Reverse showrooming involves customers visiting physical stores to examine products before purchasing them online for better deals, enhancing the in-store experience without immediate sales. Drop shipping is a retail fulfillment method where stores sell products without holding inventory, relying on third-party suppliers to ship directly to customers and reduce overhead costs. Discover how these strategies reshape the retail landscape by improving customer convenience and operational efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between reverse showrooming and dropshipping is crucial for retailers to optimize inventory management and enhance customer experience. Reverse showrooming involves customers researching products in-store but purchasing online, impacting in-store sales strategies. Dropshipping allows retailers to sell products without holding inventory, reducing overhead costs but requiring reliable supplier partnerships. Mastering these concepts helps businesses tailor marketing approaches and supply chain logistics effectively.
Comparison Table
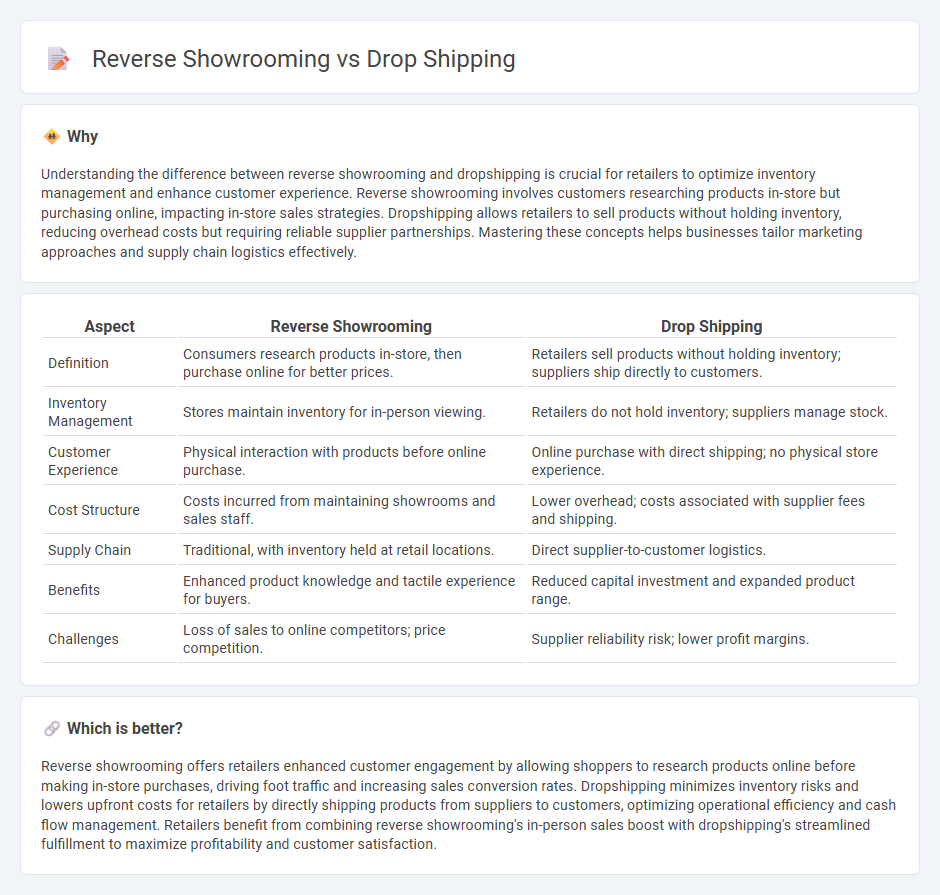
| Aspect | Reverse Showrooming | Drop Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consumers research products in-store, then purchase online for better prices. | Retailers sell products without holding inventory; suppliers ship directly to customers. |
| Inventory Management | Stores maintain inventory for in-person viewing. | Retailers do not hold inventory; suppliers manage stock. |
| Customer Experience | Physical interaction with products before online purchase. | Online purchase with direct shipping; no physical store experience. |
| Cost Structure | Costs incurred from maintaining showrooms and sales staff. | Lower overhead; costs associated with supplier fees and shipping. |
| Supply Chain | Traditional, with inventory held at retail locations. | Direct supplier-to-customer logistics. |
| Benefits | Enhanced product knowledge and tactile experience for buyers. | Reduced capital investment and expanded product range. |
| Challenges | Loss of sales to online competitors; price competition. | Supplier reliability risk; lower profit margins. |
Which is better?
Reverse showrooming offers retailers enhanced customer engagement by allowing shoppers to research products online before making in-store purchases, driving foot traffic and increasing sales conversion rates. Dropshipping minimizes inventory risks and lowers upfront costs for retailers by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, optimizing operational efficiency and cash flow management. Retailers benefit from combining reverse showrooming's in-person sales boost with dropshipping's streamlined fulfillment to maximize profitability and customer satisfaction.
Connection
Reverse showrooming, where customers research products in physical stores before purchasing online, boosts the demand for efficient drop shipping models that enable retailers to ship products directly from suppliers without holding inventory. Drop shipping supports reverse showrooming by allowing retailers to offer a wider product range online, leveraging supplier networks to fulfill orders quickly and reduce storage costs. This synergy enhances customer convenience and operational agility in the competitive retail landscape.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Drop shipping streamlines inventory management by eliminating the need for sellers to hold stock, relying instead on suppliers to fulfill orders directly to customers. Reverse showrooming requires retailers to maintain inventory levels for immediate in-store purchase while competing with online prices, demanding precise inventory forecasting and replenishment strategies. Explore the complexities of these models to enhance your inventory management and boost operational efficiency.
Customer Acquisition
Drop shipping and reverse showrooming represent contrasting strategies in customer acquisition, with drop shipping leveraging online order fulfillment directly from suppliers to customers, minimizing inventory costs and expanding product reach. Reverse showrooming involves customers researching products online but purchasing them in physical stores, emphasizing the integration of digital touchpoints with brick-and-mortar sales to drive foot traffic and conversions. Explore how mastering these models can optimize customer acquisition and boost revenue growth.
Fulfillment Model
Drop shipping relies on suppliers to directly ship products to customers, minimizing inventory management for retailers and optimizing fulfillment efficiency. Reverse showrooming involves customers researching products online but purchasing in-store, requiring seamless integration between online details and physical inventory availability. Explore more about how these fulfillment models impact customer experience and operational logistics.
Source and External Links
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a retail business model where the seller accepts customer orders without holding inventory, forwarding orders to a supplier who ships directly to the customer, reducing overhead and warehouse costs but with lower profit margins and less control over product quality and shipping.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Shopify - Dropshipping works by partnering with suppliers who handle inventory and shipping, while the seller creates an online store, sells products at their set prices, forwards orders to the supplier, and manages customer service with minimal upfront investment.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Wix.com - Dropshipping differs from traditional retail as the seller does not stock products but buys from a third party after orders are placed, outsourcing production, warehousing, and shipping to suppliers while focusing on managing their online store and sales.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com