Micro fulfillment centers utilize compact spaces within urban areas to enable rapid order processing and last-mile delivery, enhancing customer satisfaction through faster shipping times. Traditional distribution centers operate on a larger scale, focusing on bulk storage and regional distribution, which supports extensive inventory management but often results in longer delivery windows. Explore the advantages and applications of both models to optimize your retail supply chain strategy.
Why it is important
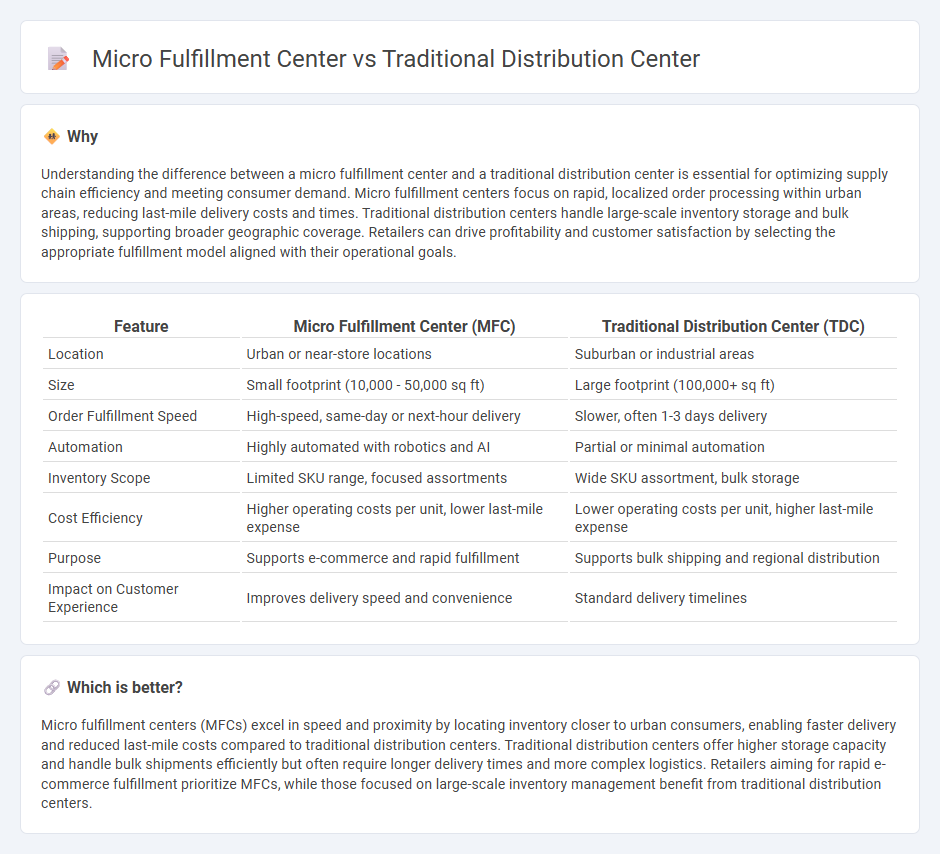
Understanding the difference between a micro fulfillment center and a traditional distribution center is essential for optimizing supply chain efficiency and meeting consumer demand. Micro fulfillment centers focus on rapid, localized order processing within urban areas, reducing last-mile delivery costs and times. Traditional distribution centers handle large-scale inventory storage and bulk shipping, supporting broader geographic coverage. Retailers can drive profitability and customer satisfaction by selecting the appropriate fulfillment model aligned with their operational goals.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Micro Fulfillment Center (MFC) | Traditional Distribution Center (TDC) |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Urban or near-store locations | Suburban or industrial areas |
| Size | Small footprint (10,000 - 50,000 sq ft) | Large footprint (100,000+ sq ft) |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | High-speed, same-day or next-hour delivery | Slower, often 1-3 days delivery |
| Automation | Highly automated with robotics and AI | Partial or minimal automation |
| Inventory Scope | Limited SKU range, focused assortments | Wide SKU assortment, bulk storage |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operating costs per unit, lower last-mile expense | Lower operating costs per unit, higher last-mile expense |
| Purpose | Supports e-commerce and rapid fulfillment | Supports bulk shipping and regional distribution |
| Impact on Customer Experience | Improves delivery speed and convenience | Standard delivery timelines |
Which is better?
Micro fulfillment centers (MFCs) excel in speed and proximity by locating inventory closer to urban consumers, enabling faster delivery and reduced last-mile costs compared to traditional distribution centers. Traditional distribution centers offer higher storage capacity and handle bulk shipments efficiently but often require longer delivery times and more complex logistics. Retailers aiming for rapid e-commerce fulfillment prioritize MFCs, while those focused on large-scale inventory management benefit from traditional distribution centers.
Connection
Micro fulfillment centers streamline last-mile delivery by using automation and proximity to urban customers, reducing lead times and transportation costs. Traditional distribution centers serve as large-scale hubs that stock bulk inventory and supply micro fulfillment centers with a wide range of products. The integration between these two enables retailers to enhance supply chain efficiency, balance inventory management, and improve customer satisfaction through faster order fulfillment.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Traditional distribution centers typically manage large-scale inventories with bulk storage, supporting longer replenishment cycles and broad product assortments, optimizing for cost efficiency. Micro fulfillment centers employ advanced automation and real-time inventory tracking to handle smaller, more precise stock quantities closer to the customer, enabling faster order fulfillment and reducing last-mile delivery costs. Explore how these inventory management strategies impact supply chain agility and customer satisfaction in modern retail.
Order Processing Speed
Traditional distribution centers generally handle large volumes of inventory but often experience longer order processing times due to complex sorting and shipping procedures. Micro fulfillment centers optimize order processing speed by using automation and proximity to end customers, reducing delivery times significantly. Explore the distinct operational benefits of each to determine the best fit for your supply chain needs.
Facility Size
Traditional distribution centers typically span hundreds of thousands of square feet, designed to store extensive inventory and support long-haul shipping routes. Micro fulfillment centers are compact, often under 10,000 square feet, strategically placed near urban or high-demand areas to enable rapid order processing and last-mile delivery efficiency. Explore the benefits and optimal use cases of each facility type to boost your supply chain strategy.
Source and External Links
Differences Between Distribution Centers & Fulfillment Centers - Traditional distribution centers act as large centralized hubs for bulk storage and distribution of goods to retail outlets or other DCs, focusing on high-volume storage and transportation efficiency within supply chains.
Distribution Center vs Warehouse: Key Differences Explained - Traditional warehouses emphasize long-term bulk storage, while distribution centers provide short-term storage combined with order fulfillment operations like picking, packing, and shipping to quickly move goods through the supply chain.
Distribution Centers Explained - Distribution centers store finished goods before picking and packing them for customer orders, often engaging in activities like cross-docking, order fulfillment, and distribution management to optimize delivery speed and efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com