Hyperlocal fulfillment focuses on delivering products within a limited geographic area, often leveraging local stores to expedite order processing and reduce last-mile delivery times. Micro-fulfillment centers are compact, technology-driven warehouses located near urban markets that optimize inventory management and accelerate shipping for e-commerce retailers. Explore the key differences and benefits of hyperlocal fulfillment versus micro-fulfillment centers for your retail strategy.
Why it is important
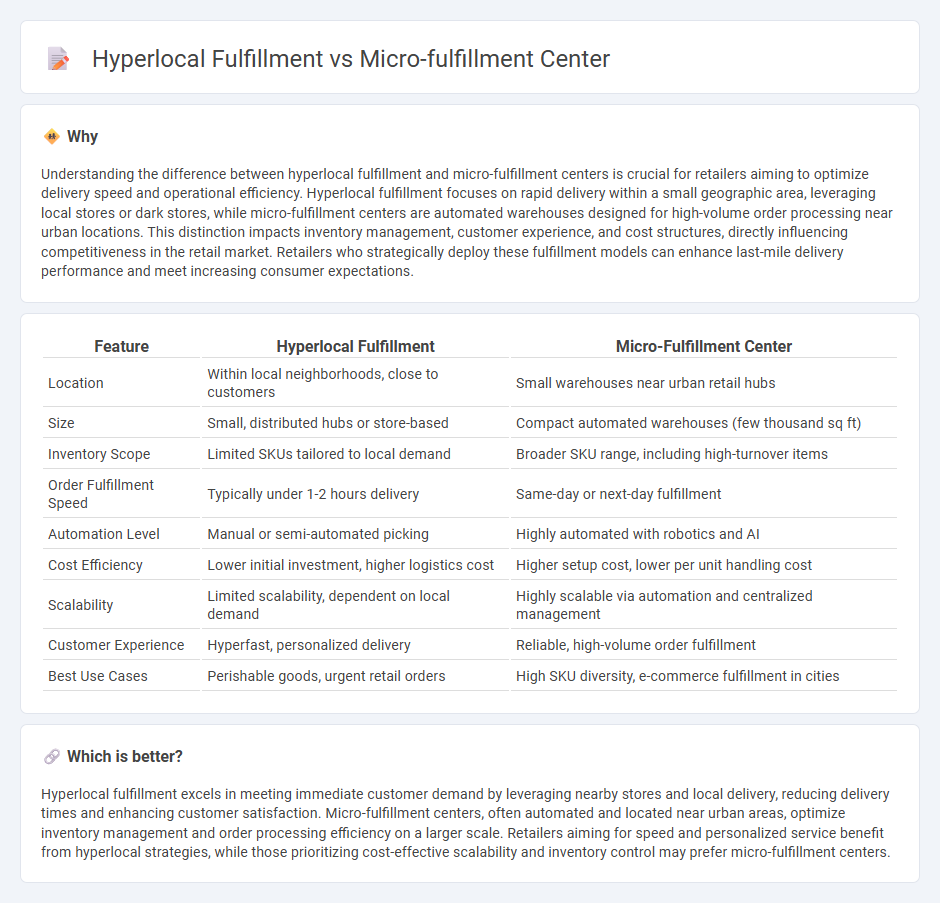
Understanding the difference between hyperlocal fulfillment and micro-fulfillment centers is crucial for retailers aiming to optimize delivery speed and operational efficiency. Hyperlocal fulfillment focuses on rapid delivery within a small geographic area, leveraging local stores or dark stores, while micro-fulfillment centers are automated warehouses designed for high-volume order processing near urban locations. This distinction impacts inventory management, customer experience, and cost structures, directly influencing competitiveness in the retail market. Retailers who strategically deploy these fulfillment models can enhance last-mile delivery performance and meet increasing consumer expectations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Hyperlocal Fulfillment | Micro-Fulfillment Center |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Within local neighborhoods, close to customers | Small warehouses near urban retail hubs |
| Size | Small, distributed hubs or store-based | Compact automated warehouses (few thousand sq ft) |
| Inventory Scope | Limited SKUs tailored to local demand | Broader SKU range, including high-turnover items |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | Typically under 1-2 hours delivery | Same-day or next-day fulfillment |
| Automation Level | Manual or semi-automated picking | Highly automated with robotics and AI |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial investment, higher logistics cost | Higher setup cost, lower per unit handling cost |
| Scalability | Limited scalability, dependent on local demand | Highly scalable via automation and centralized management |
| Customer Experience | Hyperfast, personalized delivery | Reliable, high-volume order fulfillment |
| Best Use Cases | Perishable goods, urgent retail orders | High SKU diversity, e-commerce fulfillment in cities |
Which is better?
Hyperlocal fulfillment excels in meeting immediate customer demand by leveraging nearby stores and local delivery, reducing delivery times and enhancing customer satisfaction. Micro-fulfillment centers, often automated and located near urban areas, optimize inventory management and order processing efficiency on a larger scale. Retailers aiming for speed and personalized service benefit from hyperlocal strategies, while those prioritizing cost-effective scalability and inventory control may prefer micro-fulfillment centers.
Connection
Hyperlocal fulfillment relies on micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) strategically located near urban centers to enable rapid order processing and same-day delivery. These micro-fulfillment centers utilize automated systems to optimize inventory management and streamline last-mile logistics, reducing delivery times and costs for retailers. The integration of MFCs in hyperlocal fulfillment enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability and swift fulfillment within localized markets.
Key Terms
Proximity
Micro-fulfillment centers are compact warehouses strategically located near urban areas to enable rapid order processing and delivery, significantly reducing shipping time and costs. Hyperlocal fulfillment leverages these centers alongside local stores to provide ultra-fast delivery within a small geographic radius, often within hours. Discover how optimizing proximity transforms supply chains and enhances customer satisfaction in the evolving landscape of e-commerce fulfillment.
Automation
Micro-fulfillment centers leverage advanced automation technologies such as robots and AI-driven inventory management to expedite order processing within compact urban warehouses. Hyperlocal fulfillment emphasizes rapid delivery within a limited geographic area, often integrating automated sorting systems and real-time data analytics to optimize routes and reduce last-mile delivery times. Explore these innovative automation strategies to enhance supply chain efficiency and meet rising consumer expectations.
Order Volume
Micro-fulfillment centers handle high order volumes by leveraging automated systems in compact urban warehouses, maximizing processing speed and efficiency. Hyperlocal fulfillment prioritizes smaller order batches with rapid delivery within a localized area, optimizing for immediacy rather than scale. Explore in-depth comparisons to determine which fulfillment strategy best suits your business's order volume demands.
Source and External Links
What Are Micro Fulfillment Centers? - City National Bank - Micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) are compact warehouses, typically 3,000 to 10,000 square feet, holding up to 15,000 items for rapid shipping, often using robots or human pickers to fulfill fast-moving product orders near consumers, which enables quicker inventory turnover than traditional distribution centers.
Micro fulfillment center: How it helps retailers speed up fulfillment - MFCs are small-scale fulfillment facilities located close to urban consumers to accelerate order fulfillment, often integrated into existing stores or small spaces, storing about 24-48 hours of inventory and equipped with automation to improve efficiency.
The Rise of Micro-Fulfillment Centers - Averitt - Positioned in urban areas near consumers, micro-fulfillment centers reduce delivery distances and costs by serving as spokes within a hub-and-spoke supply chain, requiring less real estate and enabling faster, cheaper last-mile delivery and in-store pickup options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com