Social shopping blends community engagement with e-commerce, enabling users to share recommendations, reviews, and purchase experiences directly within their networks. Renting platforms focus on temporary access to products, offering consumers flexibility and cost savings by borrowing items instead of owning them outright. Explore the evolving dynamics between social shopping and renting platforms to discover how consumer preferences are shaping the future of commerce.
Why it is important
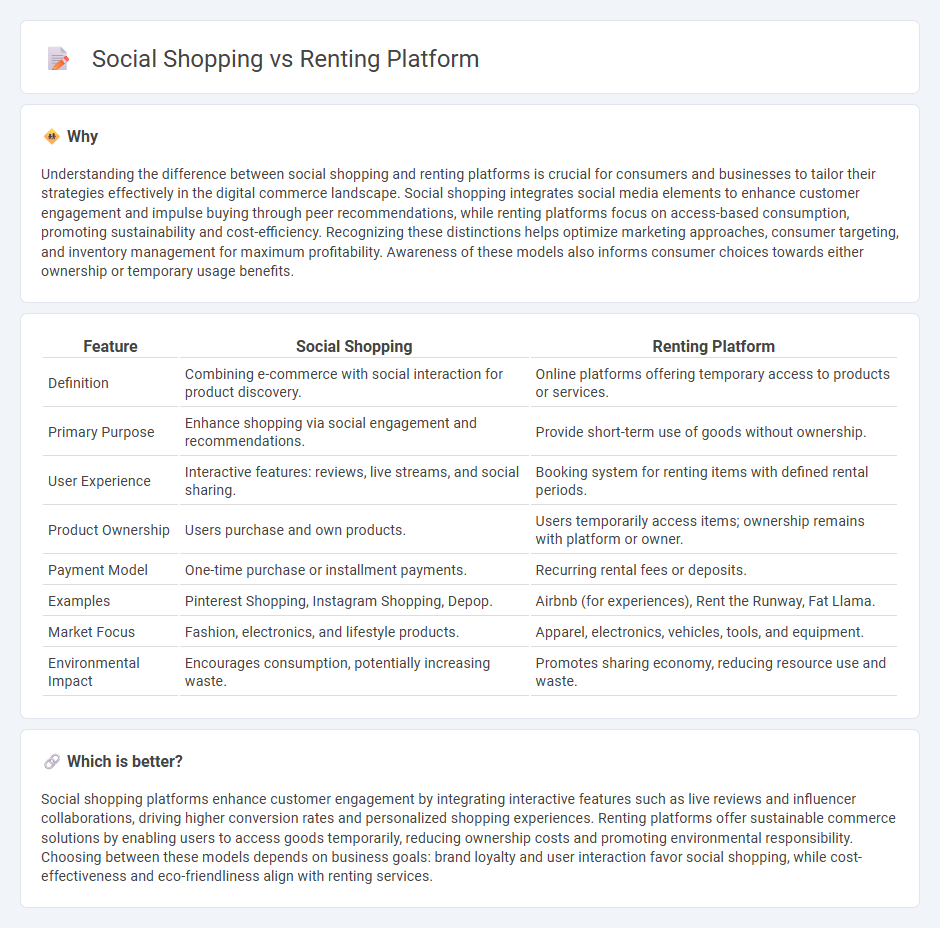
Understanding the difference between social shopping and renting platforms is crucial for consumers and businesses to tailor their strategies effectively in the digital commerce landscape. Social shopping integrates social media elements to enhance customer engagement and impulse buying through peer recommendations, while renting platforms focus on access-based consumption, promoting sustainability and cost-efficiency. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize marketing approaches, consumer targeting, and inventory management for maximum profitability. Awareness of these models also informs consumer choices towards either ownership or temporary usage benefits.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Social Shopping | Renting Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining e-commerce with social interaction for product discovery. | Online platforms offering temporary access to products or services. |
| Primary Purpose | Enhance shopping via social engagement and recommendations. | Provide short-term use of goods without ownership. |
| User Experience | Interactive features: reviews, live streams, and social sharing. | Booking system for renting items with defined rental periods. |
| Product Ownership | Users purchase and own products. | Users temporarily access items; ownership remains with platform or owner. |
| Payment Model | One-time purchase or installment payments. | Recurring rental fees or deposits. |
| Examples | Pinterest Shopping, Instagram Shopping, Depop. | Airbnb (for experiences), Rent the Runway, Fat Llama. |
| Market Focus | Fashion, electronics, and lifestyle products. | Apparel, electronics, vehicles, tools, and equipment. |
| Environmental Impact | Encourages consumption, potentially increasing waste. | Promotes sharing economy, reducing resource use and waste. |
Which is better?
Social shopping platforms enhance customer engagement by integrating interactive features such as live reviews and influencer collaborations, driving higher conversion rates and personalized shopping experiences. Renting platforms offer sustainable commerce solutions by enabling users to access goods temporarily, reducing ownership costs and promoting environmental responsibility. Choosing between these models depends on business goals: brand loyalty and user interaction favor social shopping, while cost-effectiveness and eco-friendliness align with renting services.
Connection
Social shopping platforms integrate peer recommendations and reviews, enhancing trust and engagement among users, while renting platforms enable access over ownership, promoting sustainable consumption. Both models leverage community-driven experiences and digital networks to facilitate transactions, blending social interaction with commerce. This synergy boosts user retention and expands market reach by combining social influence with flexible, cost-effective product usage.
Key Terms
Monetization Model
Renting platforms generate revenue primarily through subscription fees or rental charges, frequently incorporating commission-based earnings from each transaction to maximize profit. Social shopping platforms monetize by leveraging influencer partnerships, targeted advertising, and integrated e-commerce sales, capitalizing on user engagement and social interactions to drive revenue. Explore detailed insights into how these monetization models shape the future of digital commerce.
Peer-to-Peer Interaction
Peer-to-peer interaction on renting platforms fosters direct communication and trust between users, enhancing transparency and reliability in transactions. Social shopping integrates these interactions within broader online communities, promoting collaborative decision-making and shared product experiences. Explore how these models transform consumer engagement and create dynamic marketplaces.
User Trust
User trust in renting platforms hinges on transparent verification processes and secure payment systems that guarantee reliability and reduce fraud risk. Social shopping enhances trust through peer reviews, influencer endorsements, and community-driven recommendations, fostering a sense of authenticity and shared experience. Explore how trust mechanisms differ and drive user engagement in these evolving e-commerce models.
Source and External Links
RentSpree: Online Tenant Screening & Rent Payment - A mobile-friendly platform trusted by over 3 million users, offering comprehensive tenant screening, secure online rental applications, lease signing, and rent payment services to simplify the rental process for landlords and renters.
Avail Landlord Software: Online Property Management Tools - Provides a full suite of tools for landlords including tenant screening, rent collection, lease management, and property listings on major sites, designed especially for DIY landlords to manage rentals efficiently on any device.
Findigs | Smart Rental Screening for Property Managers - An all-in-one renting platform focused on transparent, rule-based tenant screening and verification with automation features to speed the rental process and ensure secure, fair leasing decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com