Virtual selling leverages digital platforms to connect with customers through online channels, enhancing convenience and expanding market reach beyond geographical limits. Retail selling focuses on in-person interactions at physical stores, providing immediate product experience and personalized customer service. Discover how combining these approaches can optimize your sales strategy and boost revenue.
Why it is important
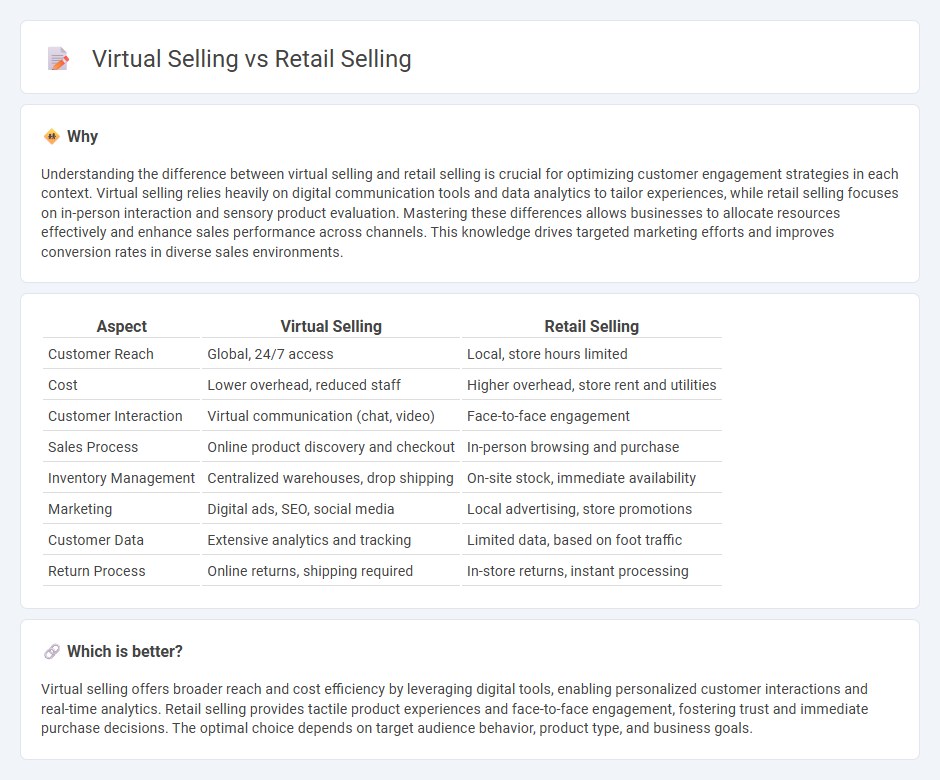
Understanding the difference between virtual selling and retail selling is crucial for optimizing customer engagement strategies in each context. Virtual selling relies heavily on digital communication tools and data analytics to tailor experiences, while retail selling focuses on in-person interaction and sensory product evaluation. Mastering these differences allows businesses to allocate resources effectively and enhance sales performance across channels. This knowledge drives targeted marketing efforts and improves conversion rates in diverse sales environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Virtual Selling | Retail Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Reach | Global, 24/7 access | Local, store hours limited |
| Cost | Lower overhead, reduced staff | Higher overhead, store rent and utilities |
| Customer Interaction | Virtual communication (chat, video) | Face-to-face engagement |
| Sales Process | Online product discovery and checkout | In-person browsing and purchase |
| Inventory Management | Centralized warehouses, drop shipping | On-site stock, immediate availability |
| Marketing | Digital ads, SEO, social media | Local advertising, store promotions |
| Customer Data | Extensive analytics and tracking | Limited data, based on foot traffic |
| Return Process | Online returns, shipping required | In-store returns, instant processing |
Which is better?
Virtual selling offers broader reach and cost efficiency by leveraging digital tools, enabling personalized customer interactions and real-time analytics. Retail selling provides tactile product experiences and face-to-face engagement, fostering trust and immediate purchase decisions. The optimal choice depends on target audience behavior, product type, and business goals.
Connection
Virtual selling and retail selling are interconnected through the integration of digital tools that enhance customer engagement and streamline the purchasing process. Omnichannel strategies blend virtual platforms with physical store experiences to boost sales performance and improve inventory management. Data analytics from virtual interactions inform retail selling tactics, enabling personalized marketing and targeted promotions.
Key Terms
**Retail Selling:**
Retail selling involves direct interaction with customers in a physical store, allowing for personalized service and immediate product access. It enables merchants to create tangible shopping experiences through visual merchandising, product trials, and on-the-spot assistance, which often leads to higher customer satisfaction. Explore more about the advantages and strategies of retail selling to enhance your business performance.
In-store Experience
Retail selling emphasizes tactile engagement, personalized customer service, and immediate product access, creating a multisensory in-store experience that builds brand loyalty. Virtual selling leverages digital tools, augmented reality, and real-time analytics to simulate and enhance customer interaction, compensating for the absence of physical presence. Discover how integrating these approaches can redefine customer satisfaction and drive sales growth.
Point-of-Sale (POS)
Retail selling relies on physical Point-of-Sale (POS) systems that process in-store transactions, manage inventory, and offer real-time sales analytics. Virtual selling utilizes cloud-based POS platforms integrated with online payment gateways, enabling seamless digital transactions and customer data tracking across multiple channels. Explore how modern POS technologies bridge the gap between traditional and virtual sales environments.
Source and External Links
Retail - Retail selling is the sale of goods and services directly to consumers in smaller quantities, typically purchased from manufacturers or wholesalers to resell for profit, and involves strategic decisions like store type, product assortment, and customer service to effectively reach consumers.
Retail Sales Definition, Categories & Techniques - Lesson - Retail selling involves a multi-step process including opening the sale with friendly questions, probing to understand customer needs, product demonstration tied to those needs, handling objections, and closing the sale to meet customers' personal consumption goals.
Boost Your Store's Sales With These 11 Retail Sales Tips - Effective retail selling also depends on customer engagement skills such as greeting warmly, creating authentic connections, handling objections skillfully, and avoiding directing customers to online ordering when they are physically present to maximize the chance of in-store sales.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com