Live dropshipping offers a flexible business model with low upfront costs by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers without holding inventory. Manufacturing requires significant investment in production facilities, raw materials, and inventory management but allows greater control over product quality and brand customization. Explore both strategies to determine which aligns best with your commerce goals and operational capabilities.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between live dropshipping and manufacturing is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and cost management in commerce. Live dropshipping involves selling products without holding inventory, relying on suppliers to ship directly to customers, which reduces upfront investment and inventory risks. Manufacturing requires overseeing production processes, quality control, and inventory storage, offering greater customization and profit margins but higher initial costs and logistical complexity. Choosing the right model impacts business scalability, customer satisfaction, and profitability in competitive markets.
Comparison Table
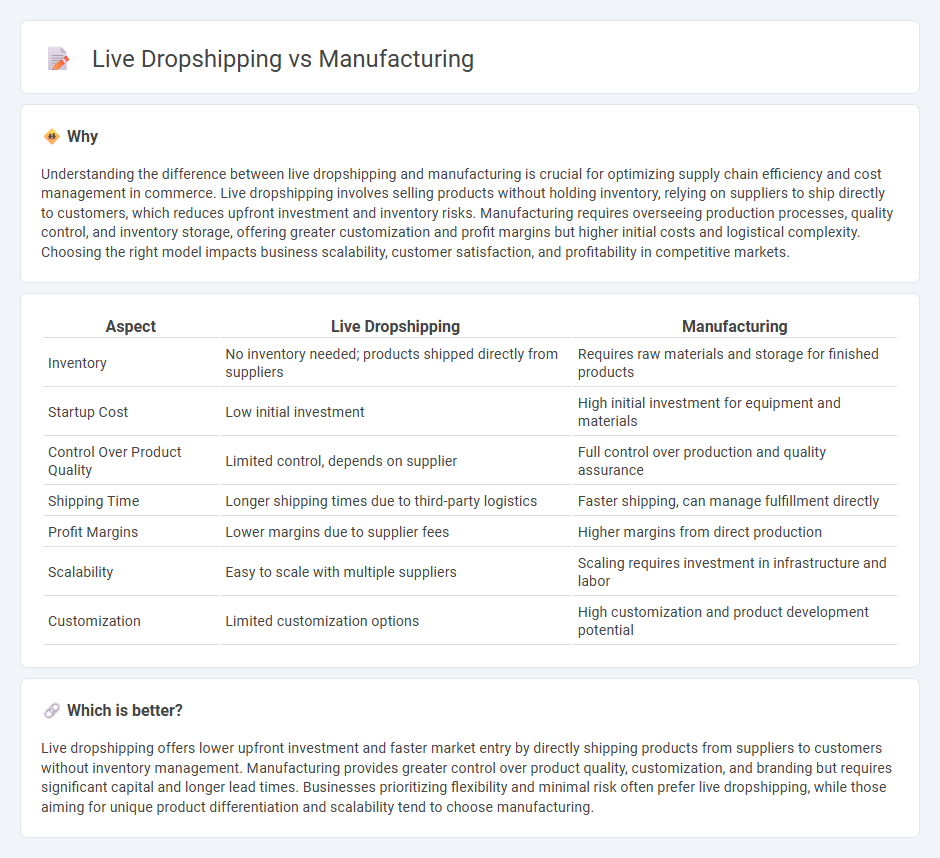
| Aspect | Live Dropshipping | Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory | No inventory needed; products shipped directly from suppliers | Requires raw materials and storage for finished products |
| Startup Cost | Low initial investment | High initial investment for equipment and materials |
| Control Over Product Quality | Limited control, depends on supplier | Full control over production and quality assurance |
| Shipping Time | Longer shipping times due to third-party logistics | Faster shipping, can manage fulfillment directly |
| Profit Margins | Lower margins due to supplier fees | Higher margins from direct production |
| Scalability | Easy to scale with multiple suppliers | Scaling requires investment in infrastructure and labor |
| Customization | Limited customization options | High customization and product development potential |
Which is better?
Live dropshipping offers lower upfront investment and faster market entry by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers without inventory management. Manufacturing provides greater control over product quality, customization, and branding but requires significant capital and longer lead times. Businesses prioritizing flexibility and minimal risk often prefer live dropshipping, while those aiming for unique product differentiation and scalability tend to choose manufacturing.
Connection
Live dropshipping streamlines commerce by directly connecting manufacturers with consumers through real-time order fulfillment, eliminating the need for inventory storage. This integration enables manufacturers to access broader markets instantly while reducing overhead costs and delivery times. Efficient communication and logistics technology bridge the gap between manufacturing production cycles and live consumer demand, enhancing supply chain responsiveness.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Manufacturing demands precise inventory management to track raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods, ensuring production schedules meet customer demand without overstocking. Live dropshipping minimizes inventory risks by shipping products directly from suppliers to customers, but requires real-time inventory synchronization to avoid stockouts or delays. Explore in-depth strategies to optimize inventory management for both manufacturing and live dropshipping models.
Fulfillment Process
Manufacturing involves producing goods in-house or through third-party factories, ensuring quality control and inventory management before order fulfillment, which can lead to longer lead times but greater product consistency. Live dropshipping relies on third-party suppliers to ship products directly to customers after an order is placed, minimizing inventory risks but requiring seamless coordination to avoid delays and errors. Explore the strengths and challenges of both fulfillment processes to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Supply Chain Control
Manufacturing offers greater supply chain control by allowing businesses to oversee production schedules, quality standards, and inventory management directly at the source. In contrast, live dropshipping relies on third-party suppliers, which can limit transparency and responsiveness in the supply chain, potentially causing delays or inconsistencies. Explore the critical differences in supply chain control between manufacturing and live dropshipping to optimize your business strategy.
Source and External Links
Manufacturing - Wikipedia - Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods using equipment, labor, and machines, transforming raw materials into finished products on a large scale, encompassing industrial design and engineering processes.
The ultimate guide to what is manufacturing - Katana Cloud Inventory - Manufacturing involves converting raw materials and components into finished products using labor, tools, and machinery, and can include mass production, batch production, or customized items.
Manufacturing in the United States - NAM - Manufacturing contributes about 10% to U.S. GDP, employs 13 million people across 239,000 manufacturers, and represents a major sector with high economic impact and job opportunities as of 2025.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com