Agrihoods integrate sustainable farming and community living, offering residents fresh produce and green spaces within neighborhoods, unlike traditional subdivisions that focus primarily on housing density and infrastructure. These innovative real estate developments emphasize environmental stewardship, local food production, and a strong sense of community. Discover how agrihoods are transforming modern living by blending agriculture and residential life.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between agrihoods and subdivisions is crucial for real estate investors and buyers because agrihoods integrate sustainable farming with residential living, offering unique lifestyle and environmental benefits compared to traditional subdivisions. Agrihoods emphasize community farming, local food production, and green spaces, which can impact property values and appeal to eco-conscious buyers. Subdivisions typically focus on standard residential development without agricultural or sustainability features. Recognizing these distinctions helps tailor real estate choices to personal priorities and market trends.
Comparison Table
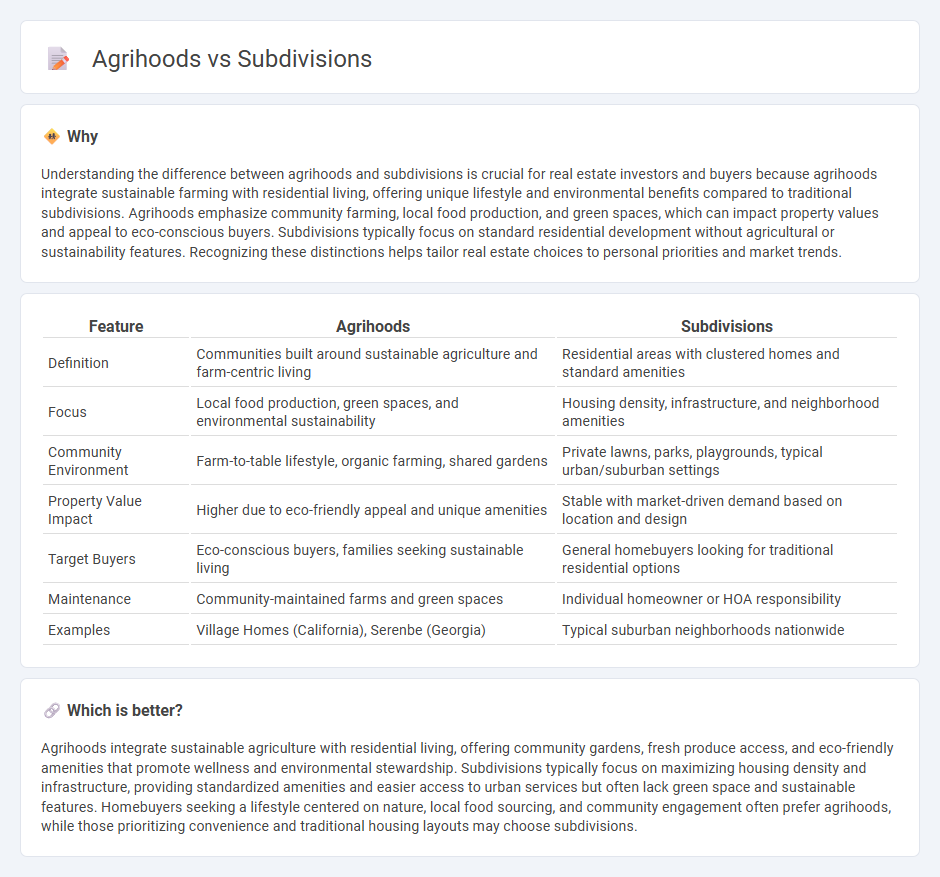
| Feature | Agrihoods | Subdivisions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Communities built around sustainable agriculture and farm-centric living | Residential areas with clustered homes and standard amenities |
| Focus | Local food production, green spaces, and environmental sustainability | Housing density, infrastructure, and neighborhood amenities |
| Community Environment | Farm-to-table lifestyle, organic farming, shared gardens | Private lawns, parks, playgrounds, typical urban/suburban settings |
| Property Value Impact | Higher due to eco-friendly appeal and unique amenities | Stable with market-driven demand based on location and design |
| Target Buyers | Eco-conscious buyers, families seeking sustainable living | General homebuyers looking for traditional residential options |
| Maintenance | Community-maintained farms and green spaces | Individual homeowner or HOA responsibility |
| Examples | Village Homes (California), Serenbe (Georgia) | Typical suburban neighborhoods nationwide |
Which is better?
Agrihoods integrate sustainable agriculture with residential living, offering community gardens, fresh produce access, and eco-friendly amenities that promote wellness and environmental stewardship. Subdivisions typically focus on maximizing housing density and infrastructure, providing standardized amenities and easier access to urban services but often lack green space and sustainable features. Homebuyers seeking a lifestyle centered on nature, local food sourcing, and community engagement often prefer agrihoods, while those prioritizing convenience and traditional housing layouts may choose subdivisions.
Connection
Agrihoods and subdivisions are connected through the integration of residential communities with agricultural landscapes, promoting sustainable living and local food production. Both development types prioritize green spaces and community engagement, with agrihoods specifically incorporating active farming elements within or adjacent to residential subdivisions. This blend enhances property value while encouraging environmental stewardship and healthier lifestyles among residents.
Key Terms
Zoning
Zoning regulations in subdivisions typically separate residential, commercial, and industrial areas, limiting mixed-use development and agricultural activities within the community. Agrihoods integrate residential living with active agricultural zones, promoting farm-to-table lifestyles and preserving open farmland through flexible zoning policies. Explore how zoning laws shape the unique benefits and challenges of subdivisions and agrihoods.
Amenities
Subdivisions typically offer standard amenities such as playgrounds, walking trails, and community pools designed for general family use. Agrihoods incorporate unique agricultural features like community gardens, farm-to-table markets, and shared greenhouses that promote sustainable living and local food production. Explore the distinctive amenities of agrihoods to see how they enhance community lifestyle and wellness.
Community Planning
Subdivisions typically emphasize individual lot development with standardized layouts, prioritizing housing density and market appeal, whereas agrihoods integrate agricultural elements and shared green spaces to foster sustainable living and community engagement. Community planning in agrihoods centers on creating connectivity through communal gardens, farm-to-table initiatives, and eco-friendly infrastructure, enhancing residents' social interaction and environmental awareness. Explore how these planning models shape long-term neighborhood vitality and resident well-being.
Source and External Links
Subdivision (land) - Subdivision refers to land divided into smaller parcels for sale or development, often via a plat, and can be used for residential, commercial, or industrial purposes.
Subdivisions Lyrics - The song "Subdivisions" by Rush, written by Neil Peart, critiques suburban life and conformity, with themes of isolation and teenage angst.
RUSH Subdivisions (Official Video) - The official video for Rush's 1982 song "Subdivisions," which explores themes of suburban life and youthful disillusionment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com