Green logistics emphasizes sustainable practices in the supply chain, aiming to minimize environmental impact through energy-efficient transportation and eco-friendly packaging. Reverse logistics focuses on the process of returning goods from consumers to businesses for reuse, recycling, or proper disposal, thereby enhancing product lifecycle management. Explore the differences and benefits of both strategies to optimize your commercial operations.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between green logistics and reverse logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain sustainability and cost efficiency. Green logistics focuses on minimizing environmental impact through eco-friendly transportation, packaging, and warehousing, while reverse logistics manages the return, recycling, or disposal of products. Businesses leveraging both strategies can enhance resource recovery and reduce carbon footprints. This knowledge enables companies to implement targeted practices that align with corporate social responsibility and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
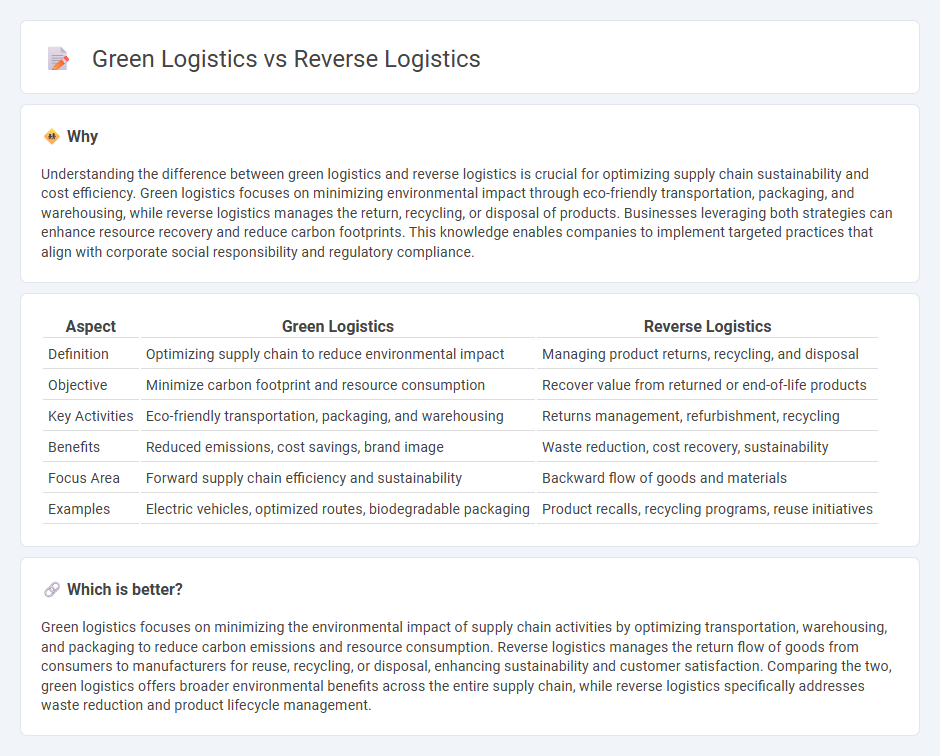
| Aspect | Green Logistics | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Optimizing supply chain to reduce environmental impact | Managing product returns, recycling, and disposal |
| Objective | Minimize carbon footprint and resource consumption | Recover value from returned or end-of-life products |
| Key Activities | Eco-friendly transportation, packaging, and warehousing | Returns management, refurbishment, recycling |
| Benefits | Reduced emissions, cost savings, brand image | Waste reduction, cost recovery, sustainability |
| Focus Area | Forward supply chain efficiency and sustainability | Backward flow of goods and materials |
| Examples | Electric vehicles, optimized routes, biodegradable packaging | Product recalls, recycling programs, reuse initiatives |
Which is better?
Green logistics focuses on minimizing the environmental impact of supply chain activities by optimizing transportation, warehousing, and packaging to reduce carbon emissions and resource consumption. Reverse logistics manages the return flow of goods from consumers to manufacturers for reuse, recycling, or disposal, enhancing sustainability and customer satisfaction. Comparing the two, green logistics offers broader environmental benefits across the entire supply chain, while reverse logistics specifically addresses waste reduction and product lifecycle management.
Connection
Green logistics and reverse logistics are interconnected through their shared focus on sustainability and environmental impact reduction within the supply chain. Green logistics optimizes transportation, warehousing, and packaging to minimize carbon emissions, while reverse logistics manages the return, recycling, and disposal of products to reduce waste. Together, these practices enhance resource efficiency and promote circular economy principles in commerce.
Key Terms
Returns Management
Reverse logistics centers on the process of returning products from consumers back to manufacturers for reuse, recycling, or disposal, optimizing returns management to reduce costs and improve customer satisfaction. Green logistics emphasizes environmentally sustainable practices across the supply chain, including minimizing carbon emissions and waste during product returns and transportation. Explore comprehensive strategies to integrate reverse and green logistics for efficient and eco-friendly returns management.
Environmental Sustainability
Reverse logistics emphasizes the efficient return, recycling, and disposal of products to minimize waste and reduce environmental impact. Green logistics focuses on optimizing transportation, warehousing, and packaging processes to lower carbon emissions and conserve natural resources. Explore the key differences and benefits of reverse and green logistics for advancing environmental sustainability.
Circular Supply Chain
Reverse logistics emphasizes the process of returning products from consumers back to manufacturers for reuse, remanufacturing, or disposal, reducing waste and recovery costs. Green logistics integrates eco-friendly practices throughout the supply chain, targeting energy efficiency, reducing carbon emissions, and promoting sustainable resource management. Discover how these strategies collectively enhance circular supply chains and drive sustainable business transformations.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from the customer back to the manufacturer or distributor for return, repair, remanufacture, recycling, or disposal, aimed at cost-effective flow and sustainability within the supply chain.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics involves returning products from customers to sellers or manufacturers, and can be optimized using clear return policies, supplier collaboration, data analytics, centralized return centers, efficient transportation, and automation.
What Is Reverse Logistics in Supply Chain Management? - Reverse logistics manages the flow of returned products back from customers to manufacturers, encompassing returns management, remanufacturing, refurbishment, and packaging management to reduce waste and recover value.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com