Vertical farming buildings maximize urban space by integrating sustainable agriculture with residential or commercial real estate, offering innovative solutions for food production in dense cities. Retirement homes focus on providing specialized living environments tailored to elderly care, emphasizing comfort, accessibility, and community support. Discover how these two real estate sectors are shaping future urban living and investment opportunities.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between vertical farming buildings and retirement homes is crucial as they serve distinct purposes: vertical farms optimize urban agriculture through controlled environments, while retirement homes provide specialized care for elderly residents. Vertical farming buildings utilize advanced technologies to enhance food production efficiency, addressing urban food security and sustainability. Retirement homes focus on healthcare, social support, and safety, catering to the aging population's unique needs. Recognizing these differences informs real estate development decisions, investment strategies, and community planning.
Comparison Table
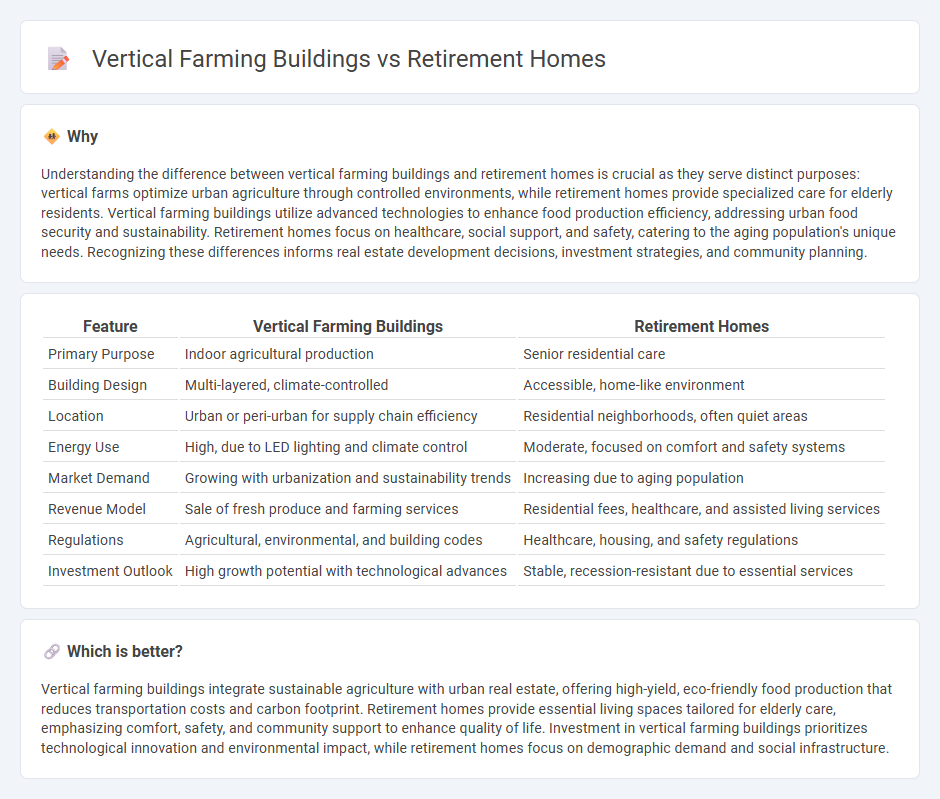
| Feature | Vertical Farming Buildings | Retirement Homes |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Indoor agricultural production | Senior residential care |
| Building Design | Multi-layered, climate-controlled | Accessible, home-like environment |
| Location | Urban or peri-urban for supply chain efficiency | Residential neighborhoods, often quiet areas |
| Energy Use | High, due to LED lighting and climate control | Moderate, focused on comfort and safety systems |
| Market Demand | Growing with urbanization and sustainability trends | Increasing due to aging population |
| Revenue Model | Sale of fresh produce and farming services | Residential fees, healthcare, and assisted living services |
| Regulations | Agricultural, environmental, and building codes | Healthcare, housing, and safety regulations |
| Investment Outlook | High growth potential with technological advances | Stable, recession-resistant due to essential services |
Which is better?
Vertical farming buildings integrate sustainable agriculture with urban real estate, offering high-yield, eco-friendly food production that reduces transportation costs and carbon footprint. Retirement homes provide essential living spaces tailored for elderly care, emphasizing comfort, safety, and community support to enhance quality of life. Investment in vertical farming buildings prioritizes technological innovation and environmental impact, while retirement homes focus on demographic demand and social infrastructure.
Connection
Vertical farming buildings and retirement homes intersect through innovative real estate developments that integrate sustainable agriculture with elderly care facilities. These mixed-use properties utilize vertical farming to provide fresh, local produce, enhancing residents' nutrition and promoting well-being while optimizing urban space. Incorporating vertical farms within retirement homes reduces food transportation costs and supports eco-friendly living environments, aligning with green building standards and future-oriented real estate trends.
Key Terms
Assisted Living
Assisted living facilities prioritize resident comfort and healthcare access, integrating communities with personalized services and safety features tailored to aging populations. Vertical farming buildings optimize space through multi-level crop production, utilizing advanced technology to enhance sustainability and food security in urban environments. Explore the evolving designs and benefits of these specialized structures to learn more about their societal impact.
Greenhouse Infrastructure
Greenhouse infrastructure in vertical farming buildings maximizes space efficiency by using multi-layered growing systems, optimizing natural light, and incorporating climate control technologies for sustainable crop production. Retirement homes commonly feature greenhouse spaces designed to promote wellness through therapeutic horticulture and provide fresh produce for resident dining programs, enhancing nutritional quality and quality of life. Explore the latest advancements in greenhouse infrastructure to understand their impact on sustainable urban living and elder care environments.
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations critically impact the development of retirement homes and vertical farming buildings by dictating land use, building height, and environmental requirements. Retirement homes often fall under residential or mixed-use zoning, necessitating accessibility and safety standards, whereas vertical farming buildings typically require commercial or industrial zoning due to their operational nature and infrastructure demands. Explore the specific zoning codes and regulatory frameworks that influence these distinct building types to better navigate planning and compliance challenges.
Source and External Links
Retirement Home - Wikipedia - A multi-residence housing facility intended for the elderly, offering options like meal-making and personal care services.
Retirement Communities | Senior Retirement Homes & 50 Plus - Provides an overview of different types of retirement communities, including assisted living, independent living, age-restricted, and lifestyle options.
Covenant Living Communities & Services - Offers a range of senior living options across the U.S., including independent living, assisted living, and continuing care retirement communities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com