Phantom inventory occurs when a product is recorded as in stock but is physically unavailable, leading to discrepancies in inventory management systems. Lost sales happen when customers cannot purchase products due to stockouts, directly impacting revenue and customer satisfaction. Explore the differences between phantom inventory and lost sales to optimize retail operations and improve profitability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between phantom inventory and lost sales is crucial for accurate inventory management and revenue forecasting in retail. Phantom inventory refers to stock that is recorded but not physically present, leading to discrepancies that can distort sales data and reorder decisions. Lost sales occur when demand exceeds available stock, resulting in missed revenue opportunities and potential customer churn. Accurate distinction helps retail managers optimize stock levels, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance profitability.
Comparison Table
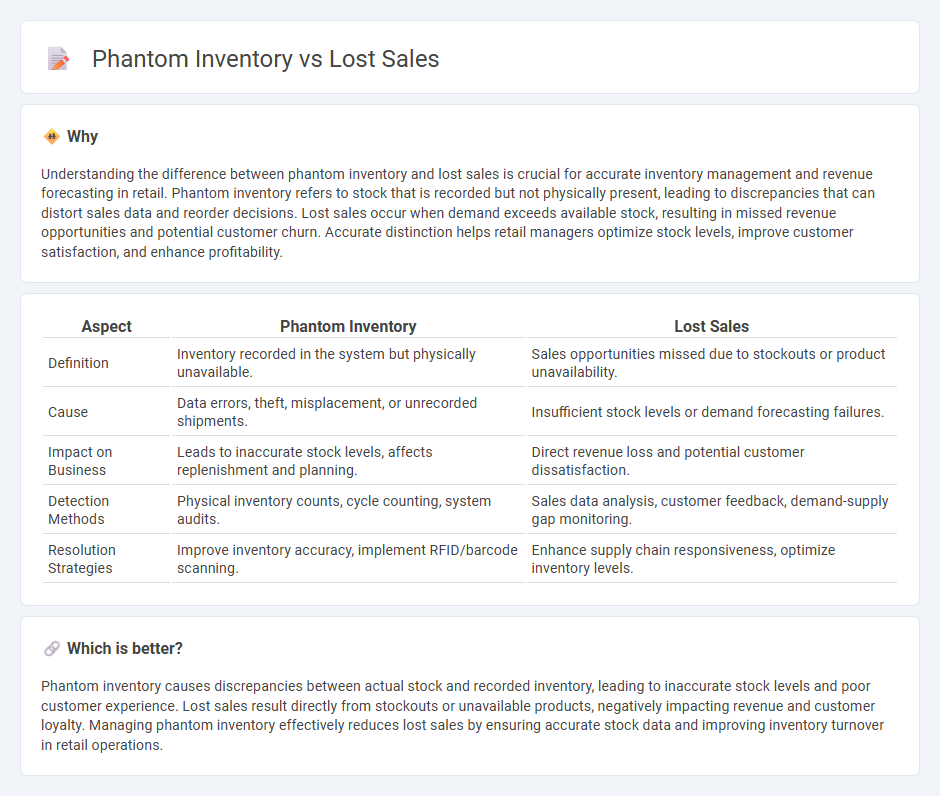
| Aspect | Phantom Inventory | Lost Sales |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inventory recorded in the system but physically unavailable. | Sales opportunities missed due to stockouts or product unavailability. |
| Cause | Data errors, theft, misplacement, or unrecorded shipments. | Insufficient stock levels or demand forecasting failures. |
| Impact on Business | Leads to inaccurate stock levels, affects replenishment and planning. | Direct revenue loss and potential customer dissatisfaction. |
| Detection Methods | Physical inventory counts, cycle counting, system audits. | Sales data analysis, customer feedback, demand-supply gap monitoring. |
| Resolution Strategies | Improve inventory accuracy, implement RFID/barcode scanning. | Enhance supply chain responsiveness, optimize inventory levels. |
Which is better?
Phantom inventory causes discrepancies between actual stock and recorded inventory, leading to inaccurate stock levels and poor customer experience. Lost sales result directly from stockouts or unavailable products, negatively impacting revenue and customer loyalty. Managing phantom inventory effectively reduces lost sales by ensuring accurate stock data and improving inventory turnover in retail operations.
Connection
Phantom inventory occurs when retail systems show stock available, but physical products are missing, leading to inaccurate inventory data. This discrepancy causes lost sales as customers cannot purchase the items they believe are in stock. Effective inventory management systems integrating real-time data and regular audits help minimize phantom inventory and reduce lost sales in retail operations.
Key Terms
Stockouts
Stockouts play a critical role in both lost sales and phantom inventory by causing missed revenue opportunities and misleading stock records, respectively. Lost sales occur when customers abandon purchases due to empty shelves, while phantom inventory results from discrepancies in stock counts that mask true product availability. Explore how understanding stockout dynamics can enhance inventory accuracy and boost sales performance.
Inventory accuracy
Lost sales occur when customers cannot purchase products due to stockouts, while phantom inventory refers to discrepancies between recorded and actual stock levels causing inventory inaccuracies. High inventory accuracy reduces lost sales by ensuring real-time stock visibility and precise replenishment, minimizing both overstock and stockouts. Explore effective strategies to enhance inventory accuracy and boost sales performance.
Point-of-Sale data
Lost sales arise when products are unavailable on shelves despite demand, causing customers to leave without purchases, while phantom inventory refers to discrepancies between system records and actual stock levels due to errors or theft. Accurate Point-of-Sale (POS) data helps identify true lost sales by reflecting real-time transactions and highlighting inventory inaccuracies influencing buying behavior. Discover how leveraging advanced POS analytics enhances inventory management and reduces lost revenue.
Source and External Links
Lost Sales Analysis: Causes, Strategies, and Solutions | Intuendi - Lost sales occur when potential transactions fail to materialize due to stockouts, pricing issues, or unmet customer needs, leading to direct revenue losses and impacting profitability, customer loyalty, and operational efficiency.
How to Avoid Lost Sales Opportunities - Inventory Planner - Lost sales happen mainly due to stockouts, overstock of slow-moving products, inadequate product information, and pricing or feature mismatches, resulting in revenue loss, increased cost per sale, and damage to customer lifetime value and brand reputation.
Lost Sales Definition and Meaning - Buske Logistics - Lost sales are missed sales opportunities caused by stockouts, pricing errors, or order fulfillment issues, which reduce revenue, customer satisfaction, and can harm business reputation, and can be mitigated through better demand forecasting and inventory management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com