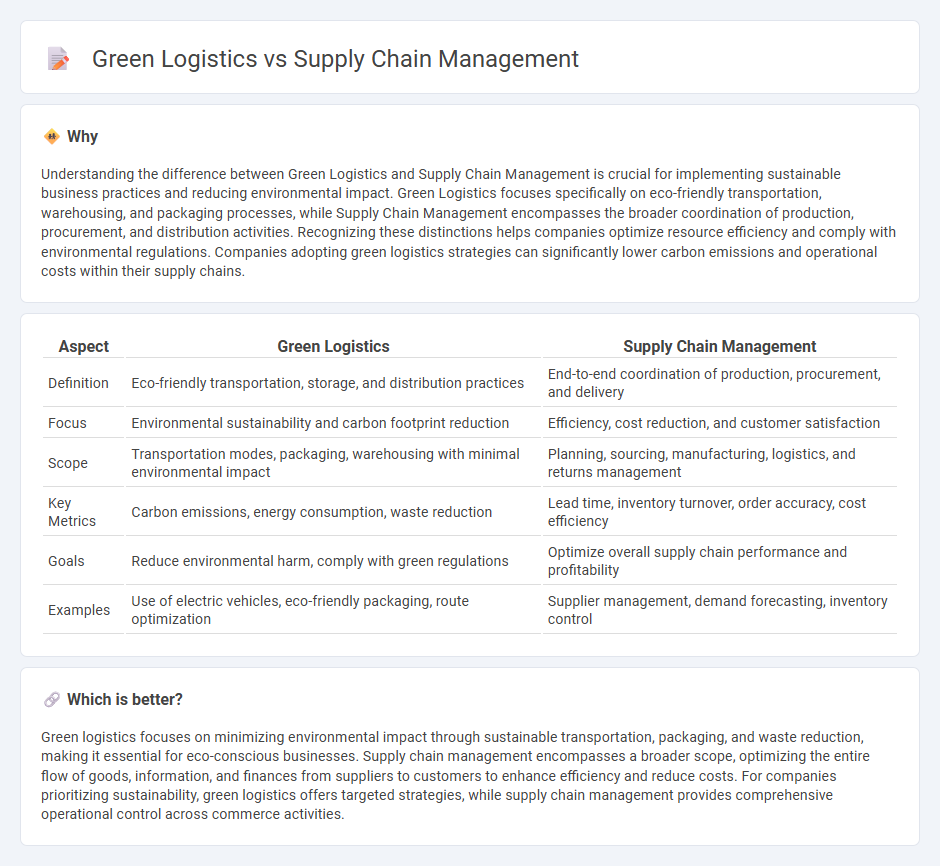
Understanding the difference between Green Logistics and Supply Chain Management is crucial for implementing sustainable business practices and reducing environmental impact. Green Logistics focuses specifically on eco-friendly transportation, warehousing, and packaging processes, while Supply Chain Management encompasses the broader coordination of production, procurement, and distribution activities. Recognizing these distinctions helps companies optimize resource efficiency and comply with environmental regulations. Companies adopting green logistics strategies can significantly lower carbon emissions and operational costs within their supply chains.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Logistics | Supply Chain Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Eco-friendly transportation, storage, and distribution practices | End-to-end coordination of production, procurement, and delivery |
| Focus | Environmental sustainability and carbon footprint reduction | Efficiency, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction |
| Scope | Transportation modes, packaging, warehousing with minimal environmental impact | Planning, sourcing, manufacturing, logistics, and returns management |
| Key Metrics | Carbon emissions, energy consumption, waste reduction | Lead time, inventory turnover, order accuracy, cost efficiency |
| Goals | Reduce environmental harm, comply with green regulations | Optimize overall supply chain performance and profitability |
| Examples | Use of electric vehicles, eco-friendly packaging, route optimization | Supplier management, demand forecasting, inventory control |
Which is better?
Green logistics focuses on minimizing environmental impact through sustainable transportation, packaging, and waste reduction, making it essential for eco-conscious businesses. Supply chain management encompasses a broader scope, optimizing the entire flow of goods, information, and finances from suppliers to customers to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. For companies prioritizing sustainability, green logistics offers targeted strategies, while supply chain management provides comprehensive operational control across commerce activities.
Connection
Green logistics integrates eco-friendly practices into supply chain management to reduce carbon footprints and enhance sustainability. Supply chain management optimizes the flow of goods, information, and resources while minimizing environmental impact through strategies such as energy-efficient transportation and waste reduction. Implementing green logistics within supply chains leads to cost savings, regulatory compliance, and improved corporate social responsibility.
Key Terms
Efficiency
Supply chain management optimizes the flow of goods, information, and capital across production, transportation, and distribution to maximize overall efficiency and reduce operational costs. Green logistics emphasizes environmentally sustainable practices within logistics, such as reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, and using eco-friendly transportation methods to enhance efficiency while lessening environmental impact. Explore the detailed strategies and benefits of integrating supply chain management and green logistics for superior operational performance and sustainability.
Sustainability
Supply chain management involves coordinating the entire production flow, from raw materials to delivering the final product, emphasizing efficiency and cost reduction. Green logistics specifically concentrates on minimizing environmental impact by optimizing transportation, packaging, and inventory to reduce carbon emissions and waste. Explore strategies and innovations driving sustainable supply chains and green logistics practices to enhance eco-friendly business operations.
Carbon footprint
Supply chain management encompasses the entire flow of goods, services, and information from suppliers to consumers, aiming to optimize efficiency and cost-effectiveness, while green logistics specifically targets reducing the environmental impact of logistics activities, particularly focusing on minimizing carbon footprint through sustainable practices such as eco-friendly transportation and energy-efficient warehousing. Carbon footprint reduction in green logistics involves strategic decisions like route optimization, use of alternative fuels, and adoption of renewable energy sources, distinguishing it from broader supply chain goals that may prioritize speed or cost. To explore comprehensive strategies and technologies for balancing supply chain performance with environmental responsibility, learn more about the intersection of supply chain management and green logistics.
Source and External Links
What is Supply Chain Management? Roles, Salaries, and ... - Supply chain management involves coordinating and overseeing activities in producing, distributing, and delivering goods or services, focusing on planning, sourcing, organizing, delivering, and managing to ensure business sustainability and customer satisfaction, with emerging trends like big data, analytics, and digitization impacting the field by 2025.
What Is Supply Chain Management? - SCM coordinates a business's entire production flow from raw materials sourcing to delivering the finished product, optimizing a complex network of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to minimize cost, waste, and time while enhancing profitability and competitiveness.
Supply chain management - SCM is a system integrating procurement, operations, logistics, and marketing to minimize total costs and conflicts between chain partners, improving trust, collaboration, inventory visibility, and enabling circular supply chains that reduce resource input and waste while driving economic and environmental benefits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com