Circular supply chains focus on resource efficiency by recycling, reusing, and reducing waste throughout the product lifecycle, promoting sustainability and cost savings. Collaborative supply chains emphasize strategic partnerships and information sharing among suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers to enhance responsiveness, innovation, and market competitiveness. Discover how integrating these supply chain models can transform commerce for sustainable growth.
Why it is important
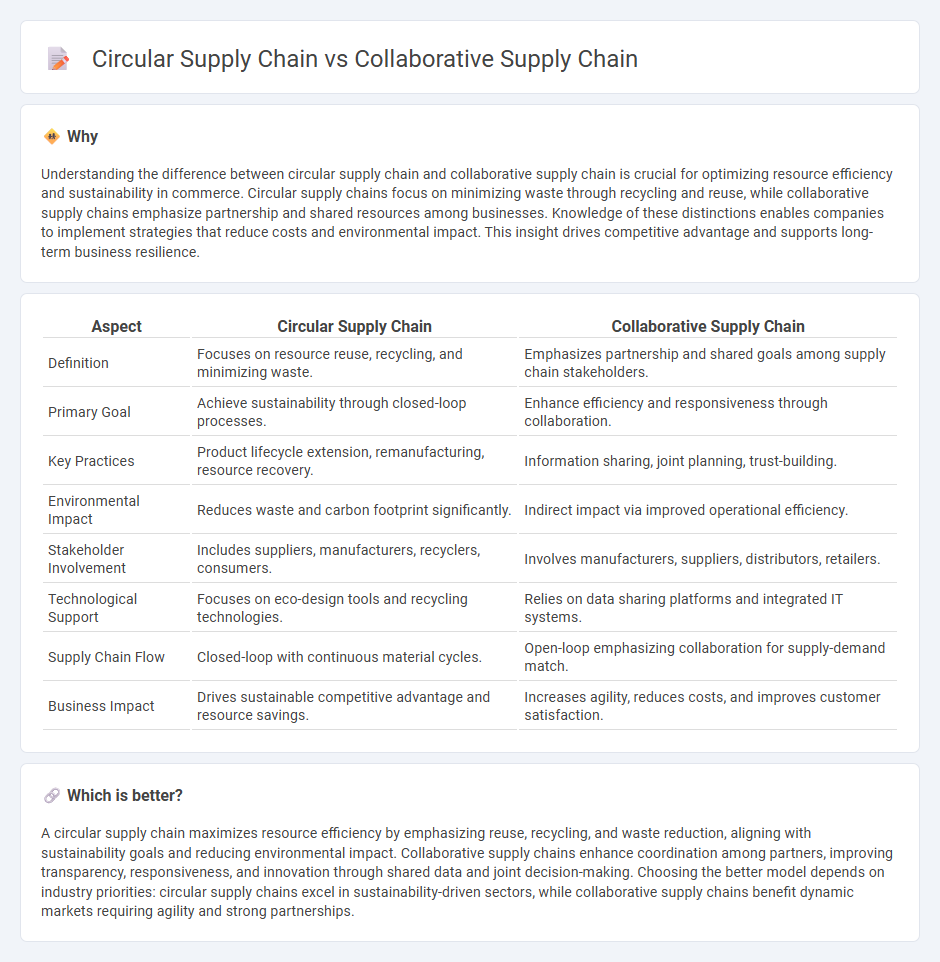
Understanding the difference between circular supply chain and collaborative supply chain is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and sustainability in commerce. Circular supply chains focus on minimizing waste through recycling and reuse, while collaborative supply chains emphasize partnership and shared resources among businesses. Knowledge of these distinctions enables companies to implement strategies that reduce costs and environmental impact. This insight drives competitive advantage and supports long-term business resilience.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Supply Chain | Collaborative Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on resource reuse, recycling, and minimizing waste. | Emphasizes partnership and shared goals among supply chain stakeholders. |
| Primary Goal | Achieve sustainability through closed-loop processes. | Enhance efficiency and responsiveness through collaboration. |
| Key Practices | Product lifecycle extension, remanufacturing, resource recovery. | Information sharing, joint planning, trust-building. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and carbon footprint significantly. | Indirect impact via improved operational efficiency. |
| Stakeholder Involvement | Includes suppliers, manufacturers, recyclers, consumers. | Involves manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, retailers. |
| Technological Support | Focuses on eco-design tools and recycling technologies. | Relies on data sharing platforms and integrated IT systems. |
| Supply Chain Flow | Closed-loop with continuous material cycles. | Open-loop emphasizing collaboration for supply-demand match. |
| Business Impact | Drives sustainable competitive advantage and resource savings. | Increases agility, reduces costs, and improves customer satisfaction. |
Which is better?
A circular supply chain maximizes resource efficiency by emphasizing reuse, recycling, and waste reduction, aligning with sustainability goals and reducing environmental impact. Collaborative supply chains enhance coordination among partners, improving transparency, responsiveness, and innovation through shared data and joint decision-making. Choosing the better model depends on industry priorities: circular supply chains excel in sustainability-driven sectors, while collaborative supply chains benefit dynamic markets requiring agility and strong partnerships.
Connection
Circular supply chains focus on resource efficiency and waste minimization by reusing, recycling, and refurbishing materials, while collaborative supply chains emphasize partnerships and information sharing among stakeholders to optimize processes. Both supply chain models rely on cross-functional collaboration to enhance sustainability and operational efficiency, facilitating the continuous flow of materials and information. Integration of these approaches leads to reduced environmental impact and improved economic value throughout the supply network.
Key Terms
Information Sharing
Collaborative supply chains emphasize real-time information sharing among partners to enhance transparency, inventory management, and demand forecasting, resulting in reduced costs and improved efficiency. Circular supply chains integrate information flow to support resource recovery, waste reduction, and product lifecycle extension, using data analytics for sustainable decision-making. Explore how advanced information-sharing technologies drive innovation in both supply chain models.
Reverse Logistics
Collaborative supply chains emphasize strategic partnerships between suppliers and manufacturers to improve efficiency and reduce costs through shared resources and information flow. Circular supply chains integrate reverse logistics to recover, refurbish, and recycle products, minimizing waste and promoting sustainability by closing the product lifecycle loop. Explore how advanced reverse logistics technologies drive innovation in both collaborative and circular supply chain models.
Resource Recovery
Collaborative supply chains emphasize real-time data sharing and joint planning among partners to optimize inventory and reduce costs, while circular supply chains prioritize resource recovery through recycling, remanufacturing, and waste minimization processes. Resource recovery in circular supply chains enhances sustainability by reintegrating materials like metals, plastics, and manufacturing byproducts back into production cycles, reducing dependency on virgin resources. Explore how these supply chain models transform resource efficiency and environmental impact.
Source and External Links
Supply Chain Collaboration: Strategies, Benefits & Solutions - Ivalua - Supply chain collaboration is a synchronized effort among internal departments and external partners focusing on knowledge sharing, horizontal and vertical cooperation, and innovation to improve supply chain efficiency and resilience through breaking down silos and facilitating integrated decision-making processes.
Supply chain collaboration - Wikipedia - Collaborative supply chain involves multiple firms jointly planning and executing operations, encompassing approaches like collaborative communication, joint decision-making, information sharing, and coordinated contracts to optimize overall supply chain performance.
What is Supply Chain Collaboration? A Look at Benefits and Trends - Supply chain collaboration includes vertical (between supply chain levels), horizontal (between peers or competitors), and full collaboration integrating both, aiming to synchronize production, reduce costs, and create value through transparency and end-to-end visibility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com