Sensory retail leverages multisensory experiences to engage customers through sight, sound, touch, smell, and taste, creating immersive physical store environments that enhance brand loyalty and increase purchase likelihood. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) retail bypasses traditional distribution channels by selling products directly online, enabling brands to control customer data, personalize marketing, and offer competitive pricing. Explore how integrating sensory elements with DTC strategies can revolutionize customer engagement and drive sales growth.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sensory retail and direct-to-consumer retail is crucial for tailoring customer experiences and optimizing sales strategies. Sensory retail emphasizes engaging customers through physical senses like sight, touch, and smell, enhancing in-store interaction and brand loyalty. Direct-to-consumer retail focuses on online sales channels, removing intermediaries to offer personalized products and streamline purchase processes. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses allocate resources effectively and meet evolving consumer expectations.
Comparison Table
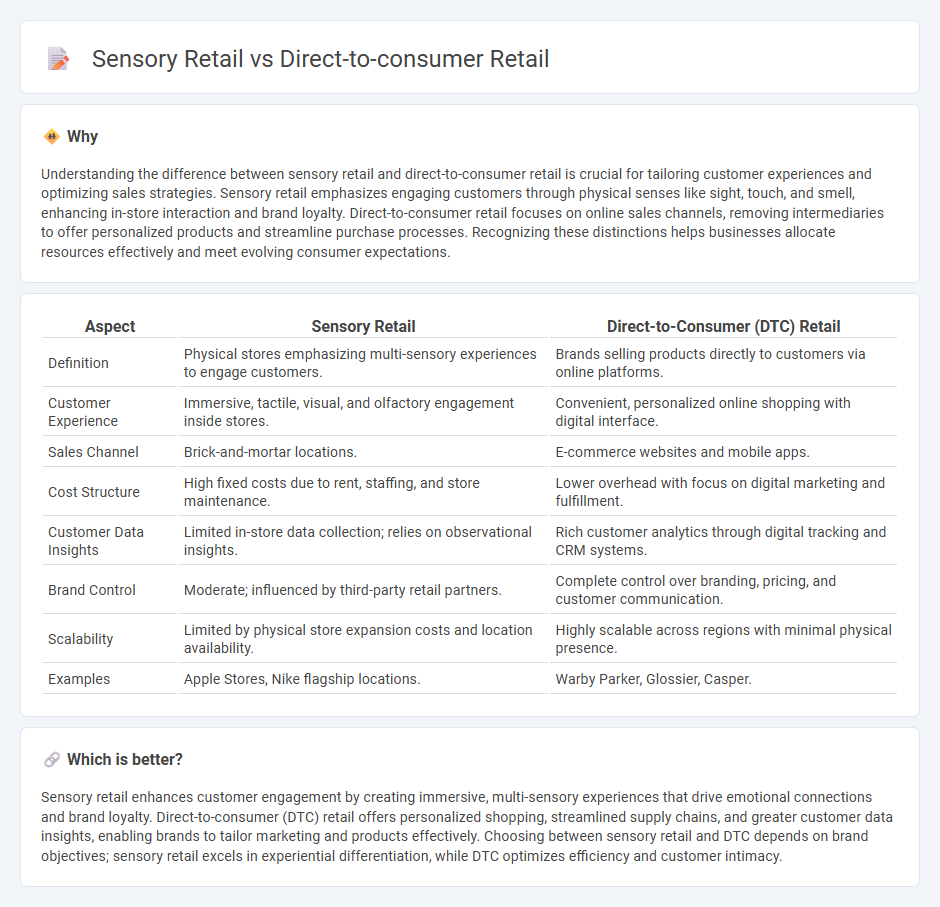
| Aspect | Sensory Retail | Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Retail |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical stores emphasizing multi-sensory experiences to engage customers. | Brands selling products directly to customers via online platforms. |
| Customer Experience | Immersive, tactile, visual, and olfactory engagement inside stores. | Convenient, personalized online shopping with digital interface. |
| Sales Channel | Brick-and-mortar locations. | E-commerce websites and mobile apps. |
| Cost Structure | High fixed costs due to rent, staffing, and store maintenance. | Lower overhead with focus on digital marketing and fulfillment. |
| Customer Data Insights | Limited in-store data collection; relies on observational insights. | Rich customer analytics through digital tracking and CRM systems. |
| Brand Control | Moderate; influenced by third-party retail partners. | Complete control over branding, pricing, and customer communication. |
| Scalability | Limited by physical store expansion costs and location availability. | Highly scalable across regions with minimal physical presence. |
| Examples | Apple Stores, Nike flagship locations. | Warby Parker, Glossier, Casper. |
Which is better?
Sensory retail enhances customer engagement by creating immersive, multi-sensory experiences that drive emotional connections and brand loyalty. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) retail offers personalized shopping, streamlined supply chains, and greater customer data insights, enabling brands to tailor marketing and products effectively. Choosing between sensory retail and DTC depends on brand objectives; sensory retail excels in experiential differentiation, while DTC optimizes efficiency and customer intimacy.
Connection
Sensory retail enhances the direct-to-consumer (DTC) model by creating immersive, multi-sensory experiences that deepen brand engagement and foster customer loyalty. DTC brands leverage sensory elements such as touch, scent, and sound to differentiate their products and build emotional connections in the absence of traditional retail environments. Integrating sensory retail strategies into DTC channels drives higher conversion rates and strengthens personalized consumer relationships.
Key Terms
**Direct-to-Consumer Retail:**
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) retail revolutionizes traditional shopping by enabling brands to sell directly to customers without intermediaries, maximizing profit margins and fostering personalized customer relationships. This model leverages e-commerce platforms, data analytics, and targeted marketing to deliver tailored experiences and streamline the purchasing process. Explore how DTC strategies can transform your business by enhancing customer engagement and driving sustainable growth.
E-commerce
Direct-to-consumer retail in e-commerce leverages personalized online platforms to build direct relationships, enhance customer data insights, and reduce costs by bypassing traditional intermediaries. Sensory retail integrates multisensory experiences, such as augmented reality and immersive product showcases, to engage customers more deeply and simulate physical interactions within virtual environments. Explore how these approaches transform online shopping dynamics and elevate consumer engagement.
Brand Ownership
Direct-to-consumer retail emphasizes complete brand ownership by controlling manufacturing, marketing, and sales channels, enabling personalized customer experiences and higher profit margins. Sensory retail focuses on enhancing brand ownership through immersive, multi-sensory store environments that strengthen emotional connections and boost customer loyalty. Discover how these strategies redefine brand ownership and shape consumer engagement.
Source and External Links
Direct-to-consumer - Direct-to-consumer (DTC) is a business model where companies sell products directly to customers, bypassing traditional retailers, wholesalers, or middlemen, often through online channels but sometimes also through physical stores as part of a clicks-and-mortar approach.
What Is Direct-to-Consumer? Everything You Need To Know (2024) - DTC retail involves brands selling directly to consumers via their own digital or physical channels, taking full control of the customer experience, fulfillment, and marketing, while focusing on building direct relationships and gathering firsthand customer insights.
Direct to Consumer (D2C) Guide | Salesforce US - In direct-to-consumer retail, manufacturers sell products straight to end users through ecommerce websites, social commerce, or apps, often complementing (rather than replacing) traditional retail channels to meet modern consumer expectations for direct access to brands.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com