Smart shelf technology enhances retail inventory management by using weight sensors and RFID tags to track product availability in real-time, reducing stockouts and improving restocking efficiency. Computer vision analytics leverages cameras and AI algorithms to monitor shopper behavior, shelf conditions, and product placement, providing valuable insights for optimizing store layouts and marketing strategies. Explore how integrating smart shelves with computer vision can transform retail operations and boost sales performance.
Why it is important
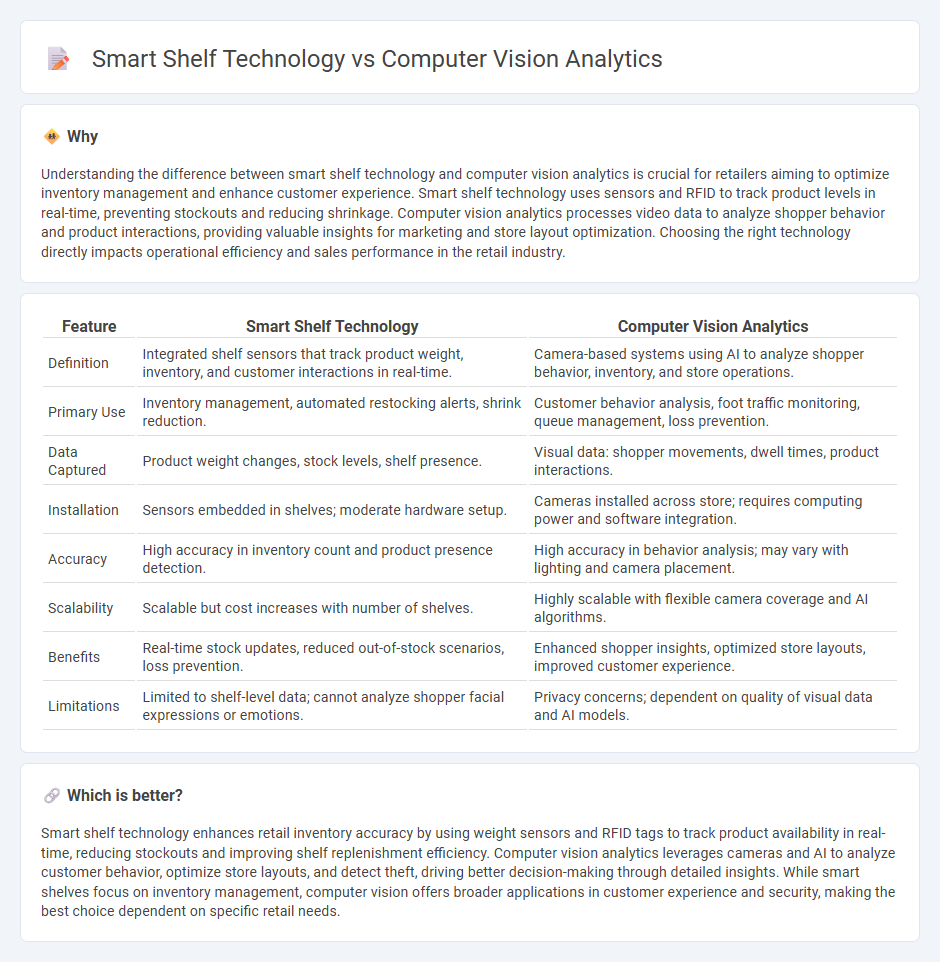
Understanding the difference between smart shelf technology and computer vision analytics is crucial for retailers aiming to optimize inventory management and enhance customer experience. Smart shelf technology uses sensors and RFID to track product levels in real-time, preventing stockouts and reducing shrinkage. Computer vision analytics processes video data to analyze shopper behavior and product interactions, providing valuable insights for marketing and store layout optimization. Choosing the right technology directly impacts operational efficiency and sales performance in the retail industry.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Shelf Technology | Computer Vision Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated shelf sensors that track product weight, inventory, and customer interactions in real-time. | Camera-based systems using AI to analyze shopper behavior, inventory, and store operations. |
| Primary Use | Inventory management, automated restocking alerts, shrink reduction. | Customer behavior analysis, foot traffic monitoring, queue management, loss prevention. |
| Data Captured | Product weight changes, stock levels, shelf presence. | Visual data: shopper movements, dwell times, product interactions. |
| Installation | Sensors embedded in shelves; moderate hardware setup. | Cameras installed across store; requires computing power and software integration. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy in inventory count and product presence detection. | High accuracy in behavior analysis; may vary with lighting and camera placement. |
| Scalability | Scalable but cost increases with number of shelves. | Highly scalable with flexible camera coverage and AI algorithms. |
| Benefits | Real-time stock updates, reduced out-of-stock scenarios, loss prevention. | Enhanced shopper insights, optimized store layouts, improved customer experience. |
| Limitations | Limited to shelf-level data; cannot analyze shopper facial expressions or emotions. | Privacy concerns; dependent on quality of visual data and AI models. |
Which is better?
Smart shelf technology enhances retail inventory accuracy by using weight sensors and RFID tags to track product availability in real-time, reducing stockouts and improving shelf replenishment efficiency. Computer vision analytics leverages cameras and AI to analyze customer behavior, optimize store layouts, and detect theft, driving better decision-making through detailed insights. While smart shelves focus on inventory management, computer vision offers broader applications in customer experience and security, making the best choice dependent on specific retail needs.
Connection
Smart shelf technology utilizes computer vision analytics to monitor product inventory and customer behavior in real time, enhancing retail store efficiency. Computer vision algorithms analyze shelf images to detect stock levels, misplaced items, and shopper interactions, enabling automated restocking alerts and personalized promotions. This integration reduces out-of-stock instances and improves the shopping experience by providing accurate, data-driven insights to retailers.
Key Terms
Image Recognition
Computer vision analytics leverages advanced algorithms to interpret and analyze visual data, enhancing image recognition accuracy in various applications such as retail and surveillance. Smart shelf technology integrates image recognition to monitor product placement, stock levels, and customer interactions, enabling real-time inventory management and personalized shopping experiences. Explore the latest advancements in computer vision and smart shelf systems to optimize operational efficiency and customer engagement.
Inventory Monitoring
Computer vision analytics leverages AI-driven image and video processing to track inventory levels, detect misplaced items, and analyze shopping behavior in real time. Smart shelf technology integrates weight sensors and RFID tags for automated stock counting and immediate replenishment alerts, enhancing accuracy and reducing out-of-stock situations. Discover how these innovative inventory monitoring solutions can transform retail operations by improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Planogram Compliance
Computer vision analytics enhances retail operations by automatically monitoring shelf conditions and detecting planogram compliance deviations in real-time through image recognition algorithms. Smart shelf technology integrates weight sensors and RFID tags to track inventory levels and product placement, ensuring accurate shelving and preventing stockouts. Explore how these technologies optimize merchandising strategies and improve retail efficiency.
Source and External Links
How Vision Analytics Identifies Objects in Images and Videos - Vision analytics uses advanced algorithms and machine learning, including deep learning models, to analyze images and videos for tasks like object detection, classification, and segmentation, with the market expected to reach $46.96 billion by 2030.
What is Computer Vision? - Computer vision is an AI field enabling machines to interpret visual input using deep learning and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) that allow automatic image recognition through pattern analysis.
Use Cases for Computer Vision in Analytics - Computer vision enhances analytics by enabling object classification, time-in-zone tracking, and object movement tracking, thereby providing richer insight from visual data for improved machine learning and data science.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com