Microfulfillment centers enhance retail efficiency by enabling rapid order processing and localized inventory management, reducing delivery times and costs. Dropshipping offers a low-risk retail model by allowing sellers to market products without holding inventory, relying on suppliers to ship directly to customers. Explore the advantages and challenges of microfulfillment and dropshipping to determine the best strategy for your retail business.
Why it is important
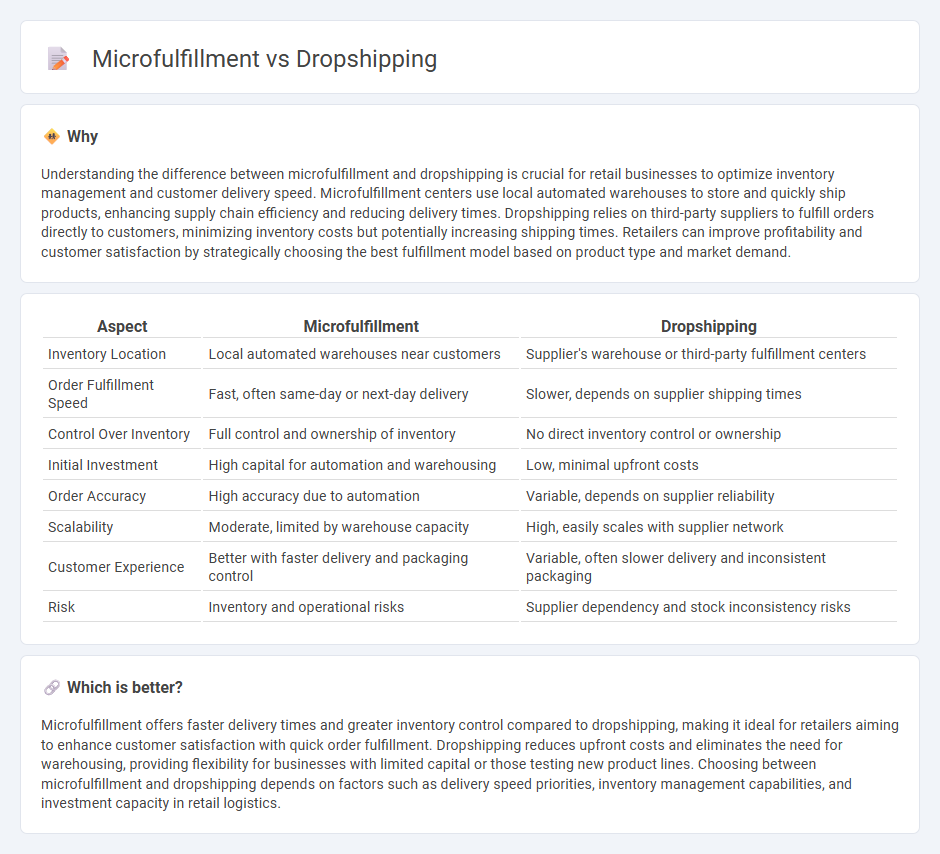
Understanding the difference between microfulfillment and dropshipping is crucial for retail businesses to optimize inventory management and customer delivery speed. Microfulfillment centers use local automated warehouses to store and quickly ship products, enhancing supply chain efficiency and reducing delivery times. Dropshipping relies on third-party suppliers to fulfill orders directly to customers, minimizing inventory costs but potentially increasing shipping times. Retailers can improve profitability and customer satisfaction by strategically choosing the best fulfillment model based on product type and market demand.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microfulfillment | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Location | Local automated warehouses near customers | Supplier's warehouse or third-party fulfillment centers |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | Fast, often same-day or next-day delivery | Slower, depends on supplier shipping times |
| Control Over Inventory | Full control and ownership of inventory | No direct inventory control or ownership |
| Initial Investment | High capital for automation and warehousing | Low, minimal upfront costs |
| Order Accuracy | High accuracy due to automation | Variable, depends on supplier reliability |
| Scalability | Moderate, limited by warehouse capacity | High, easily scales with supplier network |
| Customer Experience | Better with faster delivery and packaging control | Variable, often slower delivery and inconsistent packaging |
| Risk | Inventory and operational risks | Supplier dependency and stock inconsistency risks |
Which is better?
Microfulfillment offers faster delivery times and greater inventory control compared to dropshipping, making it ideal for retailers aiming to enhance customer satisfaction with quick order fulfillment. Dropshipping reduces upfront costs and eliminates the need for warehousing, providing flexibility for businesses with limited capital or those testing new product lines. Choosing between microfulfillment and dropshipping depends on factors such as delivery speed priorities, inventory management capabilities, and investment capacity in retail logistics.
Connection
Microfulfillment centers enhance retail efficiency by enabling rapid order processing close to urban customers, which complements dropshipping's model of direct product shipment from suppliers to consumers without holding inventory. Together, these logistics strategies optimize supply chain responsiveness and reduce delivery times, improving customer satisfaction in e-commerce. Integrating microfulfillment with dropshipping supports retailers in managing inventory risks while scaling operations quickly.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Dropshipping eliminates inventory holding by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, minimizing storage costs and reducing risk. Microfulfillment centers utilize automated warehouses close to urban areas to store and rapidly ship products, enhancing delivery speed and inventory control. Explore more to understand which inventory strategy best suits your business needs.
Order Fulfillment
Dropshipping relies on third-party suppliers to handle inventory and directly ship products to customers, reducing the need for extensive warehousing but potentially increasing delivery times. Microfulfillment centers use automated, compact warehouses located near urban areas to accelerate order processing and enhance customer experience with faster delivery. Explore the advantages and challenges of both models to determine the best order fulfillment strategy for your business.
Supply Chain Integration
Dropshipping minimizes inventory costs by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, streamlining supply chain integration through reduced handling stages. Microfulfillment centers, strategically located near urban areas, enable rapid order processing and last-mile delivery by integrating automated warehousing with local logistics networks. Explore how these supply chain strategies enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Source and External Links
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment model where the seller doesn't keep inventory but purchases items from a third-party supplier to ship directly to the customer, allowing the seller to focus on marketing and sales without handling inventory or shipping.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Dropshipping involves partnering with suppliers who store and ship products directly to customers, while the retailer sets retail prices and manages the online store, often using apps to automate order forwarding and updates.
Drop shipping - Drop shipping is a supply chain management method where the seller accepts orders but transfers them to manufacturers or wholesalers who then ship directly to the customer, minimizing inventory costs and storefront needs for the seller but reducing control over product quality and shipping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com