Value engineering enhances product or service offerings by optimizing cost and functionality to maximize customer value, while cross-selling increases revenue by suggesting complementary products during the sales process. Focusing on value engineering improves customer satisfaction and loyalty through tailored solutions, whereas cross-selling leverages existing customer relationships to boost average transaction size. Explore how integrating these strategies can transform your sales performance and business growth.
Why it is important
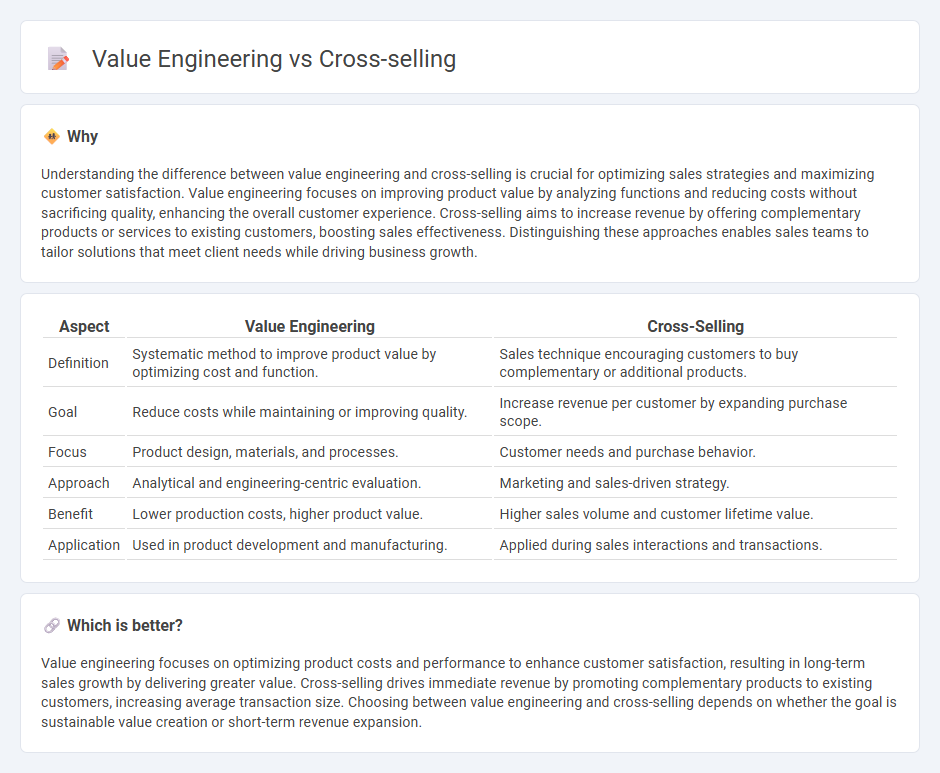
Understanding the difference between value engineering and cross-selling is crucial for optimizing sales strategies and maximizing customer satisfaction. Value engineering focuses on improving product value by analyzing functions and reducing costs without sacrificing quality, enhancing the overall customer experience. Cross-selling aims to increase revenue by offering complementary products or services to existing customers, boosting sales effectiveness. Distinguishing these approaches enables sales teams to tailor solutions that meet client needs while driving business growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Value Engineering | Cross-Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic method to improve product value by optimizing cost and function. | Sales technique encouraging customers to buy complementary or additional products. |
| Goal | Reduce costs while maintaining or improving quality. | Increase revenue per customer by expanding purchase scope. |
| Focus | Product design, materials, and processes. | Customer needs and purchase behavior. |
| Approach | Analytical and engineering-centric evaluation. | Marketing and sales-driven strategy. |
| Benefit | Lower production costs, higher product value. | Higher sales volume and customer lifetime value. |
| Application | Used in product development and manufacturing. | Applied during sales interactions and transactions. |
Which is better?
Value engineering focuses on optimizing product costs and performance to enhance customer satisfaction, resulting in long-term sales growth by delivering greater value. Cross-selling drives immediate revenue by promoting complementary products to existing customers, increasing average transaction size. Choosing between value engineering and cross-selling depends on whether the goal is sustainable value creation or short-term revenue expansion.
Connection
Value engineering enhances a product's features and cost-efficiency, creating opportunities for targeted cross-selling by aligning additional offerings with customer needs and budget constraints. Cross-selling leverages insights gained from value engineering to propose complementary products that maximize customer value while increasing overall sales revenue. This strategic integration improves customer satisfaction and drives higher profit margins through optimized product bundles.
Key Terms
Upsell
Cross-selling targets increasing revenue by suggesting complementary products or services during a purchase, effectively broadening the customer's basket. Value engineering concentrates on enhancing product functionality and cost-efficiency to deliver greater value and justify higher pricing, emphasizing product optimization. Discover how integrating cross-selling and value engineering strategies can maximize upsell success and customer satisfaction.
Cost Optimization
Cross-selling enhances cost optimization by promoting complementary products or services that maximize customer value and increase revenue per transaction. Value engineering systematically reduces costs through analyzing product functions and improving efficiency without compromising quality. Explore more about how these strategies drive cost savings and business growth.
Customer Needs
Cross-selling enhances customer satisfaction by offering complementary products that meet existing needs, increasing overall value through tailored solutions. Value engineering focuses on optimizing product design and cost efficiency without compromising customer requirements, ensuring maximum functionality and affordability. Explore how aligning both strategies can drive unparalleled customer-centric innovation.
Source and External Links
What Is Cross-Selling? Intro, Steps, and Pro Tips [+Data] - Cross-selling is a sales technique of offering customers additional products or services that complement their original purchase, such as adding fries and a drink to a burger order, distinct from upselling which offers a more expensive version of the same product.
Cross-Sell - Overview, How It Works, and Examples - Cross-selling involves selling related or complementary products or services to existing customers, which is often easier and helps increase revenue and strengthen customer relationships if done properly.
What is Cross-Selling? - Salesforce - Cross-selling is a growth strategy to increase sales and customer loyalty by offering supplementary products based on a customer's initial purchase, enhancing customer lifetime value without encouraging them to replace current choices with more expensive ones.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com