Circular supply chains focus on sustainability by reusing, refurbishing, and recycling materials to minimize waste and environmental impact, promoting a closed-loop system. Demand-driven supply chains prioritize real-time customer demand data to enhance responsiveness and reduce inventory costs through agile production and distribution processes. Explore further to understand how these supply chain models revolutionize commerce efficiency and sustainability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Circular supply chain and Demand-driven supply chain is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and customer responsiveness in commerce. The Circular supply chain focuses on sustainability by emphasizing product reuse, recycling, and waste reduction throughout the lifecycle. The Demand-driven supply chain prioritizes agility and real-time customer demand data to minimize inventory costs and enhance service levels. Knowing these distinctions enables businesses to tailor their strategies for better profitability and environmental impact.
Comparison Table
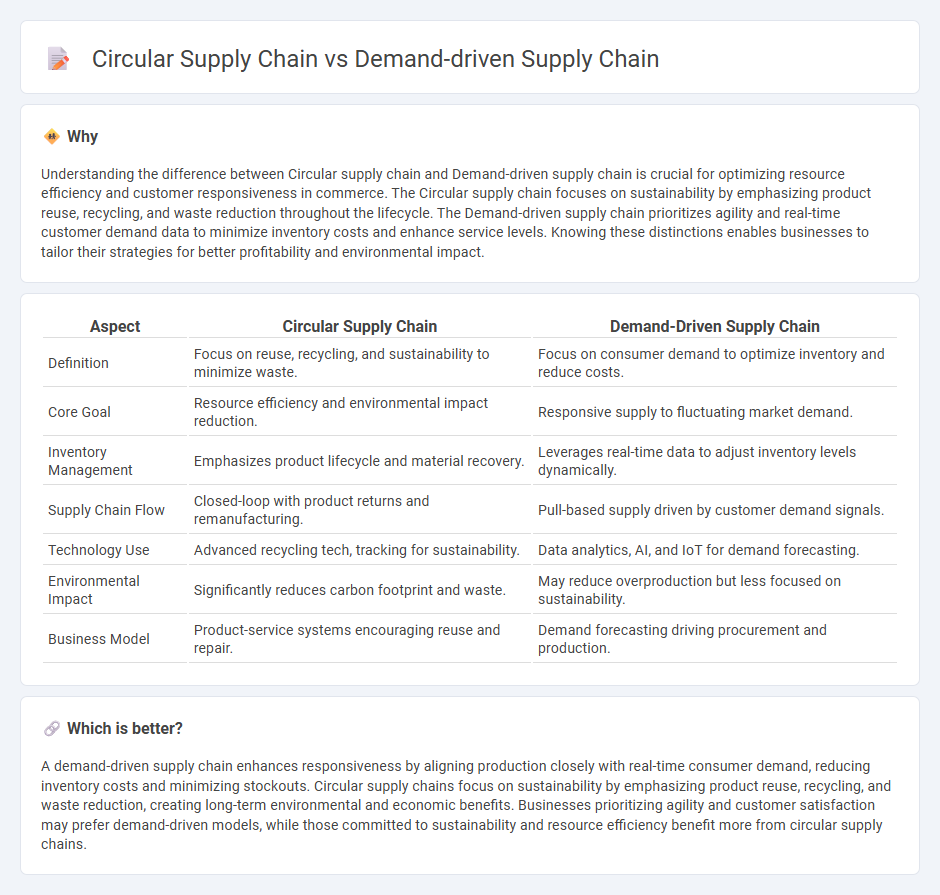
| Aspect | Circular Supply Chain | Demand-Driven Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on reuse, recycling, and sustainability to minimize waste. | Focus on consumer demand to optimize inventory and reduce costs. |
| Core Goal | Resource efficiency and environmental impact reduction. | Responsive supply to fluctuating market demand. |
| Inventory Management | Emphasizes product lifecycle and material recovery. | Leverages real-time data to adjust inventory levels dynamically. |
| Supply Chain Flow | Closed-loop with product returns and remanufacturing. | Pull-based supply driven by customer demand signals. |
| Technology Use | Advanced recycling tech, tracking for sustainability. | Data analytics, AI, and IoT for demand forecasting. |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly reduces carbon footprint and waste. | May reduce overproduction but less focused on sustainability. |
| Business Model | Product-service systems encouraging reuse and repair. | Demand forecasting driving procurement and production. |
Which is better?
A demand-driven supply chain enhances responsiveness by aligning production closely with real-time consumer demand, reducing inventory costs and minimizing stockouts. Circular supply chains focus on sustainability by emphasizing product reuse, recycling, and waste reduction, creating long-term environmental and economic benefits. Businesses prioritizing agility and customer satisfaction may prefer demand-driven models, while those committed to sustainability and resource efficiency benefit more from circular supply chains.
Connection
Circular supply chains prioritize resource efficiency by reusing and recycling materials to minimize waste, aligning closely with demand-driven supply chains that focus on real-time customer demand to optimize inventory and reduce overproduction. Both systems enhance sustainability and responsiveness by integrating feedback loops that adjust supply processes based on consumption patterns and product lifecycle data. This connection drives cost savings, reduces environmental impact, and increases supply chain agility through data-driven decision-making and circular resource flows.
Key Terms
Customer-centricity
Demand-driven supply chains prioritize real-time customer demand data to optimize inventory levels, reduce lead times, and enhance responsiveness, ensuring products are available when and where customers want them. Circular supply chains focus on sustainability by integrating product reuse, recycling, and resource recovery processes, but still emphasize customer-centricity through transparency and ethical sourcing to meet growing consumer expectations. Explore how these supply chain models balance efficiency and sustainability to elevate customer experience.
Resource recovery
Demand-driven supply chains prioritize real-time customer demand data to optimize inventory and production, reducing excess waste through efficient resource allocation. Circular supply chains emphasize resource recovery by designing products for reuse, recycling materials, and minimizing waste to create a closed-loop system. Discover more about how these models enhance sustainability and operational efficiency.
Inventory management
Demand-driven supply chains optimize inventory by aligning stock levels with real-time consumer demand, reducing excess and minimizing stockouts through responsive replenishment systems. Circular supply chains emphasize inventory management by incorporating reverse logistics, recycling, and reuse processes to maintain material flow while reducing waste and fostering sustainability. Explore how integrating both models can enhance inventory efficiency and environmental impact in your supply chain strategy.
Source and External Links
KAIZEN(tm) Article | Strategies for Demand-Driven Supply Chains - A demand-driven supply chain uses real consumer demand as the trigger for planning production and stock across all supply chain links, focusing on customer needs to increase inventory efficiency and maintain agility in adapting to changing demands.
What is a Demand-Driven Supply Chain? Benefits & Implementation - This approach integrates consumer demand directly into supply chain and production planning to improve operational efficiency, supply chain resilience, and market responsiveness via real-time information and flexible supply chain processes.
Demand-chain management - Wikipedia - Demand-driven supply networks (DDSN) build supply chains triggered by actual customer demand signals using a pull approach, ranging from purely forecast-based to fully order-driven production systems to optimize costs and value delivery.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com