Circular retail focuses on closing the product lifecycle loop by promoting reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing to minimize waste and extend the value of products. Sustainable retail encompasses broader practices that reduce environmental impact through energy efficiency, ethical sourcing, and reduced carbon emissions across the supply chain. Explore how these innovative retail models transform consumer behavior and drive eco-friendly market growth.
Why it is important
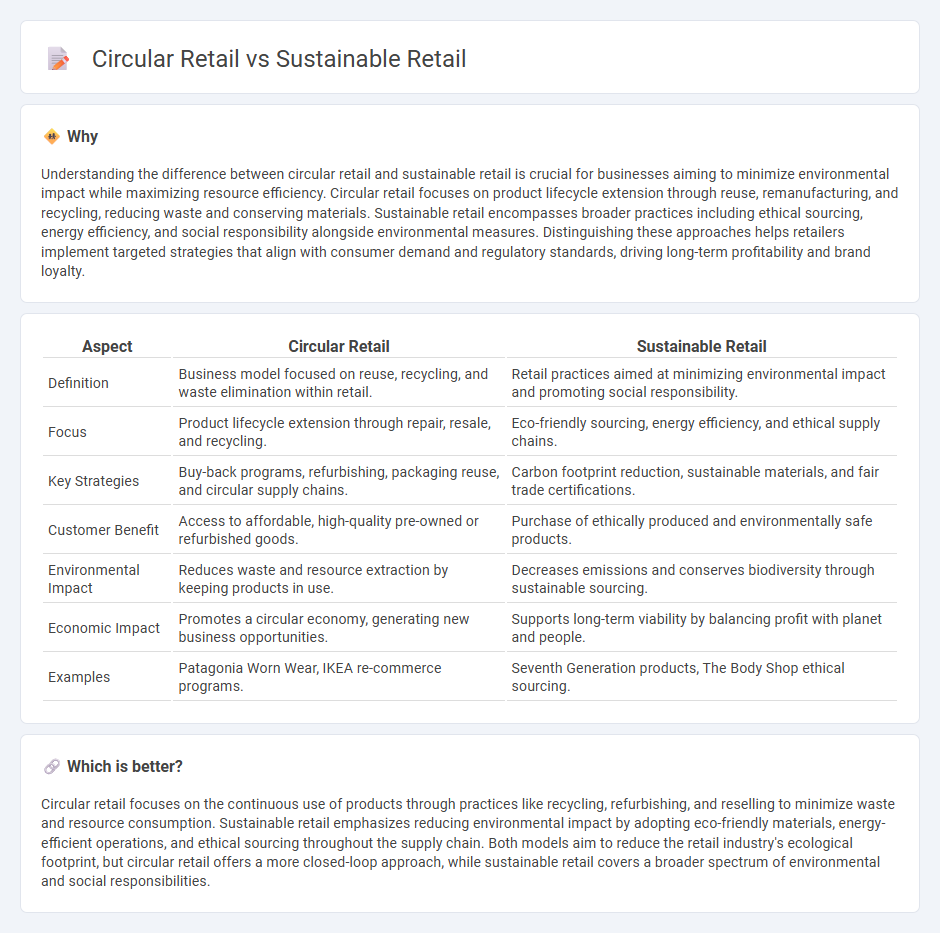
Understanding the difference between circular retail and sustainable retail is crucial for businesses aiming to minimize environmental impact while maximizing resource efficiency. Circular retail focuses on product lifecycle extension through reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling, reducing waste and conserving materials. Sustainable retail encompasses broader practices including ethical sourcing, energy efficiency, and social responsibility alongside environmental measures. Distinguishing these approaches helps retailers implement targeted strategies that align with consumer demand and regulatory standards, driving long-term profitability and brand loyalty.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Retail | Sustainable Retail |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business model focused on reuse, recycling, and waste elimination within retail. | Retail practices aimed at minimizing environmental impact and promoting social responsibility. |
| Focus | Product lifecycle extension through repair, resale, and recycling. | Eco-friendly sourcing, energy efficiency, and ethical supply chains. |
| Key Strategies | Buy-back programs, refurbishing, packaging reuse, and circular supply chains. | Carbon footprint reduction, sustainable materials, and fair trade certifications. |
| Customer Benefit | Access to affordable, high-quality pre-owned or refurbished goods. | Purchase of ethically produced and environmentally safe products. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and resource extraction by keeping products in use. | Decreases emissions and conserves biodiversity through sustainable sourcing. |
| Economic Impact | Promotes a circular economy, generating new business opportunities. | Supports long-term viability by balancing profit with planet and people. |
| Examples | Patagonia Worn Wear, IKEA re-commerce programs. | Seventh Generation products, The Body Shop ethical sourcing. |
Which is better?
Circular retail focuses on the continuous use of products through practices like recycling, refurbishing, and reselling to minimize waste and resource consumption. Sustainable retail emphasizes reducing environmental impact by adopting eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient operations, and ethical sourcing throughout the supply chain. Both models aim to reduce the retail industry's ecological footprint, but circular retail offers a more closed-loop approach, while sustainable retail covers a broader spectrum of environmental and social responsibilities.
Connection
Circular retail and sustainable retail are intrinsically linked through their shared focus on minimizing waste and promoting resource efficiency in the retail industry. Circular retail emphasizes the reuse, refurbishment, and recycling of products to extend their lifecycle, directly supporting sustainable retail's broader goals of reducing environmental impact and conserving natural resources. Both approaches foster a resilient economy by encouraging responsible consumption and production patterns aligned with global sustainability targets.
Key Terms
Resource Efficiency
Sustainable retail emphasizes reducing environmental impact by minimizing waste, energy use, and emissions across the supply chain. Circular retail prioritizes resource efficiency through product lifecycle extension, recycling, and reuse to create a closed-loop system. Explore how these approaches transform retail practices for better resource management and environmental benefits.
Product Lifecycle
Sustainable retail emphasizes minimizing environmental impact through eco-friendly sourcing, energy-efficient operations, and waste reduction across the product lifecycle. Circular retail prioritizes product design for durability, reuse, repair, and recycling to extend the lifecycle and promote a closed-loop system. Explore how these approaches transform retail sustainability by enhancing product lifecycle management.
Waste Reduction
Sustainable retail prioritizes minimizing environmental impact by adopting eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient operations, while circular retail emphasizes a closed-loop system that extends product life through reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing. Waste reduction in circular retail is achieved by designing products for durability and recoverability, significantly decreasing landfill contributions compared to traditional sustainable practices. Explore how these strategies transform retail performance and reduce waste footprints.
Source and External Links
A Guide to Sustainable Retail Industry 2025 - Carbon Trail - Sustainable retail involves setting clear goals like reducing carbon emissions and using recycled packaging, integrating sustainability across operations, and engaging employees, suppliers, and customers to support eco-friendly initiatives.
Sustainable Retail - Salsify - Sustainable retail means retail businesses adopt processes that do not harm the environment, focusing on eco-friendly product manufacturing, shipping, and selling to reduce carbon emissions and waste while appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Sustainable Retail | Everything You Need to Know - CleanHub's Blog - Sustainable retail broadly means selling products with a lower environmental impact, embedding environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles into business operations for long-term eco-friendly success.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com