Adaptive reuse transforms historic buildings into functional modern spaces by integrating new uses while maintaining structural integrity. Preservation focuses on maintaining and restoring original architectural features to protect cultural heritage and historical value. Explore the key differences and benefits of adaptive reuse versus preservation to determine the best approach for your real estate project.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse and preservation is crucial in real estate for maximizing property value and sustainability. Adaptive reuse involves repurposing old buildings for new functions, enhancing economic potential while meeting modern needs. Preservation focuses on maintaining a building's original design and historical significance, which can increase cultural value and attract heritage-conscious buyers. Real estate developers who distinguish these terms can make informed decisions that balance profitability, regulatory compliance, and community impact.
Comparison Table
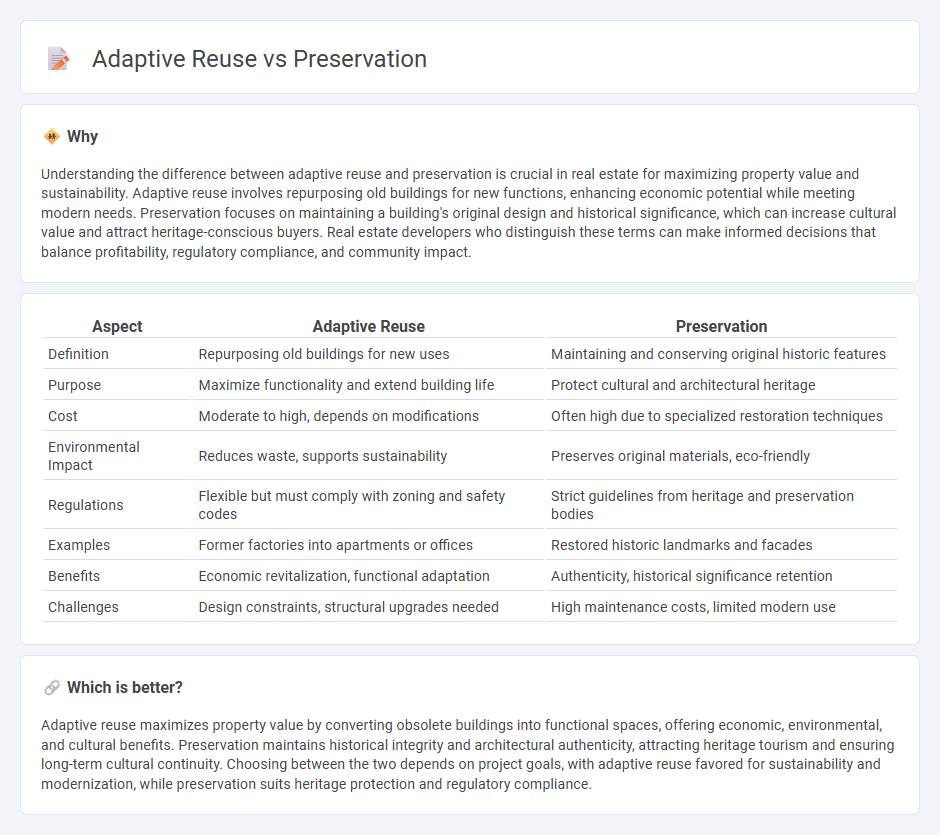
| Aspect | Adaptive Reuse | Preservation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing old buildings for new uses | Maintaining and conserving original historic features |
| Purpose | Maximize functionality and extend building life | Protect cultural and architectural heritage |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depends on modifications | Often high due to specialized restoration techniques |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste, supports sustainability | Preserves original materials, eco-friendly |
| Regulations | Flexible but must comply with zoning and safety codes | Strict guidelines from heritage and preservation bodies |
| Examples | Former factories into apartments or offices | Restored historic landmarks and facades |
| Benefits | Economic revitalization, functional adaptation | Authenticity, historical significance retention |
| Challenges | Design constraints, structural upgrades needed | High maintenance costs, limited modern use |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse maximizes property value by converting obsolete buildings into functional spaces, offering economic, environmental, and cultural benefits. Preservation maintains historical integrity and architectural authenticity, attracting heritage tourism and ensuring long-term cultural continuity. Choosing between the two depends on project goals, with adaptive reuse favored for sustainability and modernization, while preservation suits heritage protection and regulatory compliance.
Connection
Adaptive reuse and preservation in real estate are intrinsically linked through their focus on revitalizing existing structures while maintaining historical and architectural significance. This approach maximizes sustainability by conserving resources and reducing urban sprawl, enhancing property value through cultural relevance and unique character. Both strategies contribute to community identity preservation and foster economic growth by attracting tourism and business investments.
Key Terms
Historic Integrity
Preservation maintains historic integrity by safeguarding original materials, craftsmanship, and architectural features of heritage buildings, ensuring authenticity and cultural significance remain intact. Adaptive reuse balances maintaining historic elements while integrating modern functionalities, promoting sustainability and continued use without compromising character-defining aspects. Explore the nuanced impact of these strategies on heritage conservation to understand their roles in protecting historic integrity.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation in historic preservation involves repairing and updating buildings to meet modern standards while maintaining their original character, often improving structural integrity and energy efficiency. Adaptive reuse takes rehabilitation further by repurposing the building for a new function, blending preservation with contemporary utility to extend the building's lifespan and sustainability. Explore more about how rehabilitation balances history with innovation in preservation and adaptive reuse practices.
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations play a critical role in the decisions between preservation and adaptive reuse by dictating land use, building height, density, and occupancy requirements that can either restrict or facilitate project feasibility. Preservation often faces stricter zoning constraints aimed at maintaining historical character, whereas adaptive reuse projects may leverage zoning variances or special permits to accommodate new functions within old structures. Discover how zoning regulations impact your project's potential for preservation or adaptive reuse by exploring expert guidelines and case studies.
Source and External Links
The Secretary of the Interior's Standards for the Treatment of Historic Properties - Preservation is the process of applying measures to sustain the existing form, integrity, and materials of a historic property, focusing on maintenance and repair rather than replacement or new construction efforts.
SAA Dictionary: preservation - Preservation is the professional discipline of protecting materials by minimizing chemical and physical deterioration and damage to reduce information loss and extend the life of cultural property, differentiated from conservation which involves repair.
PRESERVATION definition | Cambridge English Dictionary - Preservation is the act of keeping something in its current state to prevent decay, damage, or destruction, commonly applied in contexts like building or wood preservation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com