Native checkout allows customers to complete purchases directly on a retailer's website, providing a seamless and trust-enhancing experience that can improve conversion rates. Embedded checkout integrates payment processes within third-party platforms or apps, streamlining the buying process without redirecting users away from the original interface. Explore the advantages and use cases of native versus embedded checkout to optimize your e-commerce strategy.
Why it is important
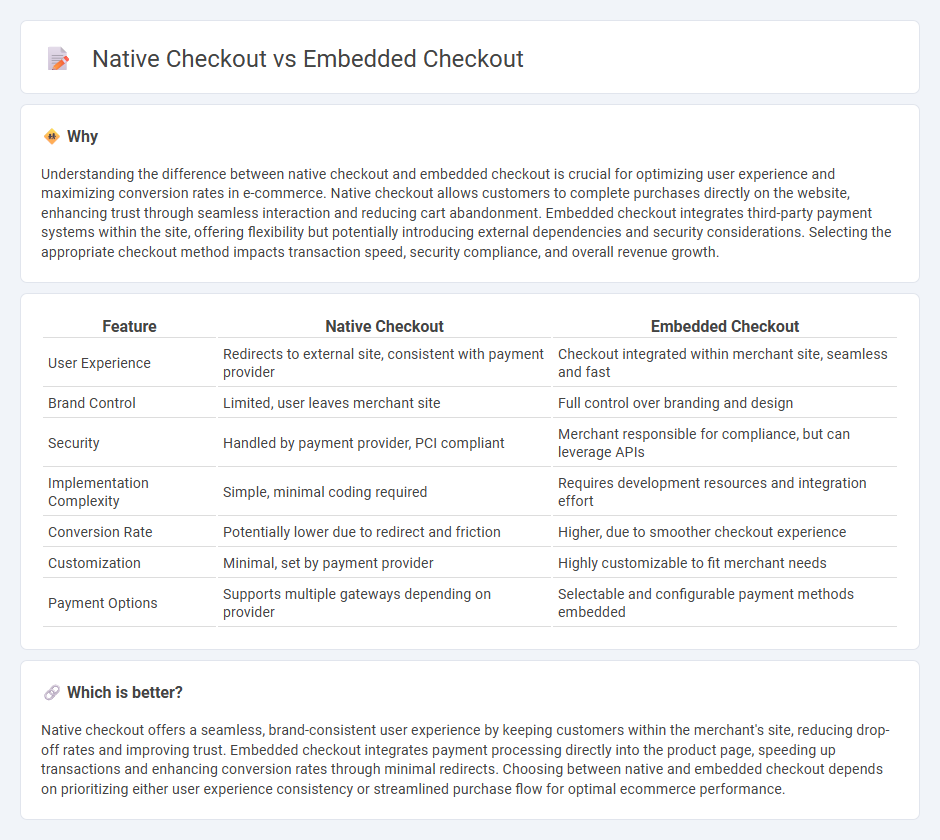
Understanding the difference between native checkout and embedded checkout is crucial for optimizing user experience and maximizing conversion rates in e-commerce. Native checkout allows customers to complete purchases directly on the website, enhancing trust through seamless interaction and reducing cart abandonment. Embedded checkout integrates third-party payment systems within the site, offering flexibility but potentially introducing external dependencies and security considerations. Selecting the appropriate checkout method impacts transaction speed, security compliance, and overall revenue growth.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Native Checkout | Embedded Checkout |
|---|---|---|
| User Experience | Redirects to external site, consistent with payment provider | Checkout integrated within merchant site, seamless and fast |
| Brand Control | Limited, user leaves merchant site | Full control over branding and design |
| Security | Handled by payment provider, PCI compliant | Merchant responsible for compliance, but can leverage APIs |
| Implementation Complexity | Simple, minimal coding required | Requires development resources and integration effort |
| Conversion Rate | Potentially lower due to redirect and friction | Higher, due to smoother checkout experience |
| Customization | Minimal, set by payment provider | Highly customizable to fit merchant needs |
| Payment Options | Supports multiple gateways depending on provider | Selectable and configurable payment methods embedded |
Which is better?
Native checkout offers a seamless, brand-consistent user experience by keeping customers within the merchant's site, reducing drop-off rates and improving trust. Embedded checkout integrates payment processing directly into the product page, speeding up transactions and enhancing conversion rates through minimal redirects. Choosing between native and embedded checkout depends on prioritizing either user experience consistency or streamlined purchase flow for optimal ecommerce performance.
Connection
Native checkout and embedded checkout both streamline the online purchasing process by integrating payment options directly within the merchant's platform. Native checkout offers a seamless, in-app payment experience tailored to specific devices or applications, enhancing user trust and reducing cart abandonment rates. Embedded checkout integrates payment forms directly into the website or app interface, enabling faster transactions and minimizing redirects, which boosts conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
Key Terms
User Experience
Embedded checkout integrates seamlessly within the website, minimizing load times and reducing cart abandonment by maintaining a consistent user interface. Native checkout directs users to an external payment platform, potentially causing friction but often providing enhanced security features and a familiar environment for transactions. Explore the differences in user experience impacts to optimize your e-commerce strategy.
Integration Complexity
Embedded checkout integrates seamlessly within the merchant's website, reducing checkout abandonment through a smoother user experience but requires moderate API integration and compliance with security protocols like PCI DSS. Native checkout leverages the platform's built-in payment system, simplifying setup with minimal coding but may limit customization and branding opportunities. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which checkout solution aligns best with your ecommerce strategy.
Data Ownership
Embedded checkout solutions often involve third-party platforms handling transaction data, which can limit merchants' control over customer information and analytics. Native checkout systems allow businesses to maintain full ownership of their data, enabling more precise customer insights and personalized marketing strategies. Explore how prioritizing data ownership in checkout processes can enhance your business control and growth opportunities.
Source and External Links
Embedded Checkout | Frontend Capabilities - Embedded Checkout embeds a hosted checkout page within your website as an iFrame, requiring creation of an HTML container and mounting the checkout inside it for a seamless payment experience.
Embedded Checkout Overview - BigCommerce's Embedded Checkout uses an HTML iframe to securely display its optimized PCI-compliant one-page checkout on external non-BigCommerce sites like WordPress.
Embedded Checkout vs. Stripe-Hosted Checkout - Stripe's Embedded Checkout enables hosting the payment form directly on your site with additional features such as a built-in success state, differing from the Stripe-hosted version which redirects to a hosted page.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com