Phantom inventory occurs when stock records show items as available despite physical absence, often caused by data errors or theft, impacting accurate demand forecasting and sales. Misplaced inventory refers to products physically present but incorrectly shelved or recorded, leading to fulfillment delays and reduced operational efficiency. Explore deeper insights on managing inventory challenges to optimize retail performance.
Why it is important
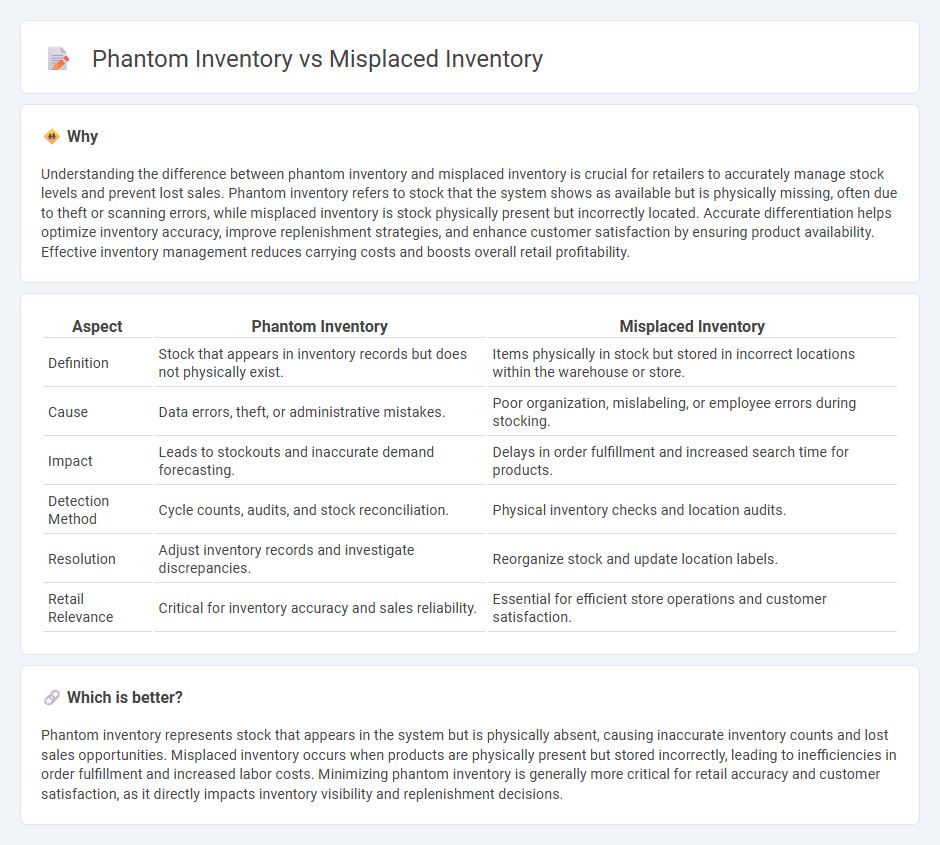
Understanding the difference between phantom inventory and misplaced inventory is crucial for retailers to accurately manage stock levels and prevent lost sales. Phantom inventory refers to stock that the system shows as available but is physically missing, often due to theft or scanning errors, while misplaced inventory is stock physically present but incorrectly located. Accurate differentiation helps optimize inventory accuracy, improve replenishment strategies, and enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability. Effective inventory management reduces carrying costs and boosts overall retail profitability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Phantom Inventory | Misplaced Inventory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stock that appears in inventory records but does not physically exist. | Items physically in stock but stored in incorrect locations within the warehouse or store. |
| Cause | Data errors, theft, or administrative mistakes. | Poor organization, mislabeling, or employee errors during stocking. |
| Impact | Leads to stockouts and inaccurate demand forecasting. | Delays in order fulfillment and increased search time for products. |
| Detection Method | Cycle counts, audits, and stock reconciliation. | Physical inventory checks and location audits. |
| Resolution | Adjust inventory records and investigate discrepancies. | Reorganize stock and update location labels. |
| Retail Relevance | Critical for inventory accuracy and sales reliability. | Essential for efficient store operations and customer satisfaction. |
Which is better?
Phantom inventory represents stock that appears in the system but is physically absent, causing inaccurate inventory counts and lost sales opportunities. Misplaced inventory occurs when products are physically present but stored incorrectly, leading to inefficiencies in order fulfillment and increased labor costs. Minimizing phantom inventory is generally more critical for retail accuracy and customer satisfaction, as it directly impacts inventory visibility and replenishment decisions.
Connection
Phantom inventory and misplaced inventory both contribute to inventory inaccuracies that disrupt retail operations and reduce sales. Phantom inventory occurs when stock records show items available that do not physically exist, often due to theft, damage, or data entry errors, while misplaced inventory refers to items physically present but stored in incorrect locations, making them effectively invisible to inventory systems. Together, these issues lead to stockouts, overstocking, and inefficient inventory management, increasing operational costs and negatively impacting customer satisfaction.
Key Terms
Stock Accuracy
Misplaced inventory refers to items physically present in the warehouse but stored in incorrect locations, leading to difficulties in accurate stock retrieval and inefficient order fulfillment. Phantom inventory occurs when inventory records indicate stock availability that does not exist physically, often caused by data entry errors or theft, resulting in discrepancies between system data and actual stock. Understanding the differences between misplaced and phantom inventory is crucial for improving stock accuracy; explore effective strategies to optimize inventory management and enhance operational efficiency.
Inventory Shrinkage
Misplaced inventory refers to products physically present in the warehouse but stored in incorrect locations, causing discrepancies during stock counts and leading to inventory shrinkage. Phantom inventory represents items that appear in the system but are missing physically due to theft, damage, or miscounting, further exacerbating shrinkage issues. Explore effective strategies to reduce inventory shrinkage by addressing both misplaced and phantom inventory.
Out-of-Stock
Misplaced inventory occurs when products are physically present but stored in incorrect locations, leading to inaccurate stock counts that complicate inventory management. Phantom inventory refers to stock that appears available in the system but is actually nonexistent due to errors like theft, miscounts, or data entry mistakes, causing false stock availability. Discover more about how addressing these inventory issues can optimize out-of-stock reductions and improve supply chain efficiency.
Source and External Links
10 Causes of Inventory Discrepancies and How to Prevent Them - Misplaced inventory is when items are physically present in a warehouse but cannot be located, often due to poor storage procedures, inconsistent adherence to protocols, incorrect placement by staff, failure to update systems, inadequate labeling, or changes in warehouse layout not communicated to employees.
Inventory Discrepancy & How to Prevent It - Extensiv - Misplaced inventory occurs when items are stored incorrectly in the wrong location within a warehouse or fulfillment center, causing discrepancies between actual and recorded inventory counts, commonly due to human error and inefficiencies in warehouse management.
Identifying and preventing inventory discrepancy - Red Stag Fulfillment - Misplaced inventory can also happen when items sit unlogged on receiving docks or are moved wrongly within the warehouse, arising from challenges in tracking SKUs across the supply chain and warehousing processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com