Multithreading enhances sales data processing by allowing simultaneous handling of multiple transactions, increasing efficiency and reducing latency. Batch processing groups sales data into large sets processed at once, optimizing resource use but potentially delaying real-time insights. Explore deeper to understand which method suits your sales operation best.
Why it is important
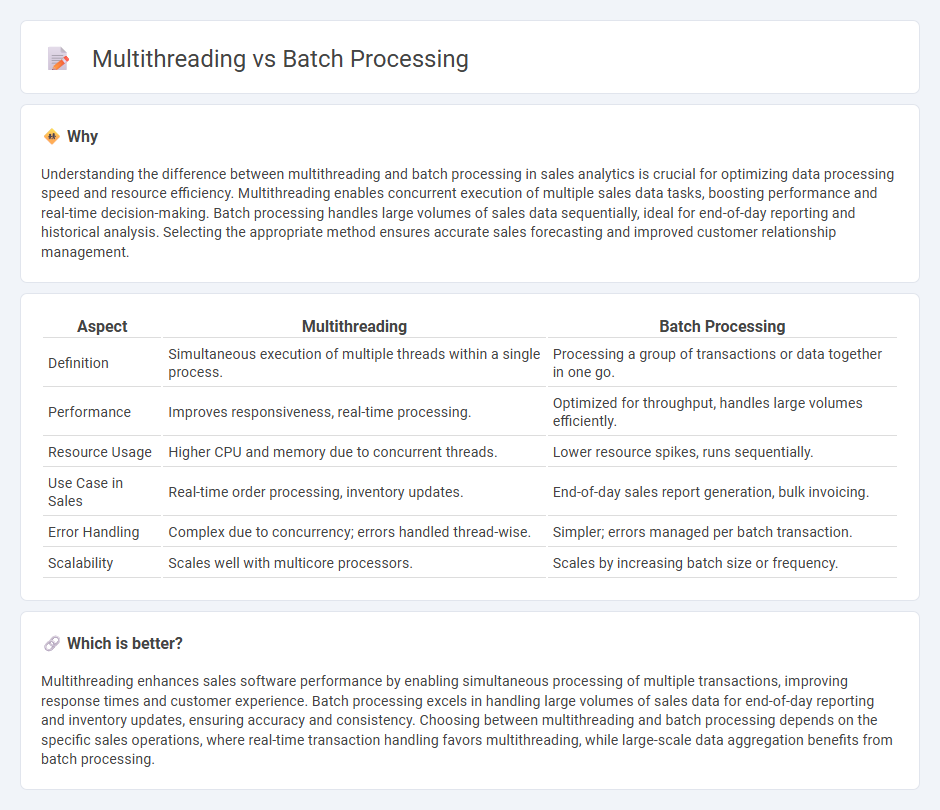
Understanding the difference between multithreading and batch processing in sales analytics is crucial for optimizing data processing speed and resource efficiency. Multithreading enables concurrent execution of multiple sales data tasks, boosting performance and real-time decision-making. Batch processing handles large volumes of sales data sequentially, ideal for end-of-day reporting and historical analysis. Selecting the appropriate method ensures accurate sales forecasting and improved customer relationship management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Multithreading | Batch Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simultaneous execution of multiple threads within a single process. | Processing a group of transactions or data together in one go. |
| Performance | Improves responsiveness, real-time processing. | Optimized for throughput, handles large volumes efficiently. |
| Resource Usage | Higher CPU and memory due to concurrent threads. | Lower resource spikes, runs sequentially. |
| Use Case in Sales | Real-time order processing, inventory updates. | End-of-day sales report generation, bulk invoicing. |
| Error Handling | Complex due to concurrency; errors handled thread-wise. | Simpler; errors managed per batch transaction. |
| Scalability | Scales well with multicore processors. | Scales by increasing batch size or frequency. |
Which is better?
Multithreading enhances sales software performance by enabling simultaneous processing of multiple transactions, improving response times and customer experience. Batch processing excels in handling large volumes of sales data for end-of-day reporting and inventory updates, ensuring accuracy and consistency. Choosing between multithreading and batch processing depends on the specific sales operations, where real-time transaction handling favors multithreading, while large-scale data aggregation benefits from batch processing.
Connection
Multithreading and batch processing enhance sales operations by enabling simultaneous handling of multiple sales transactions, reducing processing time and increasing throughput. Multithreading allows sales platforms to process numerous tasks concurrently, while batch processing groups sales data for efficient bulk analysis or updates. Together, they optimize sales system performance, improve data accuracy, and support real-time decision-making in high-volume sales environments.
Key Terms
Efficiency
Batch processing handles large volumes of data by executing tasks sequentially without interruption, maximizing throughput for bulk operations but often at the cost of latency. Multithreading enhances efficiency by running multiple threads concurrently within a single process, enabling faster task completion and improved resource utilization, especially in real-time systems. Explore further to understand which approach best aligns with your performance and scalability requirements.
Throughput
Batch processing optimizes throughput by handling large volumes of data in sequential groups, maximizing resource utilization and minimizing overhead per task. Multithreading enhances throughput by executing multiple threads concurrently within a single process, improving CPU efficiency and responsiveness. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which method best suits your throughput requirements.
Scalability
Batch processing excels in handling large volumes of data with high throughput by processing tasks sequentially, making it ideal for operations that require processing massive datasets without immediate user interaction. Multithreading enhances scalability by enabling multiple threads to run concurrently within a single application, improving resource utilization and responsiveness, especially in real-time systems. Explore further to understand how choosing between batch processing and multithreading impacts system scalability and performance optimization.
Source and External Links
An Introduction to Batch Processing - Batch processing is a computational technique where data is collected and processed together in one operation, often used for large volumes of data and can be combined with stream processing for real-time insights.
What is Batch Processing? - Batch processing refers to running high-volume repetitive data jobs by processing groups of data during a scheduled batch window, with specifics such as batch size and dependencies managed for efficient execution.
Exploring Batch Processing: Definition, Use Cases, and ... - Batch processing automates the handling of grouped tasks without human intervention, ideal for large-scale jobs where real-time processing is not necessary, such as monthly credit card billing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com