Headless commerce separates the front-end presentation layer from the back-end e-commerce functionality, enabling greater customization, faster updates, and seamless integrations with multiple channels compared to traditional commerce platforms. Traditional commerce relies on a monolithic architecture where front-end and back-end are tightly coupled, limiting flexibility and scalability for modern omnichannel experiences. Explore the benefits and challenges of headless commerce to understand how it can transform your digital sales strategy.
Why it is important
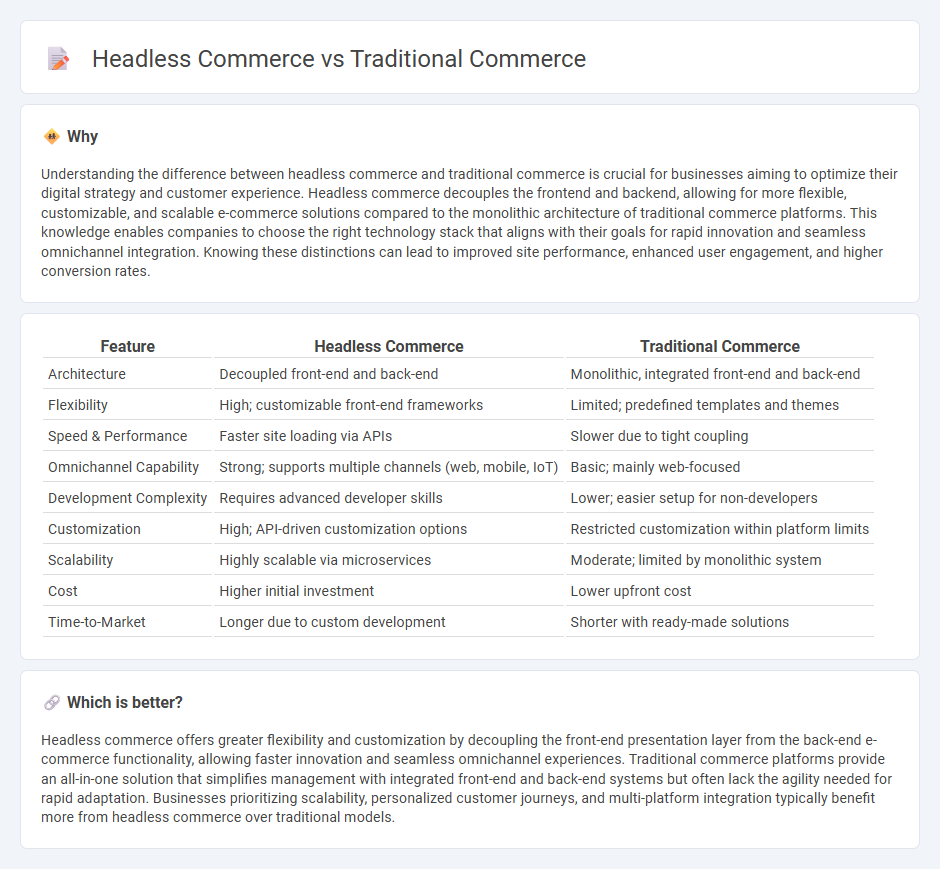
Understanding the difference between headless commerce and traditional commerce is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their digital strategy and customer experience. Headless commerce decouples the frontend and backend, allowing for more flexible, customizable, and scalable e-commerce solutions compared to the monolithic architecture of traditional commerce platforms. This knowledge enables companies to choose the right technology stack that aligns with their goals for rapid innovation and seamless omnichannel integration. Knowing these distinctions can lead to improved site performance, enhanced user engagement, and higher conversion rates.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Headless Commerce | Traditional Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Decoupled front-end and back-end | Monolithic, integrated front-end and back-end |
| Flexibility | High; customizable front-end frameworks | Limited; predefined templates and themes |
| Speed & Performance | Faster site loading via APIs | Slower due to tight coupling |
| Omnichannel Capability | Strong; supports multiple channels (web, mobile, IoT) | Basic; mainly web-focused |
| Development Complexity | Requires advanced developer skills | Lower; easier setup for non-developers |
| Customization | High; API-driven customization options | Restricted customization within platform limits |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via microservices | Moderate; limited by monolithic system |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Time-to-Market | Longer due to custom development | Shorter with ready-made solutions |
Which is better?
Headless commerce offers greater flexibility and customization by decoupling the front-end presentation layer from the back-end e-commerce functionality, allowing faster innovation and seamless omnichannel experiences. Traditional commerce platforms provide an all-in-one solution that simplifies management with integrated front-end and back-end systems but often lack the agility needed for rapid adaptation. Businesses prioritizing scalability, personalized customer journeys, and multi-platform integration typically benefit more from headless commerce over traditional models.
Connection
Headless commerce and traditional commerce intersect through their shared goal of facilitating seamless transactions and improving customer experiences across multiple channels. Headless commerce decouples the front-end presentation layer from back-end e-commerce functionalities, enabling greater flexibility and faster customization compared to traditional monolithic systems. This architectural evolution enhances the scalability and adaptability of traditional commerce platforms, meeting modern demands for personalized, omnichannel buying journeys.
Key Terms
Monolithic architecture
Monolithic architecture in traditional commerce integrates the front-end and back-end into a single unified system, which often leads to slower deployment cycles and limited customization options for scaling businesses. Headless commerce decouples the front-end presentation layer from the back-end e-commerce functionality, enabling developers to create flexible, fast, and tailored customer experiences across multiple channels. Explore the advantages of headless commerce and understand how it outperforms monolithic systems in modern digital retail environments.
API-driven
Headless commerce leverages API-driven architecture to separate the frontend presentation layer from the backend eCommerce functionalities, enabling greater flexibility and customization compared to traditional commerce platforms that integrate both layers. This API-first approach allows seamless omnichannel experiences by easily connecting with various frontends such as mobile apps, kiosks, and IoT devices through RESTful or GraphQL APIs. Discover how embracing headless commerce can revolutionize your digital strategy and improve customer engagement.
Customer experience
Traditional commerce platforms often limit customization, leading to slower site performance and less personalized shopping experiences that impact customer satisfaction. Headless commerce separates the front-end presentation layer from the back-end eCommerce functionality, enabling faster load times, seamless omnichannel integrations, and highly tailored user interfaces that boost engagement. Learn more about how headless commerce transforms customer experience and drives higher conversion rates.
Source and External Links
Traditional Commerce and eCommerce: What are The Differences? - Traditional commerce is the buying and selling of goods or services through physical stores or face-to-face transactions, characterized by physical storefronts, in-person customer interactions, and traditional payment methods, contrasting with eCommerce's online model.
Difference between Traditional Commerce and E-commerce - Traditional commerce involves person-to-person commercial transactions without the internet, such as local markets or bazaars, which are typically more time-consuming and involve physical presence.
The Fall of Traditional Retail Commerce | Nexcess - Traditional commerce evolved from mom-and-pop shops to department stores and shopping malls, culminating in big-box stores like Walmart, but has declined with the rise of digital and ecommerce platforms.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com