Recommerce focuses on the resale of pre-owned goods, promoting sustainability and cost savings by extending product lifecycles, while digital commerce leverages online platforms to facilitate the buying and selling of new or used products with enhanced convenience and reach. Both models capitalize on evolving consumer behaviors and technology innovations, yet recommerce emphasizes circular economy principles whereas digital commerce prioritizes seamless digital experiences. Explore the distinct advantages and strategies behind recommerce and digital commerce to understand their impact on modern retail.
Why it is important
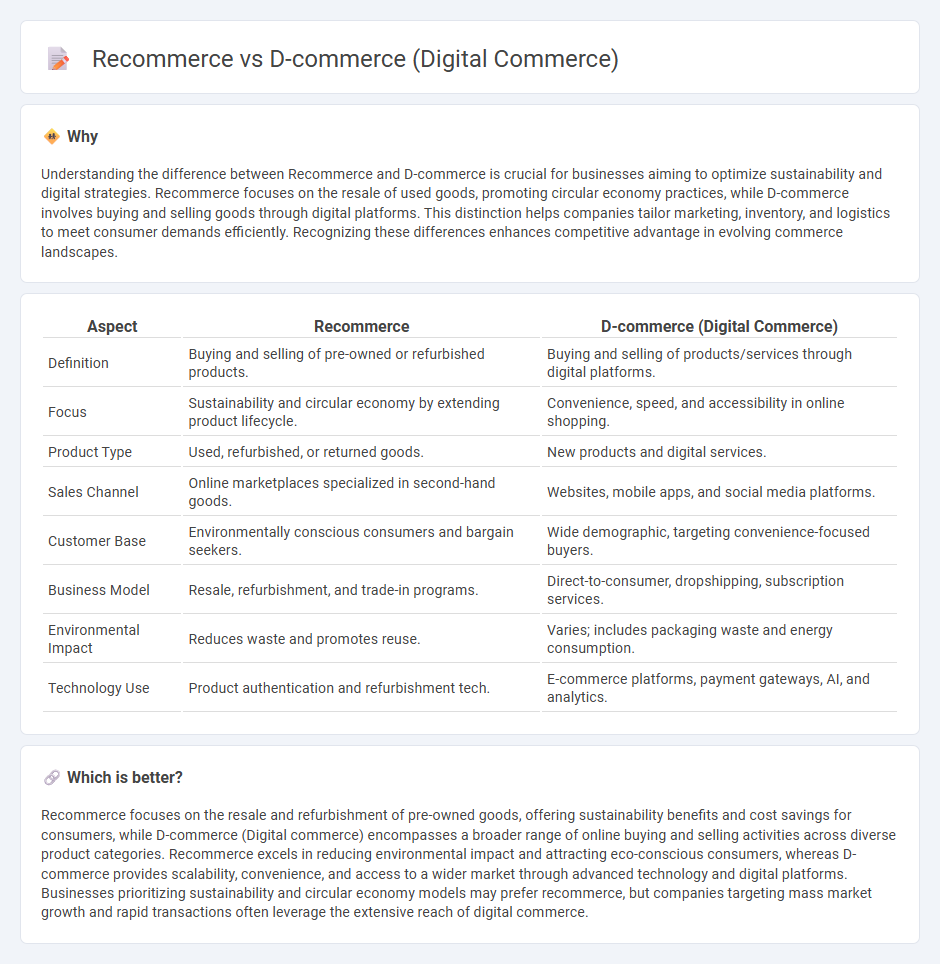
Understanding the difference between Recommerce and D-commerce is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize sustainability and digital strategies. Recommerce focuses on the resale of used goods, promoting circular economy practices, while D-commerce involves buying and selling goods through digital platforms. This distinction helps companies tailor marketing, inventory, and logistics to meet consumer demands efficiently. Recognizing these differences enhances competitive advantage in evolving commerce landscapes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Recommerce | D-commerce (Digital Commerce) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying and selling of pre-owned or refurbished products. | Buying and selling of products/services through digital platforms. |
| Focus | Sustainability and circular economy by extending product lifecycle. | Convenience, speed, and accessibility in online shopping. |
| Product Type | Used, refurbished, or returned goods. | New products and digital services. |
| Sales Channel | Online marketplaces specialized in second-hand goods. | Websites, mobile apps, and social media platforms. |
| Customer Base | Environmentally conscious consumers and bargain seekers. | Wide demographic, targeting convenience-focused buyers. |
| Business Model | Resale, refurbishment, and trade-in programs. | Direct-to-consumer, dropshipping, subscription services. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and promotes reuse. | Varies; includes packaging waste and energy consumption. |
| Technology Use | Product authentication and refurbishment tech. | E-commerce platforms, payment gateways, AI, and analytics. |
Which is better?
Recommerce focuses on the resale and refurbishment of pre-owned goods, offering sustainability benefits and cost savings for consumers, while D-commerce (Digital commerce) encompasses a broader range of online buying and selling activities across diverse product categories. Recommerce excels in reducing environmental impact and attracting eco-conscious consumers, whereas D-commerce provides scalability, convenience, and access to a wider market through advanced technology and digital platforms. Businesses prioritizing sustainability and circular economy models may prefer recommerce, but companies targeting mass market growth and rapid transactions often leverage the extensive reach of digital commerce.
Connection
Recommerce and D-commerce are connected through their shared use of digital platforms to facilitate the buying and selling of goods, often focusing on sustainability and convenience. Recommerce leverages D-commerce's online marketplaces and digital payment systems to efficiently resell pre-owned or refurbished products, extending product lifecycles. This integration supports circular economy principles by reducing waste and enabling consumers to participate in eco-friendly commerce through seamless digital experiences.
Key Terms
**D-commerce (Digital commerce):**
D-commerce (Digital commerce) represents the buying and selling of goods and services through online platforms, leveraging advanced technologies like AI, big data, and mobile applications to enhance customer experience and streamline operations. The global digital commerce market is projected to surpass $7 trillion by 2025, driven by increasing internet penetration and mobile device usage. Explore more about how D-commerce reshapes retail strategies and consumer behavior in the digital era.
E-commerce platforms
D-commerce leverages digital channels and technologies to facilitate direct sales, enhancing user experience through personalized marketing and seamless transactions. Recommerce focuses on the resale of pre-owned goods, emphasizing sustainability and cost-effectiveness within e-commerce platforms. Discover how these models transform consumer behavior and business strategies in the evolving digital market.
Online payment systems
D-commerce relies heavily on integrating diverse online payment systems such as digital wallets, credit card processing, and instant bank transfers to streamline customer transactions and enhance user experience. Recommerce platforms prioritize secure, efficient payment gateways tailored to secondhand goods, often incorporating escrow services and buyer protection to build trust in the resale market. Explore our detailed comparison to understand how payment technologies shape the future of digital and recommerce ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Different Types of Digital Commerce: A Simple Guide - D-commerce (digital commerce) broadly includes all electronically mediated transactions, extending beyond e-commerce to encompass digital banking, contactless payments, IoT applications, AI-driven personalization, blockchain transactions, and innovative payment methods like cryptocurrency.
Digital Commerce: How It Works and Trends for 2024 - Digital commerce involves buying and selling goods and services via digital channels such as the internet, apps, and social media, covering all stages from marketing and payment technologies to logistics, thus expanding much beyond traditional e-commerce.
eCommerce vs. Digital Commerce: The future of shopping - Digital commerce integrates marketing, sales, customer service, product development, and fulfillment across multiple platforms to create a seamless, continuous customer journey that includes engagement, conversion tracking, and retention strategies, distinguishing it from simple e-commerce.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com