Phantom inventory refers to stock recorded in inventory systems but physically missing, often caused by miscounts or data errors, while shrinkage denotes actual loss of inventory due to theft, damage, or administrative inaccuracies. Both issues critically impact retail profitability and inventory accuracy, with shrinkage typically accounting for billions in annual losses globally. Explore detailed strategies to detect and prevent phantom inventory and shrinkage in retail operations.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between phantom inventory and shrinkage is crucial for retail businesses to accurately manage stock levels, optimize inventory control, and prevent financial losses. Phantom inventory refers to discrepancies where stock records show items that are physically absent, often caused by data errors or miscounts. Shrinkage involves actual loss of inventory due to theft, damage, or administrative errors. Accurate identification helps retailers implement targeted strategies for loss prevention and operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
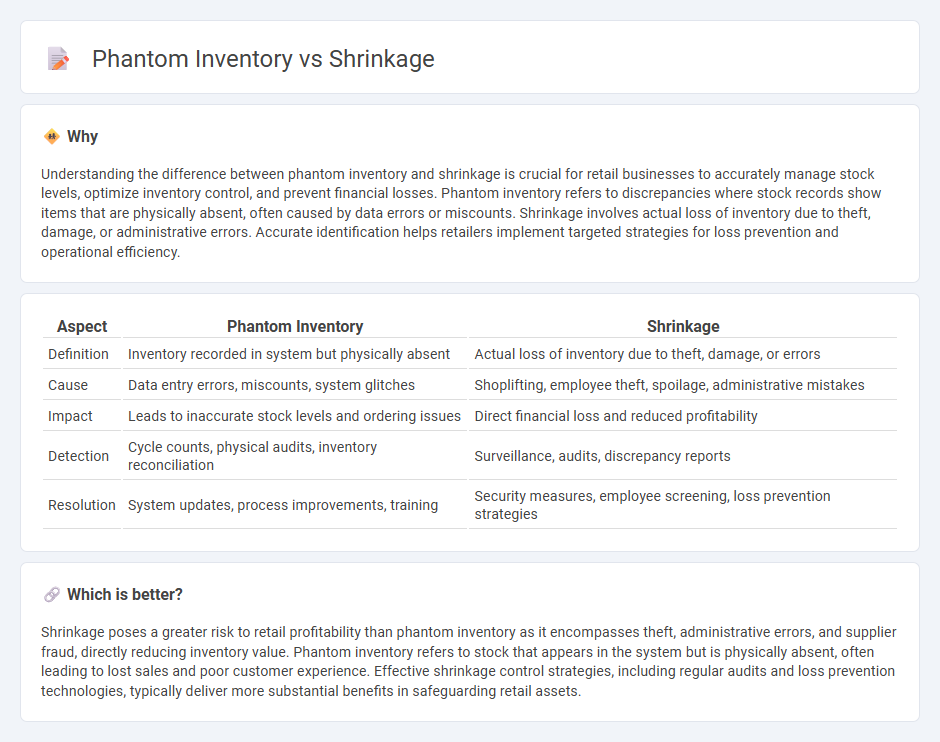
| Aspect | Phantom Inventory | Shrinkage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inventory recorded in system but physically absent | Actual loss of inventory due to theft, damage, or errors |
| Cause | Data entry errors, miscounts, system glitches | Shoplifting, employee theft, spoilage, administrative mistakes |
| Impact | Leads to inaccurate stock levels and ordering issues | Direct financial loss and reduced profitability |
| Detection | Cycle counts, physical audits, inventory reconciliation | Surveillance, audits, discrepancy reports |
| Resolution | System updates, process improvements, training | Security measures, employee screening, loss prevention strategies |
Which is better?
Shrinkage poses a greater risk to retail profitability than phantom inventory as it encompasses theft, administrative errors, and supplier fraud, directly reducing inventory value. Phantom inventory refers to stock that appears in the system but is physically absent, often leading to lost sales and poor customer experience. Effective shrinkage control strategies, including regular audits and loss prevention technologies, typically deliver more substantial benefits in safeguarding retail assets.
Connection
Phantom inventory, which refers to stock that appears available in the system but is missing physically, directly contributes to retail shrinkage by creating discrepancies between recorded and actual inventory levels. These inaccuracies lead to inventory losses that are difficult to track, complicating efforts to pinpoint theft, damage, or administrative errors. Effective inventory management systems and regular physical audits help mitigate phantom inventory, reducing overall shrinkage in retail operations.
Key Terms
Inventory Loss
Inventory shrinkage refers to the loss of products due to theft, damage, or administrative errors, directly impacting financial performance. Phantom inventory represents stock recorded in the system but is physically absent, often caused by data inaccuracies or unnoticed theft. Explore comprehensive strategies to minimize inventory loss and enhance accuracy in supply chain management.
Stock Discrepancy
Stock discrepancy often arises from shrinkage, the loss of inventory due to theft, damage, or administrative errors, whereas phantom inventory refers to stock that appears in records but physically does not exist. Understanding the distinctions between shrinkage and phantom inventory is crucial for improving inventory accuracy and optimizing supply chain operations. Explore more about effective strategies to minimize stock discrepancies and enhance inventory management.
Theft
Shrinkage refers to the loss of inventory due to theft, damage, or administrative errors, with theft being a primary contributor that negatively impacts profit margins in retail and supply chains. Phantom inventory occurs when the stock is physically unavailable due to theft or misplacement, but the inventory management system incorrectly shows it as available, leading to inaccurate stock records and missed sales opportunities. Explore effective strategies to minimize theft-related shrinkage and phantom inventory for optimized inventory control.
Source and External Links
What Is Shrinkage? - Shrinkage refers to the loss of inventory or assets due to theft, damage, errors, or other factors not accounted for in sales or production.
Shrinkage | Cambridge Dictionary - Shrinkage is a reduction in the size of something, or the process of becoming smaller.
Shrinkage (statistics) - In statistics, shrinkage refers to the reduction in the effects of sampling variation in regression analysis.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com