Recommerce involves the buying and selling of pre-owned goods, emphasizing sustainability and cost savings, while subscription commerce offers consumers curated products or services on a recurring basis, focusing on convenience and personalized experiences. Both business models tap into evolving consumer preferences for value and experience, influencing retail strategies globally. Explore how each model reshapes commerce and consumer behavior.
Why it is important
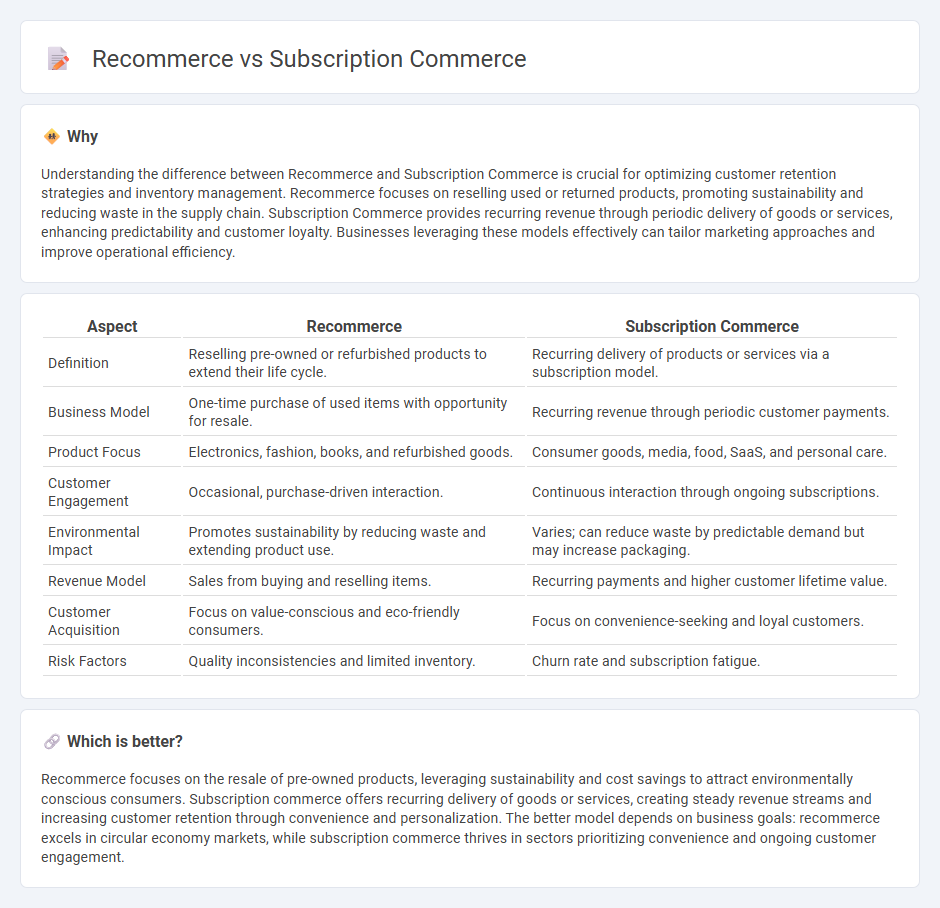
Understanding the difference between Recommerce and Subscription Commerce is crucial for optimizing customer retention strategies and inventory management. Recommerce focuses on reselling used or returned products, promoting sustainability and reducing waste in the supply chain. Subscription Commerce provides recurring revenue through periodic delivery of goods or services, enhancing predictability and customer loyalty. Businesses leveraging these models effectively can tailor marketing approaches and improve operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Recommerce | Subscription Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reselling pre-owned or refurbished products to extend their life cycle. | Recurring delivery of products or services via a subscription model. |
| Business Model | One-time purchase of used items with opportunity for resale. | Recurring revenue through periodic customer payments. |
| Product Focus | Electronics, fashion, books, and refurbished goods. | Consumer goods, media, food, SaaS, and personal care. |
| Customer Engagement | Occasional, purchase-driven interaction. | Continuous interaction through ongoing subscriptions. |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainability by reducing waste and extending product use. | Varies; can reduce waste by predictable demand but may increase packaging. |
| Revenue Model | Sales from buying and reselling items. | Recurring payments and higher customer lifetime value. |
| Customer Acquisition | Focus on value-conscious and eco-friendly consumers. | Focus on convenience-seeking and loyal customers. |
| Risk Factors | Quality inconsistencies and limited inventory. | Churn rate and subscription fatigue. |
Which is better?
Recommerce focuses on the resale of pre-owned products, leveraging sustainability and cost savings to attract environmentally conscious consumers. Subscription commerce offers recurring delivery of goods or services, creating steady revenue streams and increasing customer retention through convenience and personalization. The better model depends on business goals: recommerce excels in circular economy markets, while subscription commerce thrives in sectors prioritizing convenience and ongoing customer engagement.
Connection
Recommerce and subscription commerce intersect by promoting sustainable consumption through repeated use and recurring purchases, reducing waste and maximizing product lifecycle value. Recommerce extends product usability by reselling refurbished or pre-owned goods, while subscription commerce ensures consistent customer engagement with curated product deliveries. Both models harness digital platforms and data analytics to optimize inventory management and enhance customer retention strategies.
Key Terms
Recurring Revenue
Subscription commerce generates recurring revenue by offering customers regular product or service deliveries, ensuring steady cash flow and customer retention. Recommerce focuses on reselling pre-owned goods, leveraging sustainability and cost savings while building a circular economy. Explore detailed strategies to maximize profitability and growth in recurring revenue models.
Circular Economy
Subscription commerce offers consumers recurring delivery of new products, promoting continuous use and convenience, while recommerce focuses on reselling pre-owned goods, extending product lifecycle and reducing waste. Both business models contribute to the circular economy by minimizing resource consumption and supporting sustainable consumption patterns. Explore how subscription commerce and recommerce drive environmental impact and economic benefits within circular economy frameworks.
Product Lifecycle
Subscription commerce extends product lifecycle by promoting recurring use through regular deliveries, enhancing customer retention and reducing waste via predictable consumption patterns. Recommerce focuses on extending product lifespan by facilitating resale, refurbishment, or recycling of used goods, significantly minimizing environmental impact and resource depletion. Explore the benefits and strategies behind subscription commerce and recommerce to optimize product lifecycle management.
Source and External Links
Subscription Commerce Definition and Meaning - Recharge - Subscription commerce is a business model where companies offer products or services on a recurring basis, providing convenience to consumers and predictable recurring revenue for businesses, often measured by monthly or annual recurring revenue.
Subscription Business Model: How and Why It Works (2025) - This model involves customers paying a recurring fee to receive goods or services, allowing businesses to build steady revenue streams and improve customer relationships, commonly seen in industries like SaaS, streaming, and ecommerce subscription boxes.
What Is Subscription Commerce: Know Models, Benefits ... - Subscription commerce enables businesses to create personalized, recurring product or service deliveries, using models like curation and replenishment subscriptions to enhance customer convenience and loyalty while ensuring predictable income.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com