Ship from store leverages existing retail locations to fulfill online orders quickly, reducing delivery times and shipping costs. Drop shipping allows retailers to sell products without holding inventory by coordinating directly with suppliers who ship goods to customers. Explore how these fulfillment methods can optimize your retail strategy and enhance customer satisfaction.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Ship from Store and Drop Shipping is crucial for optimizing inventory management and reducing delivery times in retail operations. Ship from Store uses existing brick-and-mortar stores as distribution centers, enhancing local fulfillment speed. Drop Shipping allows retailers to sell products without holding inventory, relying on suppliers to ship directly to customers, which lowers overhead costs but can affect control over delivery quality. Retailers leveraging these models strategically can improve customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
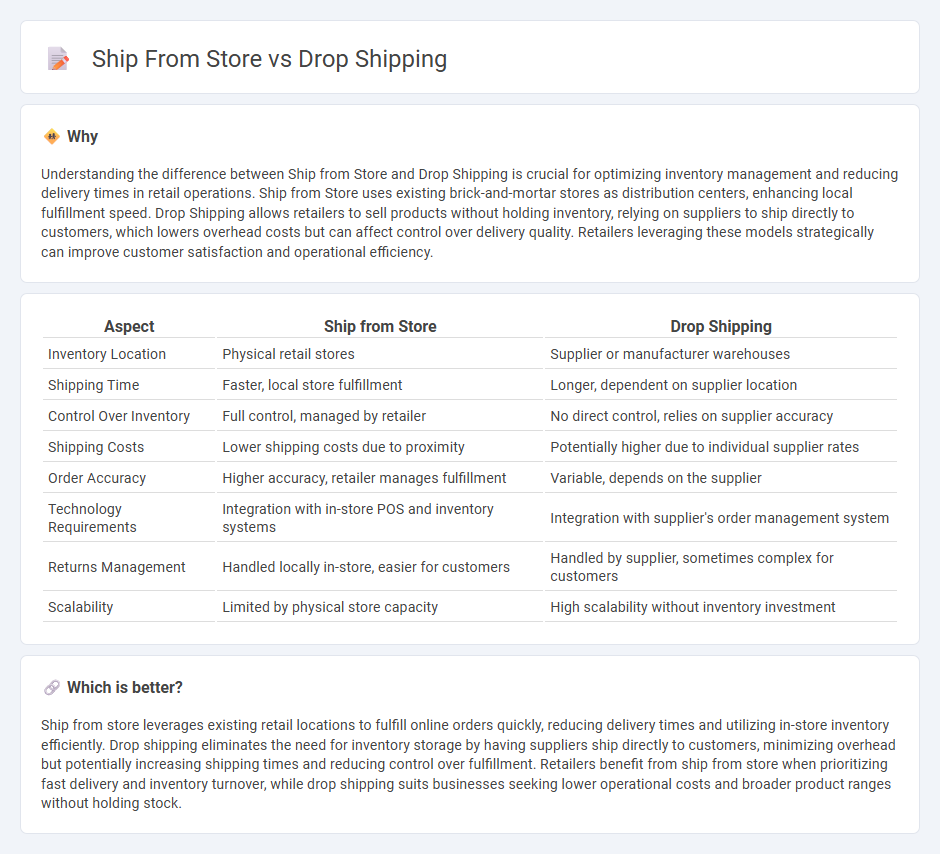
| Aspect | Ship from Store | Drop Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Location | Physical retail stores | Supplier or manufacturer warehouses |
| Shipping Time | Faster, local store fulfillment | Longer, dependent on supplier location |
| Control Over Inventory | Full control, managed by retailer | No direct control, relies on supplier accuracy |
| Shipping Costs | Lower shipping costs due to proximity | Potentially higher due to individual supplier rates |
| Order Accuracy | Higher accuracy, retailer manages fulfillment | Variable, depends on the supplier |
| Technology Requirements | Integration with in-store POS and inventory systems | Integration with supplier's order management system |
| Returns Management | Handled locally in-store, easier for customers | Handled by supplier, sometimes complex for customers |
| Scalability | Limited by physical store capacity | High scalability without inventory investment |
Which is better?
Ship from store leverages existing retail locations to fulfill online orders quickly, reducing delivery times and utilizing in-store inventory efficiently. Drop shipping eliminates the need for inventory storage by having suppliers ship directly to customers, minimizing overhead but potentially increasing shipping times and reducing control over fulfillment. Retailers benefit from ship from store when prioritizing fast delivery and inventory turnover, while drop shipping suits businesses seeking lower operational costs and broader product ranges without holding stock.
Connection
Ship from store and drop shipping both streamline retail logistics by enabling faster order fulfillment through distributed inventory sources. Ship from store leverages physical retail locations to dispatch products directly to customers, reducing delivery times and enhancing local inventory utilization. Drop shipping eliminates the need for holding stock by having suppliers ship items directly to buyers, complementing ship from store strategies to expand product availability without increasing retailer inventory costs.
Key Terms
Inventory Ownership
Drop shipping involves suppliers maintaining inventory and directly shipping products to customers, reducing the retailer's need to manage stock and warehousing expenses. Conversely, ship from store utilizes local retail locations to fulfill online orders, allowing stores to maintain control over inventory and enable faster delivery times. Explore further to understand the key benefits and challenges of inventory ownership in each fulfillment model.
Fulfillment Location
Drop shipping relies on suppliers shipping products directly to customers, eliminating the need for inventory storage and reducing fulfillment location constraints. Ship from store utilizes retail outlets as mini-warehouses, enabling faster delivery and localized inventory management by fulfilling orders near the customer. Explore the benefits and challenges of each fulfillment strategy to optimize your supply chain efficiency.
Delivery Speed
Drop shipping typically results in longer delivery times due to reliance on third-party suppliers and multiple handling points, whereas ship from store leverages local inventory to enable faster order fulfillment and same-day or next-day delivery. The ship from store model reduces transit distances and processing delays, improving customer satisfaction through quicker access to products. Explore how optimizing delivery speed with these methods can enhance your e-commerce strategy.
Source and External Links
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a retail business model where the seller accepts customer orders without holding inventory, instead forwarding orders to a supplier who ships directly to the customer, minimizing overhead and investment but reducing control over product quality and shipping.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Shopify Blog - Dropshipping involves partnering with suppliers who store, package, and ship directly to customers while the seller markets the products in their online store and forwards orders to the supplier, often with automation tools to streamline the process.
What Is dropshipping? How does it work in 2025? - Amazon Seller Central - Dropshipping lets entrepreneurs outsource product handling and shipping to a third party, focusing on sales and customer service but facing challenges in branding and profit margins due to competition and limited control over products.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com