Peer-to-peer payments enable instant money transfers directly between individuals using digital platforms such as Venmo and PayPal, enhancing convenience and reducing reliance on traditional banking systems. Buy now, pay later (BNPL) services like Afterpay and Klarna allow consumers to split purchases into interest-free installments, promoting flexible spending and boosting e-commerce sales. Explore the advantages and unique features of these payment solutions to understand their impact on modern commerce.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between peer-to-peer payments and buy now, pay later is crucial for managing personal finances effectively. Peer-to-peer payments involve direct money transfers between individuals, facilitating quick and secure transactions without intermediaries. Buy now, pay later options allow consumers to purchase goods immediately and pay in installments over time, impacting credit and budgeting strategies. Knowing these distinctions helps optimize spending decisions and avoid debt pitfalls.
Comparison Table
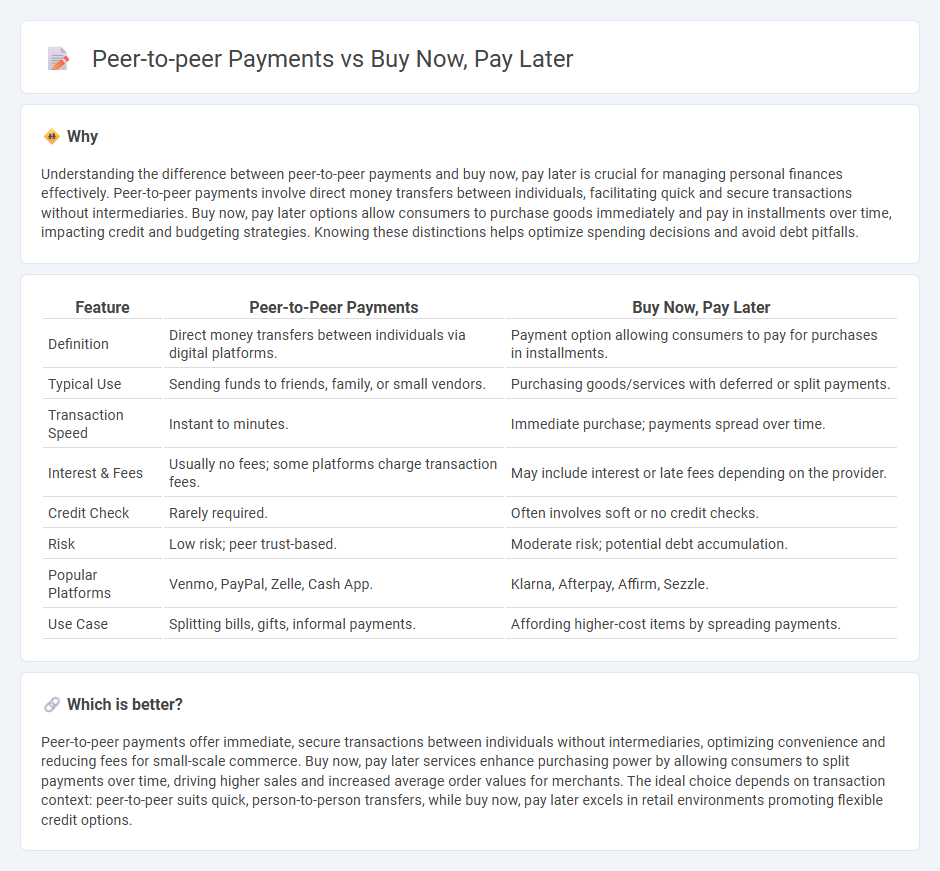
| Feature | Peer-to-Peer Payments | Buy Now, Pay Later |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct money transfers between individuals via digital platforms. | Payment option allowing consumers to pay for purchases in installments. |
| Typical Use | Sending funds to friends, family, or small vendors. | Purchasing goods/services with deferred or split payments. |
| Transaction Speed | Instant to minutes. | Immediate purchase; payments spread over time. |
| Interest & Fees | Usually no fees; some platforms charge transaction fees. | May include interest or late fees depending on the provider. |
| Credit Check | Rarely required. | Often involves soft or no credit checks. |
| Risk | Low risk; peer trust-based. | Moderate risk; potential debt accumulation. |
| Popular Platforms | Venmo, PayPal, Zelle, Cash App. | Klarna, Afterpay, Affirm, Sezzle. |
| Use Case | Splitting bills, gifts, informal payments. | Affording higher-cost items by spreading payments. |
Which is better?
Peer-to-peer payments offer immediate, secure transactions between individuals without intermediaries, optimizing convenience and reducing fees for small-scale commerce. Buy now, pay later services enhance purchasing power by allowing consumers to split payments over time, driving higher sales and increased average order values for merchants. The ideal choice depends on transaction context: peer-to-peer suits quick, person-to-person transfers, while buy now, pay later excels in retail environments promoting flexible credit options.
Connection
Peer-to-peer payments streamline digital transactions by enabling direct money transfers between users, facilitating immediate settlement. Buy now, pay later services leverage this framework by integrating flexible payment options within e-commerce platforms, allowing consumers to split purchases into installments. Both innovations enhance customer convenience and drive the growth of cashless commerce by simplifying payment processes and increasing purchasing power.
Key Terms
Credit risk
Buy now, pay later (BNPL) services assess credit risk by analyzing real-time consumer data and integrating with credit bureaus to minimize default rates, while peer-to-peer (P2P) payments typically involve lower credit risk as transactions are funded by users' existing account balances without lending. BNPL providers implement advanced risk models and fraud detection algorithms to evaluate creditworthiness, contrasting with P2P platforms where the primary concern is transaction security rather than credit exposure. Explore the nuances of credit risk management in BNPL and P2P systems to understand their operational impacts and consumer protections.
Transaction fees
Buy now, pay later (BNPL) services often charge merchants transaction fees ranging from 2-8%, impacting retailer margins, while peer-to-peer (P2P) payments typically have lower or no fees for users, depending on platforms like Venmo or PayPal. BNPL providers generate revenue through merchant fees and sometimes late payment charges, whereas P2P payment platforms may earn from currency conversion or instant transfer fees. Explore further to understand how these fee structures influence consumer choice and business models.
User verification
User verification in buy now, pay later systems typically involves comprehensive credit checks and identity authentication to mitigate fraud and ensure borrower credibility, leveraging data from credit bureaus and government databases. Peer-to-peer payment platforms prioritize swift verification methods such as biometric authentication and two-factor authentication to protect user accounts while facilitating seamless transactions. Explore more to understand how these verification processes impact security and user experience in digital financial services.
Source and External Links
The 'Buy Now Pay Later' Trap, Explained - YouTube - Buy Now Pay Later programs like Klarna, Afterpay, and Affirm allow you to purchase immediately and pay in installments, often interest-free, but they function like modern layaway plans and can involve hidden costs or temptation to overspend.
Afterpay: Pay over time 4+ - App Store - Afterpay lets you split purchases into 4 interest-free payments and offers longer-term payment options (up to 24 months) for larger items through its app with no sign-up fees.
Buy Now Pay Later | Pay in 4 | Pay Monthly | PayPal US - PayPal offers Pay in 4 interest-free payments for purchases between $30 and $1,500 and monthly installment plans for larger amounts, all with no sign-up or late fees and included purchase protection.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com