Circular supply chains focus on sustainability by reusing and recycling materials within a closed system to minimize waste and resource consumption. Open-loop supply chains involve multiple independent entities where products or materials exit the original system and re-enter a different supply chain, often limiting closed-loop benefits. Explore the advantages and challenges of each model to optimize supply chain strategies.
Why it is important
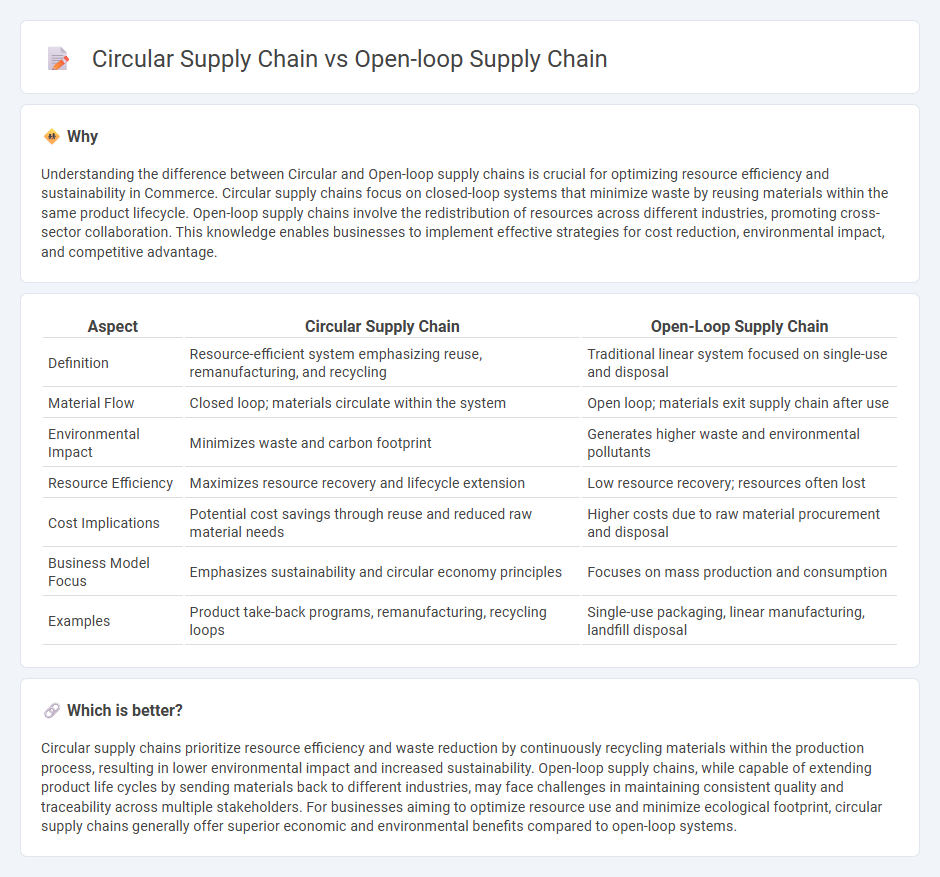
Understanding the difference between Circular and Open-loop supply chains is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and sustainability in Commerce. Circular supply chains focus on closed-loop systems that minimize waste by reusing materials within the same product lifecycle. Open-loop supply chains involve the redistribution of resources across different industries, promoting cross-sector collaboration. This knowledge enables businesses to implement effective strategies for cost reduction, environmental impact, and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Supply Chain | Open-Loop Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Resource-efficient system emphasizing reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling | Traditional linear system focused on single-use and disposal |
| Material Flow | Closed loop; materials circulate within the system | Open loop; materials exit supply chain after use |
| Environmental Impact | Minimizes waste and carbon footprint | Generates higher waste and environmental pollutants |
| Resource Efficiency | Maximizes resource recovery and lifecycle extension | Low resource recovery; resources often lost |
| Cost Implications | Potential cost savings through reuse and reduced raw material needs | Higher costs due to raw material procurement and disposal |
| Business Model Focus | Emphasizes sustainability and circular economy principles | Focuses on mass production and consumption |
| Examples | Product take-back programs, remanufacturing, recycling loops | Single-use packaging, linear manufacturing, landfill disposal |
Which is better?
Circular supply chains prioritize resource efficiency and waste reduction by continuously recycling materials within the production process, resulting in lower environmental impact and increased sustainability. Open-loop supply chains, while capable of extending product life cycles by sending materials back to different industries, may face challenges in maintaining consistent quality and traceability across multiple stakeholders. For businesses aiming to optimize resource use and minimize ecological footprint, circular supply chains generally offer superior economic and environmental benefits compared to open-loop systems.
Connection
Circular supply chains and open-loop supply chains are interconnected through their shared focus on sustainability and resource efficiency by extending product life cycles and promoting material reuse beyond the initial supply loop. Circular supply chains prioritize closed-loop processes within a single system, while open-loop supply chains facilitate resource recovery and redistribution across different industries or markets. Both models enhance environmental impact reduction, cost savings, and the transition toward a circular economy through optimized material flow and reduced waste.
Key Terms
Resource Flow
Open-loop supply chains primarily emphasize one-way resource flow, where raw materials move from suppliers to manufacturers and eventually to consumers, often leading to waste or disposal after use. Circular supply chains prioritize closed-loop resource flow by designing processes that recycle, reuse, and regenerate materials, thereby minimizing waste and enhancing sustainability. Explore how optimizing resource flow in these supply chain models can drive environmental and economic benefits.
Waste Management
Open-loop supply chains often result in increased waste as products are discarded after use, leading to linear resource consumption and environmental degradation. In contrast, circular supply chains emphasize waste reduction through recycling, refurbishing, and reusing materials, promoting sustainability and resource efficiency. Explore how innovative waste management strategies in circular supply chains can transform environmental impact and business performance.
Product Lifecycle
Open-loop supply chains emphasize a linear product lifecycle, where raw materials are transformed into products and ultimately disposed of after use, often leading to waste and resource depletion. Circular supply chains prioritize extending product lifecycles through reuse, refurbishment, and recycling, minimizing waste and promoting sustainability by closing the loop on materials flow. Explore the benefits of adopting a circular supply chain approach to enhance product lifecycle management.
Source and External Links
Open-Loop Supply Chain - Lasso - An open-loop supply chain is a linear, one-directional process where products flow from raw material extraction to consumption without any return or recycling back into the system, ending at disposal.
What is Open Loop Supply Chain - This system focuses on forward flow of goods without reverse logistics, offering benefits like cost efficiency, simplified operations, faster time-to-market, and flexibility by avoiding product returns for reuse or recycling.
How Does A Traditional/Forward-Loop Supply Chain Differ ... - An open-loop supply chain features single-direction material flow without feedback loops from customers, typically for standardized products, and provides increased flexibility and improved efficiency through enhanced communication among supply chain partners.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com