Micro fulfillment centers leverage automation and proximity to consumers to expedite last-mile delivery, enhancing e-commerce efficiency and reducing shipping times. Cross-docking minimizes inventory holding by quickly transferring products from inbound to outbound transportation, optimizing supply chain flow and lowering storage costs. Explore how each strategy can transform your commerce operations for maximum agility and customer satisfaction.
Why it is important
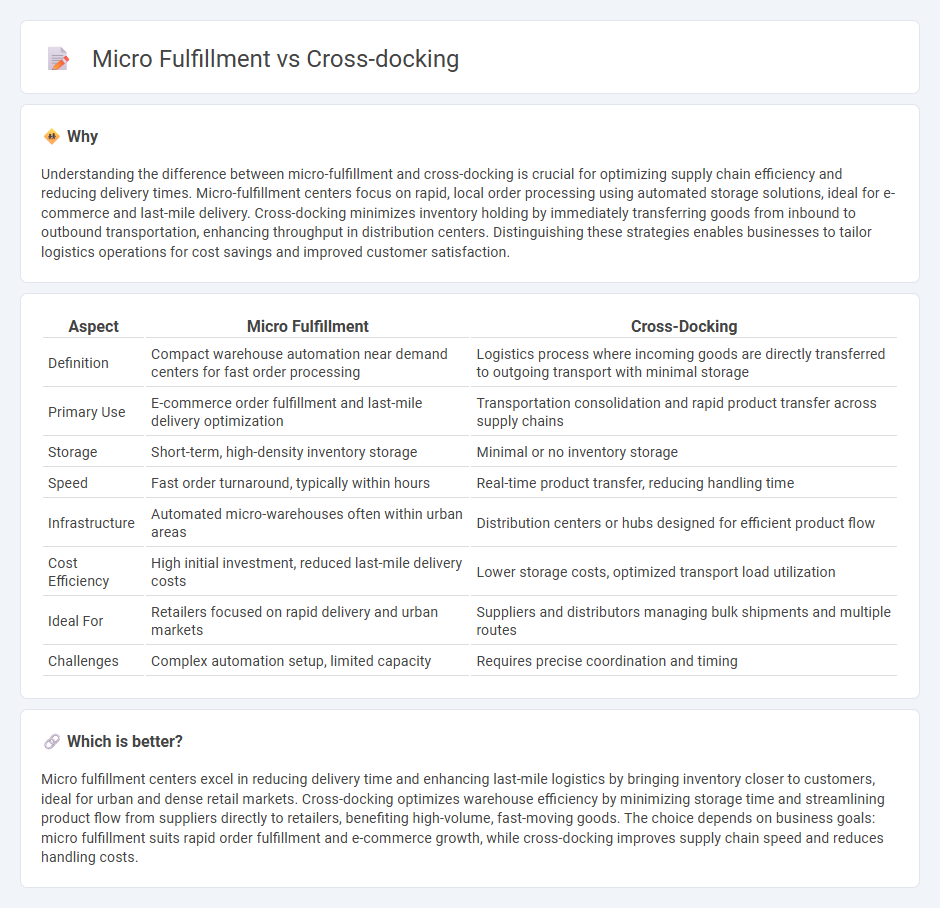
Understanding the difference between micro-fulfillment and cross-docking is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing delivery times. Micro-fulfillment centers focus on rapid, local order processing using automated storage solutions, ideal for e-commerce and last-mile delivery. Cross-docking minimizes inventory holding by immediately transferring goods from inbound to outbound transportation, enhancing throughput in distribution centers. Distinguishing these strategies enables businesses to tailor logistics operations for cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Micro Fulfillment | Cross-Docking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compact warehouse automation near demand centers for fast order processing | Logistics process where incoming goods are directly transferred to outgoing transport with minimal storage |
| Primary Use | E-commerce order fulfillment and last-mile delivery optimization | Transportation consolidation and rapid product transfer across supply chains |
| Storage | Short-term, high-density inventory storage | Minimal or no inventory storage |
| Speed | Fast order turnaround, typically within hours | Real-time product transfer, reducing handling time |
| Infrastructure | Automated micro-warehouses often within urban areas | Distribution centers or hubs designed for efficient product flow |
| Cost Efficiency | High initial investment, reduced last-mile delivery costs | Lower storage costs, optimized transport load utilization |
| Ideal For | Retailers focused on rapid delivery and urban markets | Suppliers and distributors managing bulk shipments and multiple routes |
| Challenges | Complex automation setup, limited capacity | Requires precise coordination and timing |
Which is better?
Micro fulfillment centers excel in reducing delivery time and enhancing last-mile logistics by bringing inventory closer to customers, ideal for urban and dense retail markets. Cross-docking optimizes warehouse efficiency by minimizing storage time and streamlining product flow from suppliers directly to retailers, benefiting high-volume, fast-moving goods. The choice depends on business goals: micro fulfillment suits rapid order fulfillment and e-commerce growth, while cross-docking improves supply chain speed and reduces handling costs.
Connection
Micro fulfillment centers enhance e-commerce efficiency by enabling rapid order processing close to consumers, reducing delivery times and costs. Cross-docking optimizes supply chains by transferring products directly from inbound to outbound shipments, minimizing storage needs and accelerating inventory turnover. Together, micro fulfillment and cross-docking streamline last-mile delivery, improve inventory management, and support scalable commerce operations.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Cross-docking minimizes inventory holding by transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation, reducing storage needs and accelerating order fulfillment. Micro-fulfillment centers store smaller inventory quantities closer to customers, enhancing responsiveness while maintaining tighter stock control for high-demand items. Explore how these strategies optimize inventory management to improve supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Distribution Center
Cross-docking in distribution centers streamlines inventory movement by directly transferring products from inbound to outbound transportation, minimizing storage time and reducing handling costs. Micro fulfillment centers, integrated within or near distribution hubs, enhance last-mile delivery efficiency by rapidly picking and packing orders for faster customer fulfillment. Explore how these innovative strategies optimize distribution center operations for improved supply chain performance and customer satisfaction.
Last-Mile Delivery
Cross-docking streamlines last-mile delivery by transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation, minimizing storage time and expediting order fulfillment. Micro-fulfillment centers enhance last-mile delivery efficiency by using automated systems in urban locations to quickly pick and pack orders close to the customer. Explore the advantages of both strategies to optimize your last-mile delivery process.
Source and External Links
Cross Docking: Definition, History, and Process - Inbound Logistics - Cross docking is a shipping method transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound transport with minimal storage, using methods like continuous, consolidation, and de-consolidation to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
What Is Cross-Docking? Definition, Types & Advantages - NetSuite - Cross-docking is a supply chain strategy for transferring goods directly from incoming to outgoing vehicles with little or no storage time, enhancing delivery speed, reducing labor and warehouse costs, and optimizing inventory.
Understanding cross-docking: A comprehensive guide - Maersk - Cross-docking involves minimal storage time by quickly transferring products from suppliers to customers via different methods like pre-distribution, post-distribution, continuous, consolidation, and deconsolidation, adapted to industries such as retail, manufacturing, and e-commerce.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com