Product information management (PIM) focuses on organizing, enriching, and centralizing product data such as descriptions, specifications, and images to ensure consistent and accurate information across sales channels. Inventory management, on the other hand, concentrates on tracking stock levels, managing replenishments, and optimizing warehouse operations to prevent stockouts or overstocking. Explore the distinctions and benefits of both systems to enhance your commerce strategy.
Why it is important
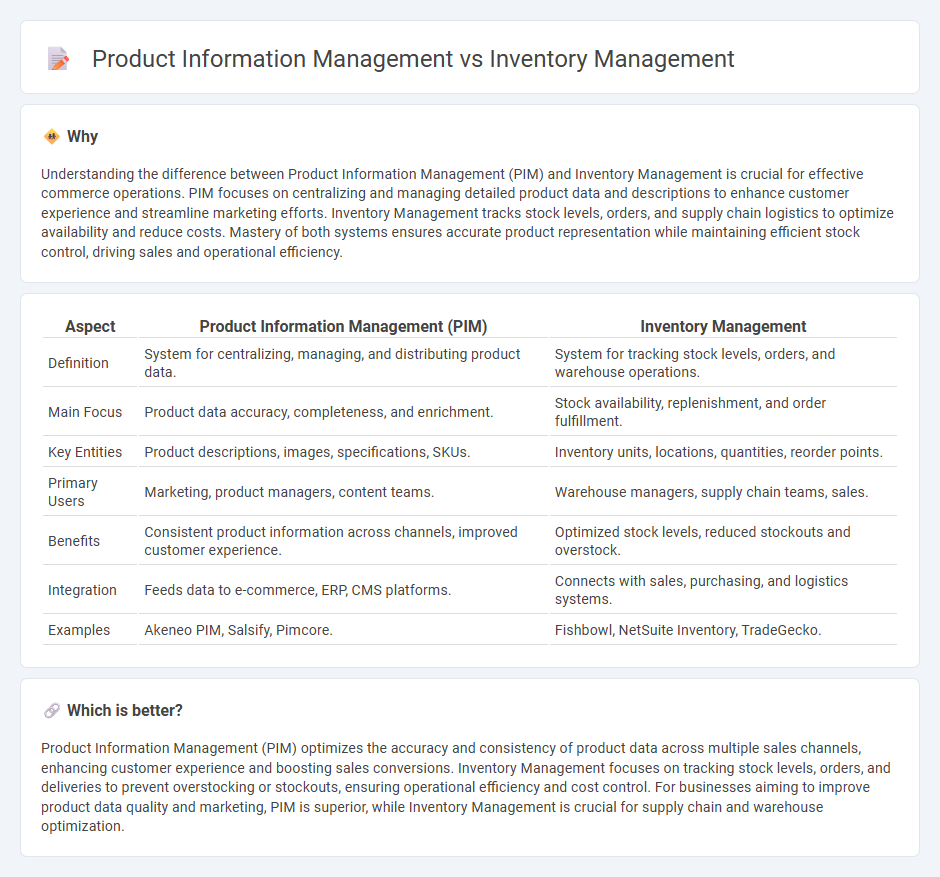
Understanding the difference between Product Information Management (PIM) and Inventory Management is crucial for effective commerce operations. PIM focuses on centralizing and managing detailed product data and descriptions to enhance customer experience and streamline marketing efforts. Inventory Management tracks stock levels, orders, and supply chain logistics to optimize availability and reduce costs. Mastery of both systems ensures accurate product representation while maintaining efficient stock control, driving sales and operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Product Information Management (PIM) | Inventory Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | System for centralizing, managing, and distributing product data. | System for tracking stock levels, orders, and warehouse operations. |
| Main Focus | Product data accuracy, completeness, and enrichment. | Stock availability, replenishment, and order fulfillment. |
| Key Entities | Product descriptions, images, specifications, SKUs. | Inventory units, locations, quantities, reorder points. |
| Primary Users | Marketing, product managers, content teams. | Warehouse managers, supply chain teams, sales. |
| Benefits | Consistent product information across channels, improved customer experience. | Optimized stock levels, reduced stockouts and overstock. |
| Integration | Feeds data to e-commerce, ERP, CMS platforms. | Connects with sales, purchasing, and logistics systems. |
| Examples | Akeneo PIM, Salsify, Pimcore. | Fishbowl, NetSuite Inventory, TradeGecko. |
Which is better?
Product Information Management (PIM) optimizes the accuracy and consistency of product data across multiple sales channels, enhancing customer experience and boosting sales conversions. Inventory Management focuses on tracking stock levels, orders, and deliveries to prevent overstocking or stockouts, ensuring operational efficiency and cost control. For businesses aiming to improve product data quality and marketing, PIM is superior, while Inventory Management is crucial for supply chain and warehouse optimization.
Connection
Product Information Management (PIM) and Inventory Management are interconnected through their shared goal of ensuring accurate and up-to-date product data across sales channels. PIM centralizes detailed product attributes, descriptions, and specifications, which directly inform inventory tracking systems about stock levels and availability. Synchronizing PIM with Inventory Management enhances order fulfillment accuracy, reduces stockouts, and streamlines supply chain operations.
Key Terms
Stock Levels (Inventory management)
Inventory management involves tracking and controlling stock levels to prevent overstocking or stockouts, ensuring optimal supply chain efficiency. Product information management focuses on maintaining accurate product data but does not directly manage physical stock quantity. Explore the distinctions between inventory and product information management to optimize your business operations.
SKU Data (Product information management)
Inventory management tracks stock levels, order quantities, and product availability to optimize supply chain efficiency. Product Information Management (PIM) centralizes and enriches SKU data, including detailed attributes, descriptions, and specifications, ensuring consistent and accurate product information across channels. Explore how mastering SKU data through PIM enhances inventory accuracy and boosts sales performance.
Reorder Point (Inventory management)
Reorder Point (ROP) in inventory management is the critical inventory level that triggers a replenishment order to prevent stockouts and maintain smooth operations. Product Information Management (PIM), in contrast, centralizes detailed product data but does not directly influence reorder decisions; its role supports accurate inventory classification and forecasting. Explore more to understand how integrating PIM enhances reorder point accuracy and overall supply chain efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Is Inventory Management? Benefits, Types, & Techniques - Inventory management is the process of tracking and controlling the flow of goods, involving steps such as demand planning, ordering, delivery, inventory tracking and storage, sales fulfillment, reporting, and replenishment to optimize stock levels and supply chains.
Inventory Management: How it Works and Tools (2025) - Shopify - Inventory management involves overseeing the flow of goods and utilizes techniques like economic order quantity (EOQ), demand planning, and technologies such as RFID and barcodes to balance stock, reduce costs, and improve cash flow.
Inventory Management Guide + Methods & Examples - Extensiv - Inventory management includes methods like spreadsheets, automated systems, ERP software, and multichannel inventory management to maintain optimal stock levels and improve accuracy and efficiency across sourcing, storing, and selling processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com